Sucrose Stearate
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
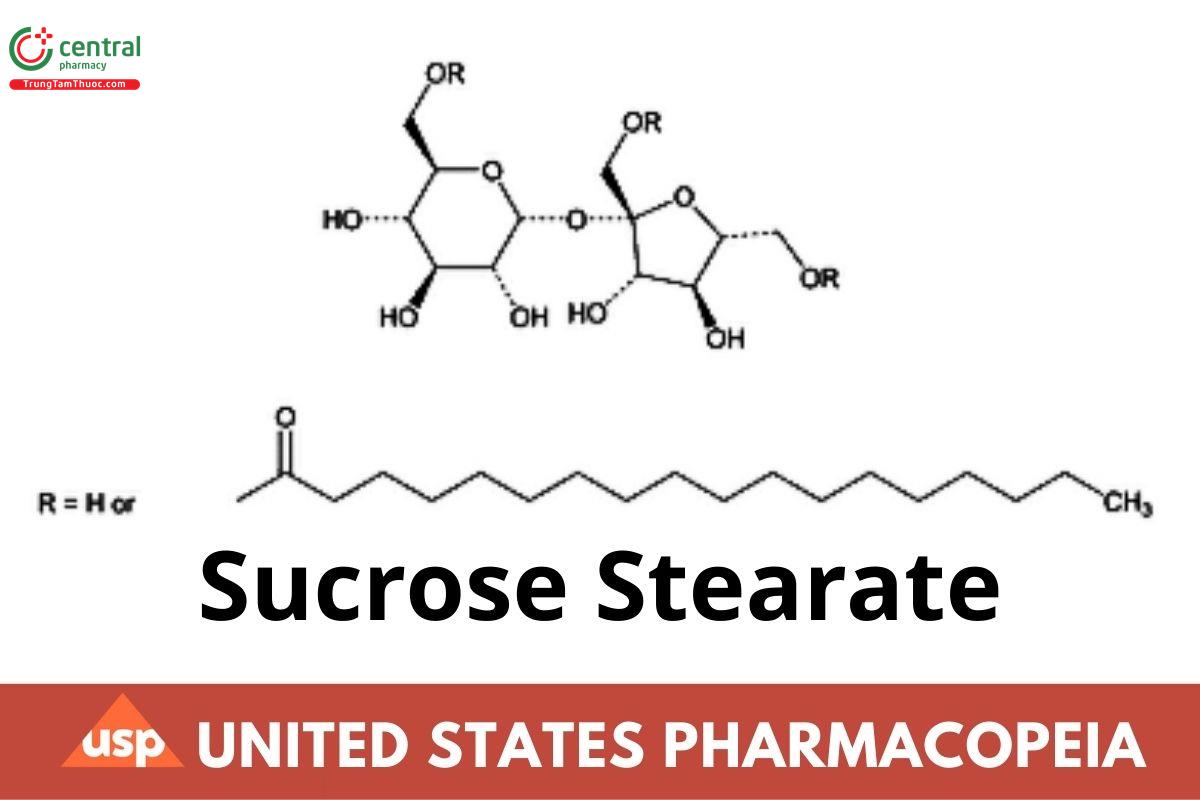
C30H56O12 608.76
C48H90O13 875.22
C66H124O14 1141.68
Sucrose monostearate;
Sucrose octadecanoate CAS RN®: 25168-73-4.
1 DEFINITION
Sucrose Stearate is a mixture of sucrose esters, mainly sucrose stearate, obtained by transesterication of stearic acid methyl esters derived from vegetable origin with sucrose. The manufacture of the fatty acid methyl esters includes a distillation step. The mono- and diesters requirements differ for the two types of sucrose stearate as set forth in the following table.
| Content of Monoesters (%) | Content of Diesters (%) | Sum of Triesters and Polyesters (%) | |
Type I | NLT 50.0 | NMT 40.0 | NMT 25.0 |
Type II | 20.0–45.0 | 30.0–40.0 | NMT 30.0 |
2 IDENTIFICATION
A. It meets the requirements of the Fatty Acid Composition test.
B. It meets the requirements of Content of Monoesters, Diesters, Triesters, and Polyesters.
3 ASSAY
Content of Monoesters, Diesters, Triesters, and Polyesters
Mobile phase: Tetrahydrofuran
Sample solution: 15 mg/mL of Sucrose Stearate in tetrahydrofuran
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC, size-exclusion
Detector: Differential refractometer
Column: 7-mm × 60-cm; packing L21, 100 Å. [Note—Two 7-mm × 30-cm L21 columns may be used in place of one 60-cm column, provided system suitability requirements are met.]
Flow rate: 1.2 mL/min
Injection size: 20 µL
Analysis
Sample: Sample solution
[Note—The relative retention time with reference to the monoester peak (retention time is approximately 10 min) is about 0.92 for diesters, and about 0.90 for triesters and polyesters.]
[Note—Disregard solvent peaks and peaks having a signal-to-noise ratio less than 10.]
Calculate the percentage of monoesters in the portion of Sucrose Stearate taken:
Result = A × (100 − D − S − E)/100
A = percentage of monoesters determined by peak normalization
D = percentage of free fatty acids, obtained by AV × 284.5/561.1, where AV is the acid value
S = percentage of free sucrose (see Free Sucrose in Organic Impurities)
E = percentage of water (see Water Determination, Ia in Specific Tests)
AV = acid value
Calculate the percentage of diesters in the portion of Sucrose Stearate taken:
Result = B × (100 − D − S − E)/100
B = percentage of diesters determined by peak normalization
D = percentage of free fatty acids (above)
S = percentage of free sucrose (see Free Sucrose in Organic Impurities)
E = percentage of water (see Water Determination, Ia in Specific Tests)
Calculate the percentage of triesters and polyesters in the portion of Sucrose Stearate taken:
Result = C × (100 − D − S − E)/100
C = percentage of triesters and polyesters determined by peak normalization
D = percentage of free fatty acids (above)
S = percentage of free sucrose (see Free Sucrose in Organic Impurities)
E = percentage of water (see Water Determination, Ia in Specific Tests)
Fatty Acid Composition: Sucrose Stearate exhibits the following composition proles of fatty acids, as determined in Fats and Fixed Oils 〈401〉, Fatty Acid Composition.
Fatty Acid | Percentage (%) |
Lauric acid | NMT 3.0 |
Myristic acid | NMT 3.0 |
Palmitic acid | 25.0–40.0 |
Stearic acid | 55.0–75.0 |
Sum of the contents of palmitic acid and stearic acid | 4 NLT 90.0 |
IMPURITIES
Inorganic Impurities
Fats and Fixed Oils, Acid Value 〈401〉: NMT 6, determined on a 3-g sample. Use a freshly neutralized mixture of 2-propanol and water (2:1), and gently heat.
Organic Impurities
Procedure: Free Sucrose
Solution A: 10 µg/mL of ammonium acetate in acetonitrile
Solution B: 10 µg/mL of ammonium acetate in tetrahydrofuran and water (90:10)
Diluent: Tetrahydrofuran and water (87.5:12.5)
System suitability solution: 500 µg/mL of USP Sucrose RS in Diluent
Standard solutions: 0.50, 1.0, 2.0, and 2.5 mg/mL of USP Sucrose RS in Diluent
Sample solution: 50 mg/mL of Sucrose Stearate in Diluent
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: Evaporative light-scattering. [Note—If the detector has different setting parameters, adjust the detector settings so as to comply with the System Suitability requirements.]
Carrier gas: Nitrogen
Detector temperature: 45°
Nebulizer temperature: 40°
Column: 4.6-mm × 0.25-m; packing L8
Injection size: 20 µL
Mobile phase and flow rate: See the gradient table below.
Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) | Flow Rate (mL/min) |
1 | 100 | 0 | 1.0 |
8 | 0 | 100 | 1.0 |
7 | 0 | 100 | 1.0 |
0.01 | 0 | 100 | 2.5 |
15.99 | 0 | 100 | 2.5 |
1 | 100 | 0 | 2.5 |
3 | 100 | 0 | 1.0 |
System suitability
Sample: System suitability solution
[Note—The retention time for sucrose stearate is about 26 min.]
Suitability requirements
Signal-to-noise ratio: 10:1
Analysis
Samples: Standard solutions and Sample solution
Prepare a standard curve by plotting the peak response versus concentration of sucrose in the Standard solution. Calculate the quantity of free sucrose in the Sucrose Stearate taken.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 4.0%
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
Water Determination, Method Ia 〈921〉: NMT 4.0%, on a 0.20-g sample
Total Ash
Analysis: Heat a silica or platinum crucible to redness for 30 min, allow to cool in a desiccator, and weigh. Transfer a 1.0-g sample into a crucible. Dry at 100°–105° for 1 h and ignite to constant weight in a muffle furnace at 600 ± 25°, allowing the crucible to cool in a desiccator after each ignition. Flames should not be produced at any time during the procedure. If after prolonged ignition the ash still contains black particles, add hot water, pass through an ashless filter paper, and ignite the residue and the filter paper. Combine the filtrate with the ash, carefully evaporate to dryness, and ignite to constant weight.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 1.5%
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Labeling: Label to indicate whether it is Type I or Type II.
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in a well-closed container. Protect from humidity and avoid high temperatures.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Sucrose RS


