Valproic Acid
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
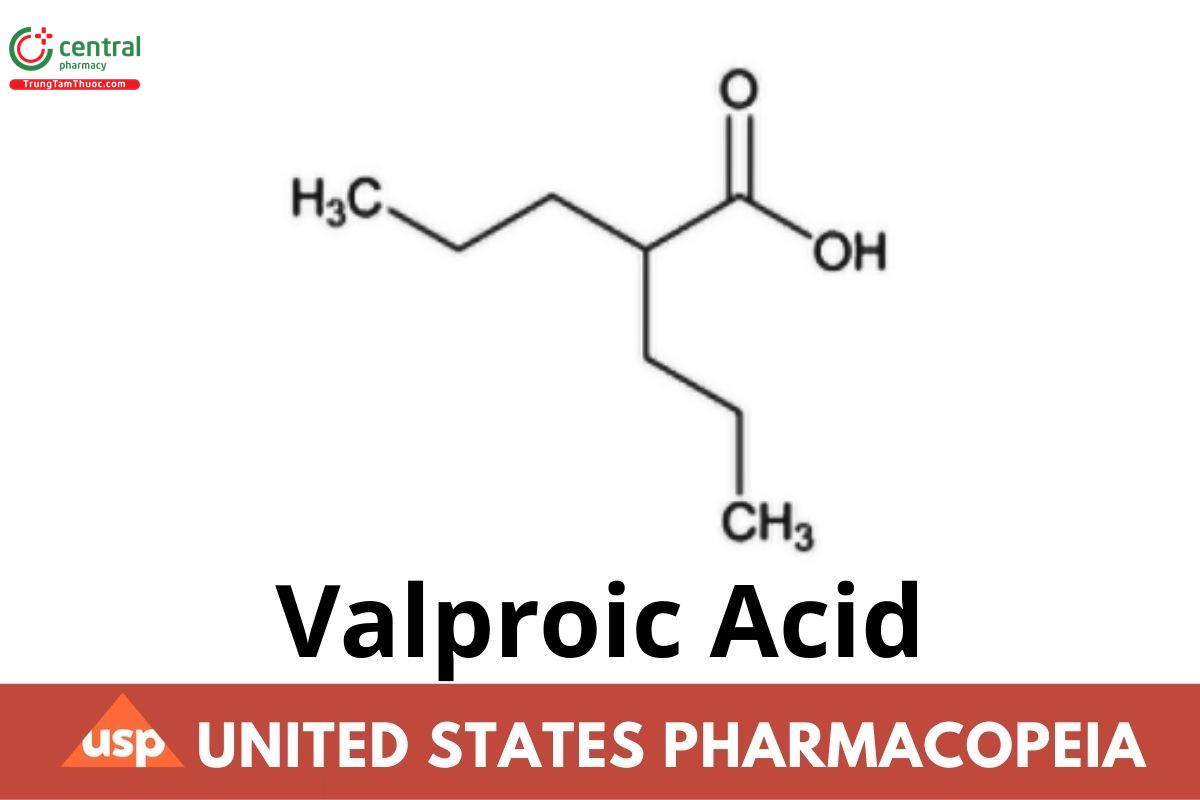
C₈H₁₆O₂ 144.21
Pentanoic acid, 2-propyl-;
Propylvaleric acid CAS RN®: 99-66-1; UNII: 614OI1Z5WI.
1 DEFINITION
Valproic Acid contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of valproic acid (C₈H₁₆O₂), calculated on the anhydrous basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
A. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197F
B. The retention time of the major peak of the Sample solution corresponds to that of the Standard solution, as obtained in the Assay.
3 ASSAY
3.1 Procedure
Buffer: 3.5 g/L of monobasic sodium phosphate in water. Adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 3.5.
Mobile phase: Acetonitrile and Buffer (45:55)
Diluent: Acetonitrile and water (45:55)
System suitability solution: 0.05 mg/mL of USP Valproic Acid Related Compound B RS and 0.5 mg/mL of USP Valproic Acid RS in Diluent
Standard solution: 0.5 mg/mL of USP Valproic Acid RS in Diluent
Sample solution: 0.5 mg/mL of Valproic Acid in Diluent
Chromatographic system
- (See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
- Mode: LC
- Detector: UV 215 nm
- Column: 4.6-mm × 15-cm; 5-µm packing L7
- Flow rate: 1 mL/min
- Injection volume: 20 µL
System suitability
- Samples: System suitability solution and Standard solution
- Suitability requirements
- Resolution: NLT 2.0 between valproic acid related compound B and valproic acid, System suitability solution
- Tailing factor: NMT 1.5, Standard solution
- Relative standard deviation: NMT 1.0%, Standard solution
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of valproic acid (C₈H₁₆O₂) in the portion of Valproic Acid taken:
Result = (rᵤ/rₛ) × (Cₛ/Cᵤ) × 100
rᵤ = peak response of valproic acid from the Sample solution
rₛ = peak response of valproic acid from the Standard solution
Cₛ = concentration of USP Valproic Acid RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
Cᵤ = concentration of Valproic Acid in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: 98.0%–102.0% on the anhydrous basis
4 IMPURITIES
4.1 Residue on Ignition 〈281〉: NMT 0.1%
Change to read:
4.2 Organic Impurities
System suitability solution: 0.5 mg/mL of USP Valproic Acid RS, 0.05 mg/mL of USP Valproic Acid Related Compound B RS, and 0.05 mg/mL of USP Valproic Acid Related Compound K RS in n-heptane
Standard solution: 0.005 mg/mL of USP Valproic Acid RS in n-heptane
Sensitivity solution: 0.0025 mg/mL of USP Valproic Acid RS from Standard solution in n-heptane
Sample solution: 5 mg/mL of Valproic Acid in n-heptane
Chromatographic system
- (See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
- Mode: GC
- Detector: Flame ionization
- Column: 0.32-mm × 60-m capillary; coated with a 0.5-µm film of phase G35
- Temperatures
- Injection port: 220°
- Detector: 220°
- Column: See Table 1.
Table 1
| Initial Temperature (°) | Temperature Ramp (°/min) | Final Temperature (°) | Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
| 100 | 0 | 100 | 5 |
| 100 | 4 | 200 | 15 |
- Carrier gas: Helium
- Flow rate: 2.0 mL/min
- Injection volume: 2.0 µL
- Injection type: Split, split ratio 5:1. [Note-Use of a split liner, deactivated with glass wool, is recommended.]
System suitability
- Samples: System suitability solution, Standard solution, and Sensitivity solution
- [Note-The relative retention times for valproic acid related compound B, valproic acid, and valproic acid related compound A (also known as 2-allylpent-4-enoic acid) are about 0.97, 1.0, and 1.13, respectively. For other relative retention times, see Table 2.]
- Suitability requirements
- Resolution: NLT 1.5 between valproic acid related compound B and valproic acid related compound K, System suitability solution
- Tailing factor: NMT 1.5 for valproic acid, Standard solution
- Signal-to-noise ratio: NLT 10 for valproic acid, Sensitivity solution
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Valproic Acid taken:
Result = (rᵤ/rₛ) × (Cₛ/Cᵤ) × (1/F) × 100
rᵤ = peak response of each impurity from the Sample solution
rₛ = peak response of valproic acid from the Standard solution
Cₛ = concentration of USP Valproic Acid RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
Cᵤ = concentration of valproic acid in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
F = relative response factor (see Table 2)
Acceptance criteria: See Table 2. The reporting threshold is 0.05%.
Table 2
| Name | Relative Retention Time | Relative Response Factor | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
| Valproic acid related compound K | 0.98 | 0.89 | 0.15 |
| Valproic acid | 1.0 | 1.0 | - |
| Any individual impurity | - | 1.0 | 0.1 |
| Total impurities | - | - | 0.3 |
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
Water Determination 〈921〉, Method I: NMT 1.0%
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in tight glass, stainless steel, or polyethylene (HDPE) containers.
Change to read:
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Valproic Acid RS
USP Valproic Acid Related Compound B RS
2-Isopropylpentanoic acid;
Also known as (2RS)-2-(1-Methylethyl)pentanoic acid.
C₈H₁₆O₂ 144.21
USP Valproic Acid Related Compound K RS
Ethylmethylvaleric acid;
Also known as 2-Ethyl-2-methylpentanoic acid.
C₈H₁₆O₂ 144.21


