Tobramycin Sulfate
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
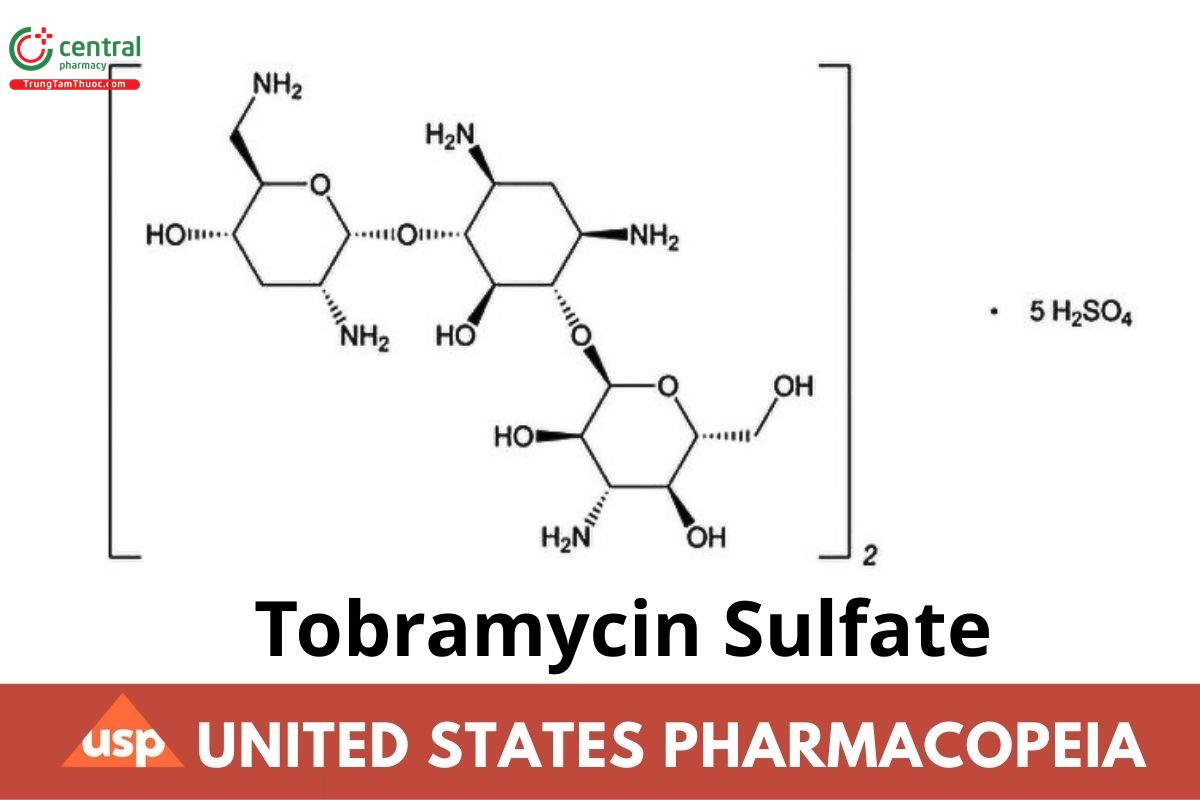
(C₁₈H₃₇N₅O₉) · 5H₂SO₄ 1425.42
d-Streptamine, O-3-amino-3-deoxy-α-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-O-[2,6-diamino-2,3,6-trideoxy-α-d-ribo-hexopyranosyl-(1→4)]-2-deoxy-, sulfate (2:5) (salt);
O-3-Amino-3-deoxy-α-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-O-[2,6-diamino-2,3,6-trideoxy-α-d-ribo-hexopyranosyl-(1→6)]-2-deoxy-l-streptamine, sulfate (2:5) (salt)
CAS RN®: 79645-27-5.
1 DEFINITION
Tobramycin Sulfate has a potency of NLT 634 µg/mg and NMT 739 µg/mg of tobramycin (C₁₈H₃₇N₅O₉).
2 IDENTIFICATION
2.1 A. Thin-Layer Chromatography
Diluent: Butyl alcohol and pyridine (100:1)
Standard solution: 6 mg/mL of USP Tobramycin RS in water
Sample solution: 6 mg/mL of Tobramycin in water
Solution A: Standard solution and Sample solution (1:1)
Chromatographic system
- (See Chromatography 〈621〉, Thin-Layer Chromatography.)
- Adsorbent: 0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel mixture
- Application volume: 3 µL
- Developing solvent system: Methanol, chloroform, and ammonium hydroxide (60:25:30)
- Spray reagent: 10 mg/mL of ninhydrin in Diluent
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution, Sample solution, and Solution A
Apply the Standard solution, the Sample solution, and Solution A to the plate. Place the plate in a suitable chromatographic chamber, and develop the chromatogram in the Developing solvent system until the solvent front has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate from the chamber, allow the solvent to evaporate, and heat the plate at 110° for 15 min. Immediately locate the spots on the plate by spraying it with Spray reagent.
Acceptance criteria: Tobramycin appears as a pink spot, and the Rf values of the spots of the Sample solution and of Solution A, respectively, correspond to those of the Standard solution.
2.2 B.
The retention time of the major peak of the Derivatized sample solution corresponds to that of the Derivatized standard solution obtained as directed in the Assay.
2.3 C.
Identification Tests-General, Sulfate 〈191〉: Meets the requirements
3 ASSAY
3.1 Procedure
Mobile phase: Dissolve 2.0 g of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane in 800 mL of water. Add 20 mL of 1 N sulfuric acid, and dilute with acetonitrile to obtain 2000 mL of solution. Cool, and pass through a filter of 0.2-µm or finer pore size.
Solution A: 10 mg/mL of 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene in alcohol. This solution may be used for 5 days if refrigerated when not in use.
Solution B: 15 mg/mL of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane in water. This solution may be used for 1 month if refrigerated when not in use.
Solution C: 3 mg/mL of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane prepared as follows. Transfer 40 mL of Solution B to a 200-mL volumetric flask. Add Dimethyl sulfoxide while mixing, and dilute with dimethyl sulfoxide to volume. Use this reagent within 4 h. If kept immersed in an ice-water bath below 10°, the reagent may be used for up to 8 h.
Standard stock solution: 1.1 mg/mL of USP Tobramycin RS prepared as follows. Transfer 55 mg of USP Tobramycin RS into a 50-mL volumetric flask. Add 1 mL of 1 N sulfuric acid and enough water to dissolve it, and dilute with water to volume.
Standard solution: 0.22 mg/mL of USP Tobramycin RS from Standard stock solution in water
Sample solution: Nominally 0.2 mg/mL of tobramycin from Tobramycin Sulfate in water
Derivatized standard solution, Derivatized sample solution, and Blank solution: Proceed as follows. Heat all solutions at the same temperature and for the same duration of time as indicated. Move all flasks to and from the 60° constant temperature bath at the same time.
To separate 50-mL volumetric flasks transfer 4.0 mL of the Standard solution, 4.0 mL of the Sample solution, and 4.0 mL of water. To each flask add 10 mL of Solution A and 10 mL of Solution C, shake, and insert the stopper. Place the flasks in a constant temperature bath at 60 ± 2°, and heat for 50 ± 5 min. Remove the flasks from the bath, and allow to stand for 10 min. Add acetonitrile to about 2 mL below the 50-mL mark, allow to cool to room temperature, then dilute with acetonitrile to volume. The solutions thus obtained are the Derivatized standard solution, the Derivatized sample solution, and the Blank solution, respectively.
System suitability stock solution: 0.24 mg/mL of p-naphtholbenzein in acetonitrile. Prepare freshly.
System suitability solution: Transfer 2 mL of the System suitability stock solution to a 10-mL volumetric flask, dilute with Derivatized standard solution to volume, and use promptly.
Chromatographic system
- (See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
- Mode: LC
- Detector: UV 365 nm
- Column: 3.9-mm × 30-cm; packing L1
- Flow rate: 1.2 mL/min
- Injection volume: 20 µL
System suitability
- Samples: Derivatized standard solution and System suitability solution
- [Note-The relative retention times for p-naphtholbenzein and tobramycin are about 0.6 and 1.0, respectively.]
- Suitability requirements
- Resolution: NLT 4.0 between p-naphtholbenzein and tobramycin, System suitability solution
- Relative standard deviation: NMT 2.0%, Derivatized standard solution
Analysis
Samples: Derivatized standard solution, Derivatized sample solution, and Blank solution
Use the Blank solution to identify the solvent and reagent peaks.
Calculate the quantity, in µg/mg, of tobramycin (C₁₈H₃₇N₅O₉) in the portion of Tobramycin Sulfate taken:
Result = (rᵤ/rₛ) × (Cₛ/Cᵤ) × P
rᵤ = peak area of tobramycin from the Derivatized sample solution
rₛ = peak area of tobramycin from the Derivatized standard solution
Cₛ = concentration of USP Tobramycin RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
Cᵤ = concentration of Tobramycin Sulfate in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
P = potency of tobramycin in USP Tobramycin RS (µg/mg)
Acceptance criteria: 634–739 µg/mg
4 IMPURITIES
4.1 Residue on Ignition 〈281〉
Analysis: Moisten the charred residue with 2 mL of nitric acid and 5 drops of sulfuric acid.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 1.0%
4.2 Organic Impurities
Solution A: Dilute 20 mL of sodium hypochlorite solution with water to 100 mL.
Solution B: Dissolve 1.1 g of potassium iodide in 60 mL of water, boil for 15 min, and slowly add a suspension of 1.5 g of soluble starch in 10 mL of water. Add 25 mL of water, and boil for 10 min. Allow to cool, and dilute with water to 100 mL.
Solution C: 29.2 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL of water
Sample solution: Transfer 50 mg of Tobramycin Sulfate to a 10-mL volumetric flask, add 7 mL of water to dissolve it, and adjust with 1 N sulfuric acid to a pH of 5.5 ± 0.4. Dilute with water to volume.
Standard solution: 0.05 mg/mL of tobramycin from Sample solution in water
Chromatographic system
- (See Chromatography 〈621〉, Thin-Layer Chromatography.)
- Mode: TLC
- Adsorbent: 0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel
- Application volume: 1 µL
- Developing solvent system: Alcohol, Solution C, and water (30:50:20)
Analysis
Samples: Sample solution and Standard solution
Apply the Sample solution and the Standard solution to the plate. Develop the chromatogram in a saturated chromatographic chamber containing the Developing solvent system until the solvent front has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate from the chromatographic chamber, evaporate the solvent in a current of hot air, then heat the plate at 110° for 10 min. Lightly spray the hot plate with Solution A. Dry the plate in a current of cold air until a sprayed area of the plate below the origin gives at most a faint blue color with a drop of Solution B. Then spray the plate with Solution B.
Acceptance criteria: Bluish-purple spots are immediately visible. Other than the principal tobramycin spot, no spot observed in the Sample solution is more intense than the principal spot from the Standard solution (1.0%).
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
pH 〈791〉
- Sample solution: 40 mg/mL
- Acceptance criteria: 6.0–8.0
Water Determination 〈921〉, Method I: NMT 7.0%
Sterility Tests 〈71〉: Where the label states that Tobramycin Sulfate is sterile, it meets the requirements in Test for Sterility of the Product to Be Examined, Membrane Filtration.
Bacterial Endotoxins Test 〈85〉: Where the label states that Tobramycin Sulfate is sterile or must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms, it contains NMT 2.00 USP Endotoxin Units/mg of tobramycin.
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in tight containers.
Labeling: Where Tobramycin Sulfate is intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms, the label states that it is sterile or must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Tobramycin RS


