Urea C 13
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
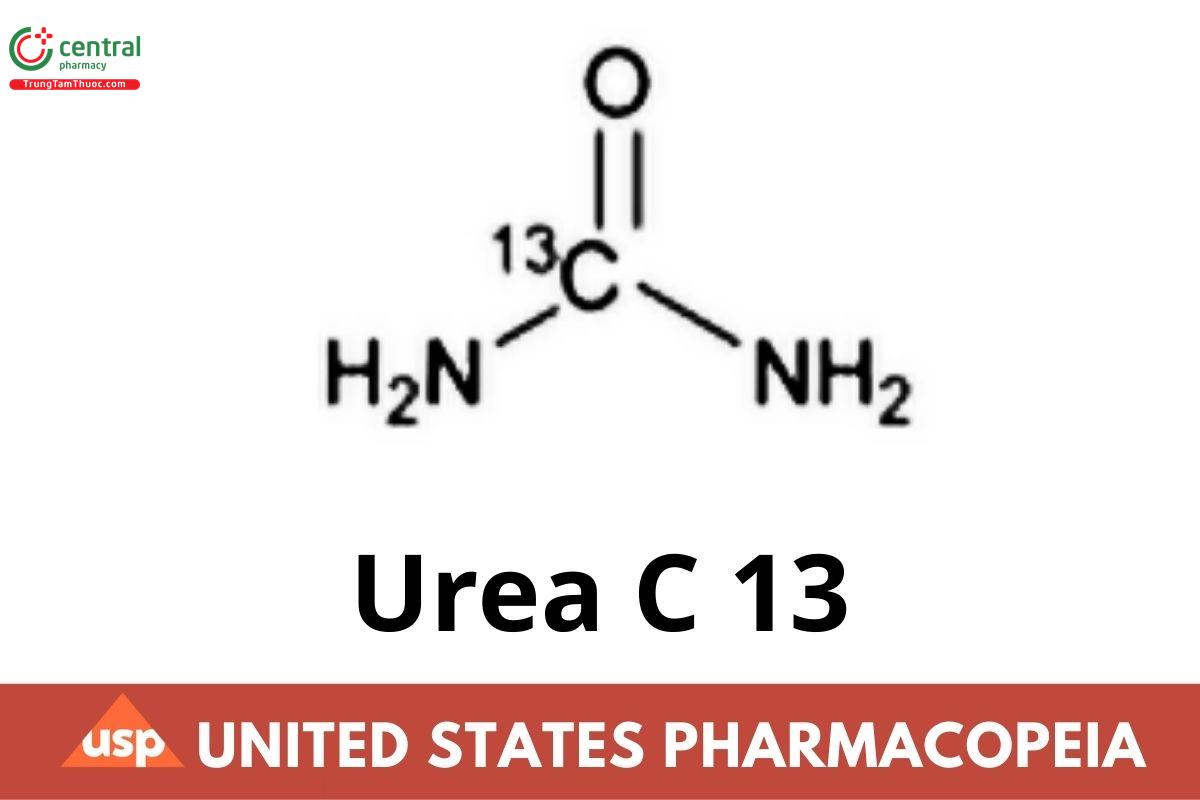
(13CH4N2O) 61.05
Urea [13C] CAS RN: 58069-82-2.
1 DEFINITION
Urea C 13 contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of urea C 13 (13CH4N2O).
2 IDENTIFICATION
A. SPECTROSCOPIC IDENTIFICATION TESTS (197), Infrared Spectroscopy: 197A or 197K
B. The intensity of the major peak with mass-to-charge (m/z) ratio of 190 in the Sample solution corresponds to that of the System suitability solution, as obtained in the test for Isotopic Purity.
3 ASSAY
PROCEDURE
Mobile phase: Acetonitrile, methanol, and water (89:10:1)
System suitability solution: 2.5 mg/mL of USP Urea C 13. RS and 0.003 mg/mL of biuret in Mobile phase
Standard solution: 2 mg/mL of USP Urea C 13 RS in Mobile phase
Sample solution: 2 mg/mL of Urea C 13 in Mobile phase
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography (621), System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 200 nm
Column: 4.6-mm x 25-cm; 5-µm packing L8
Flow rate: 0.8 mL/min
Injection volume: 20 µL
System suitability
Samples: System suitability solution and Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 1.5 between urea and biuret, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation: NMT 1%, Standard solution
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of urea C 13 (13CH4N2O) in the portion of Urea C 13 taken:
Result = (ru /rs ) × (Cs /Cu ) × 100
ru = peak response of urea C 13 from the Sample solution
rs = peak response of urea C 13 from the Standard solution
Cs = concentration of USP Urea C 13 RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
Cu = concentration of Urea C 13 in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: 98.0%–102.0%
4 IMPURITIES
Residue on Ignition 〈281〉: NMT 0.1%
4.1 Limit of Biuret
Standard solution: 0.033 mg/mL of biuret in water
Sample solution: 33.3 mg/mL of Urea C 13 in water
Analysis: Treat 3 ml. of the Sample solution and 3 mL of the Standard solution separately as follows. To each solution add 3 mL of sodium hydroxide solution (10 in 100) and 3 drops of copper sulfate solution (0.5 in 100), and allow to stand for 5 min.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.1%; any reddish-violet color in the Sample solution is not more intense than that in the Standard solution.
Change to read:
4.2 ISOTOPIC PURITY
Control stock solution: 2.0 mg/mL of USP Urea RS in dimethylformamide
Control solution: Transfer 0.5 mL of the Control stock solution to a vial. Add 0.5 mL of bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide with trimethylchlorosilane (TMS) derivatizing agent. Cap the vial and shake about 10 times. Heat at 90-110° on a heating block for about 60 min.
System suitability stock solution: 2.0 mg/mL of USP Urea C 13 RS in dimethylformamide
System suitability solution: Transfer 0.5 mL of the System suitability stock solution to a vial. Add 0.5 mL of TMS derivatizing agent. Cap the vial and shake about 10 times. Heat at 90°-110° on a heating block for about 60 min.
Sample stock solution: 2.0 mg/mL of Urea C 13 in dimethylformamide
Sample solution: Transfer 0.5 mL of the Sample stock solution to a vial. Add 0.5 mL of TMS derivatizing agent. Cap the vial and shake about 10 times. Heat at 90-110° on a heating block for about 60 min.
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography (621), System Suitability.)
Mode: GC
Detector: Mass spectrometer, positive ionization
Monitoring mode: Selected ion monitoring set up to monitor all ions individually in the m/z ratio range of 188-193
Solvent delay: Suitable time. [NOTE-Time may vary depending on the instrument and manufacturer's instructions.]
Column: 0.25-mm x 30-m capillary; coated with a 0.25-µm film of phase G27
Temperatures
Detector: 280°
Injection port: 280°
Column: See Table 1.
Table 1
| Initial Temperature (°) | Temperature Ramp (°/min) | Final Temperature (°) | Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
| 50 | 10 | 250 | 0 |
Carrier gas: Helium
Flow rate: 1 mL/min (ERR 1-Sep-2023)
Injection volume: 1 μL
Injection type: Split, split ratio 16:1
System suitability
Samples: Control solution and System suitability solution
Suitability requirements
Most abundant ion: Fragment at m/z 189, Control solution
Relative standard deviation: NMT 5%, Control solution
Most abundant ion: Fragment at m/z 190, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation: NMT 5%, System suitability solution
Carbon-13: NLT 99% in USP Urea C 13 RS, System suitability solution
Analysis
Samples: Control solution, System suitability solution, and Sample solution
Inject each solution in triplicate. [Note—Calculate the average responses of all the fragments between m/z 188 and m/z 193 from triplicate injections of each solution.]
Carbon-13 enrichment calculation
Calculate the contribution of carbon-13 (C) due to natural abundance to the response of derivatized Urea C 13:
C = (A × D)/E
A = average response of the m/z 190 fragment in urea C 13, System suitability solution or Sample solution
D = average response of the m/z 188 fragment in urea, Control solution
E = average response of the m/z 189 fragment in urea, Control solution
Calculate the percentage of carbon-13 enrichment in USP Urea C 13 RS and Urea C 13:
Result = [A/(A + B − C)] × 100
A = average response of the m/z 190 fragment in urea C 13, System suitability solution or Sample solution
B = average response of the m/z 189 fragment in urea C 13, System suitability solution or Sample solution
C = contribution due to natural abundance of carbon-13, System suitability solution or Sample solution
Oxygen-18 enrichment calculation
Step 1: Determine the measured mass of urea TMS in each injection of the Control solution:
Result = (Ʃ Mi × ri)/Ʃri
Mi = mass of the fragment for m/z 189, 190, 191, 192, and 193
ri = response of the corresponding m/z fragment
Calculate the average measured mass (M ) of urea TMS derivative.
Determine the mass correction factor (Δ):
Result = Mc,ave − Mc,theor
Mc,ave = average mass of urea TMS derivative
Mc,theor = theoretical mass of urea TMS derivative, 189.385
Step 2: Determine the measured mass of urea C 13 TMS in each injection of the Sample solution:
Result = (Ʃ Mi × ri)/Ʃri
Mi = mass of the fragment for m/z 189, 190, 191, 192, and 193
ri = response of the corresponding m/z fragment
Calculate the average measured mass (M ) of the urea C 13 TMS derivative characteristic ion from the triplicate injections of the
Sample solution.
Step 3: Calculate the measured molecular weight (M ) of urea C 13 in the Sample solution:
Result = Mu,ave − Δ − MTMS
Mu,ave = average mass of urea C 13 TMS derivative in the Sample solution from Step 2
Δ = correction factor from Step 1
MTMS = theoretical mass of the Si C H fragment, 129.329
Step 4: Calculate the average mass of oxygen (O ) in the Sample solution:
Result = MU − MT
MU = average mass of urea C 13 in the Sample solution from Step 3
MT = theoretical mass of the 13CN2H4 fragment, 45.044
Step 5: Calculate the percentage of enrichment of oxygen-18 in the Urea C 13 taken:
Result = [(Ou − A1 )/(A2 − A1 )] × 100
Ou = average mass of oxygen in the Sample solution from Step 4
A1 = theoretical mass of the natural isotope of oxygen, 15.995
A2 = theoretical mass of the oxygen-18 isotope, 17.999
Acceptance criteria
Carbon-13: NLT 99%
Oxygen-18: NMT 15%
5 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in well-closed containers at room temperature.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Urea RS
USP Urea C 13 RS


