Soybean Phospholipids
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
Soy Phospholipids;
Soya Phospholipids.
1 DEFINITION
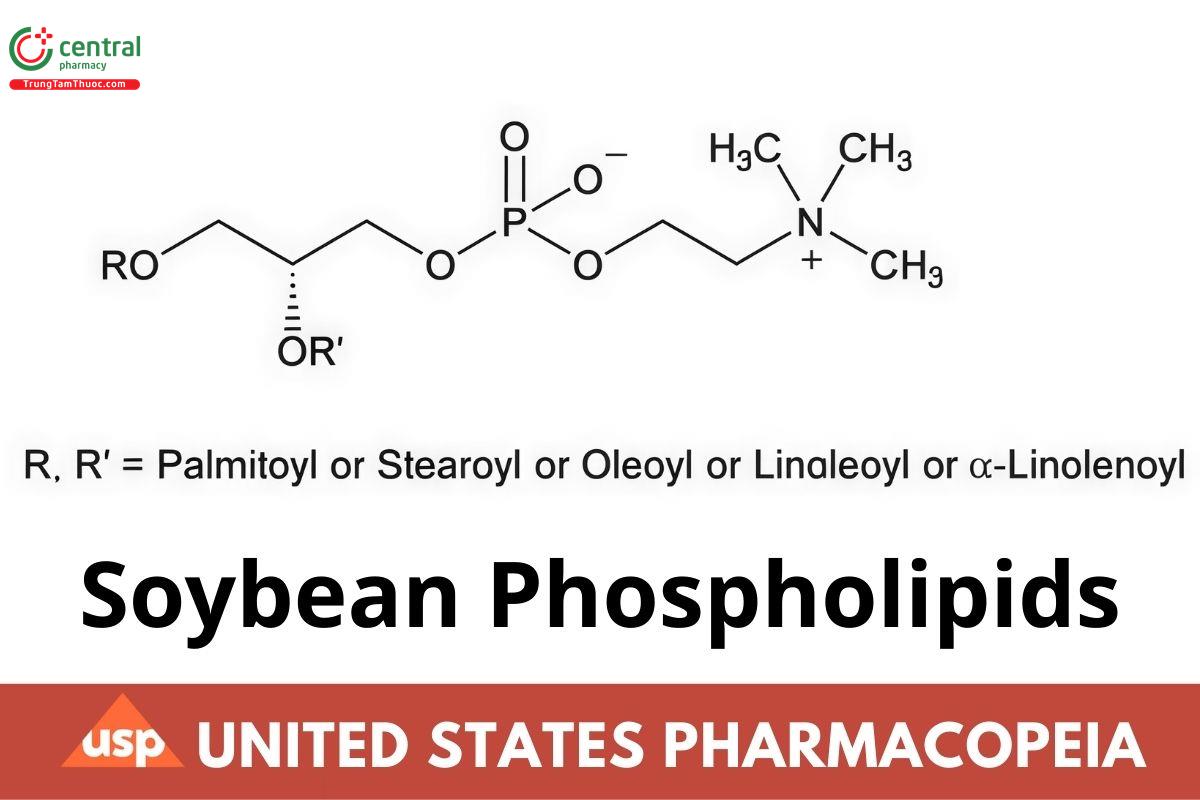
Soybean Phospholipids is a mixture of phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, lysophosphatidylcholine, phosphatidic acid, phosphatidylinositol, and N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine obtained from the soybean source. It contains NLT 65.0% and NMT 89.9% of phosphatidylcholine, NLT 6.0% and NMT 11.0% of phosphatidylethanolamine, NMT 6.0% of lysophosphatidylcholine, NMT 3.0% of phosphatidic acid, NMT 1.5% of phosphatidylinositol, and NMT 6.0% of N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine, calculated on the anhydrous basis. The phospholipids are in L-isomer forms. It may contain a suitable antioxidant.
2 IDENTIFICATION
2.1 A. IDENTIFICATION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS BY THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY
Developing solvent system: Chloroform, methanol, and water (65:25:4, v/v/v)
Standard solution A: 10 mg/ml, of USP Phosphatidic Acid (Soy) Monosodium RS and 10 mg/mL of USP Phosphatidylcholine (Soy) RS in the Developing solvent system
Standard solution B: 7 mg/mL of USP Phosphatidylethanolamine (Soy) RS and 7 mg/mL of USP Lysophosphatidylcholine (Soy) RS in the Developing solvent system
Sample solution: 20 mg/mL of Soybean Phospholipids in the Developing solvent system
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography (621), General Procedures. Thin-Layer Chromatography.)
Mode: TLC
Plate: 20-cm x 20-cm, silica gel 60 on aluminum foil, 0.2-mm layer
Application volume: 20 µL
Spray reagent: Transfer 600 mL of water and then 80 mL of phosphoric acid to a 1-L volumetric flask. While stirring, add 100 g of anhydrous cupric sulfate. After stirring for 10 min, most of the cupric sulfate is dissolved. Add water to volume and continue stirring until the solid completely dissolves.
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution A, Standard solution B, and Sample solution
Fill the chromatographic chamber with the Developing solvent system to a height of about 0.5 cm. Place a fat-free, U-shaped filter paper in the glass trough and press it against the wall. Sufficient saturation is reached once the Developing solvent system has permeated to the upper rim of the filter paper. Apply the Samples to the previously marked starting point on a TLC plate. Place the TLC plate in the saturated chromatographic chamber. When the Developing solvent system front has reached the mark (12 cm above the starting point), remove the TLC plate, and dry it using a dryer. Spray or immerse the TLC plate in the Spray reagent, and dry it again with a dryer (a current of hot air). Heat the plate to 170° for 10 min. Develop all lipids by charring as dark brown spots.
Acceptance criteria: The retardation factor (RF) values of the spots for phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidic acid, and lysophosphatidylcholine from the Sample solution correspond to those from Standard solution A and Standard solution B. [NOTE-Depending on the sample tested, if a Phospholipid component presents in a low amount in the sample, the corresponding spot in the Sample solution on the TLC may not be visualized.]
2.2 B. IDENTITY BY FATTY ACID COMPOSITION
Standard solution: Prepare a mixture of methyl esters of fatty acids listed in Table 2 with each of the methyl esters at 0.3 mg/mL.1
Sample solution: Accurately weigh 50 ± 10 mg of Soybean Phospholipids into a headspace vial. Fill the vial with nitrogen gas and seal it with a septum. Add 1.2 mL of 0.5 N sodium methoxide in methanol.2 Allow the reaction to proceed at room temperature for 10 min. Add 3 mL of isooctane and 1 ml of water to the reaction mixture and shake vigorously. After phase separation, remove the upper organic layer, dry it over sodium sulfate anhydrous, and transfer it to a brown gas chromatographic vial. Before the injection, dilute the solution with isooctane (1:1, v/v). [NOTE-During all of the steps, the samples should be protected from daylight.]
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography (621), System Suitability.)
Mode: GC
Detector: Flame ionization
Column: 0.32-mm x 50-m fused silica capillary; 0.2-um layer of phase G52
Temperatures
Injection port: 220°
Detector: 260°
Column: See Table 1.
Table 1
| Initial Temperature (°) | Temperature Ramp (°/min) | Final Temperature (°) | Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
| 70 | 0 | 70 | 2 |
| 70 | 5 | 240 | 25 |
Carrier gas: Helium
Pressure: Constant pressure at 135 kPa
Injection volume: 1 µL
Injection type: Split, split ratio 20:1
System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
FIC respectively.]
[ NOTE-The relative retention times for methyl palmitate, methyl stearate, methyl oleate, methyl linoleate, and methyl alpha-linolenate are approximately 0.82, 0.93, 0.94, 0.97, and 1.0,
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 1.8 between methyl stearate and methyl oleate peaks
Relative standard deviation: NMT 1.0% for the peak area ratio of methyl palmitate to methyl stearate; NMT 6.0% for the peak areas of methyl palmitate and methyl stearate
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Identify the fatty acid ester peaks in the chromatogram of the Sample solution by comparing the retention times of these peaks with those in the chromatogram of the Standard solution.
Calculate the percentage of each fatty acid component in the portion of Soybean Phospholipids taken:
Result = (rA/rT) x 100
rA = peak area of each individual fatty acid ester component
rT = sum of the peak areas of all of the peaks, excluding the solvent peak, in the chromatogram from the Sample solution
Acceptance criteria: Soybean Phospholipids exhibit the composition profile of fatty acids in Table 2.
Table 2
| Carbon-Chain Length | Number of Double Bonds | Percentage (%) |
| 16 | 0 | 6–25 |
| 18 | 0 | 2–5 |
| 18 | 1 | 6–15 |
| 18 | 2 | 49–74 |
| 18 | 3 | 4–9 |
3 ASSAY
CONTENT OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS
Solution A: A mixture of 1342 g (2.0L) of n-hexane, 334.1 g (425 mL) of isopropyl alcohol, 39.4 g (38 mL) of acetic acid, glacial, and 1.45 g (2.0 mL) of triethylamine
Solution B: A mixture of 663.5 g (850 mL) of isopropyl alcohol, 15.8 g (15 mL) of acetic acid, glacial, 140.0 g (140 mL) of water, and 0.58 g (0.8 mL) of triethylamine
Diluent: Solution A
Mobile phase: See Table 3.
Table 3
| Program Step | Time (min) | Flow Rate (mL/min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) |
| 1 | 0 | 1.0 | 95 | 5 |
| 2 | 5.0 | 1.0 | 80 | 20 |
| 3 | 8.5 | 1.0 | 60 | 40 |
| 4 | 14.0 | 1.0 | 55 | 45 |
| 5 | 15.0 | 1.0 | 0 | 100 |
| 6 | 17.5 | 1.0 | 0 | 100 |
| 7 | 17.6 | 1.0 | 95 | 5 |
| 8 | 21.0 | 1.0 | 95 | 5 |
| 9 | 22.0 | 2.0 | 95 | 5 |
| 10 | 27.0 | 2.0 | 95 | 5 |
| 11 | 29.0 | 1.0 | 95 | 5 |
Standard stock solution A: 2.0 mg/mL of USP Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholine (Soy) RS and 0.25 mg/mL of USP Phosphatidylethanolamine (Soy.) RS in Diluent. [NOTE-Due to the highly hygroscopic nature of phospholipids, take special precaution in the standard stock solution preparation.]
Standard stock solution B: 0.5 mg/mL of N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine prepared from USP N-Acylphosphatidylethanolamine (Soy). Ammonium RS, 0.25 mg/mL of phosphatidylinositol prepared from USP Phosphatidylinositol (Soy) Sodium RS, 0.5 mg/mL of phosphatidic acid prepared from USP Phosphatidic Acid (Soy) Monosodium RS, and 0.5 mg/mL of USP Lysophosphatidylcholine (Sov) RS in Diluent.
[NOTE-Due to the highly hygroscopic nature of phospholipids, take special precaution in the standard stock solution preparation.]
Standard solutions A1-A5: Prepare the solutions in Diluent following the dilution scheme in Table 4 for 25-mL volumetric flasks. [NOTE-The solutions are prepared from the highest concentration to the lowest. It is recommended to inject the solutions from the lowest concentration to the highest.]
Table 4
| Standard Solution | Dilution Factor | Volume of Standard Stock Solution A (mL) |
| A1 | 1.429 | 17.5 |
| A2 | 1.667 | 15.0 |
| A3 | 2.000 | 12.5 |
| A4 | 2.500 | 10.0 |
| A5 | 3.333 | 7.5 |
Standard solutions B1-B5: Prepare the solutions in Diluent following the dilution scheme in Table 5. [NOTE-The solutions are prepared from the highest concentration to the lowest. It is recommended to inject the solutions from the lowest concentration to the highest.]
Table 5
| Standard Solution | Dilution Factor | Preparation |
| B1 | 1 | Standard stock solution B |
| B2 | 2 | Standard solution B1 and Diluent (1:1, v/v) |
| B3 | 4 | Standard solution B2 and Diluent (1:1, v/v) |
| B4 | 8 | Standard solution B3 and Diluent (1:1, v/v) |
| B5 | 16 | Standard solution B4 and Diluent (1:1, v/v) |
System suitability solution: Mix equal volumes of Standard stock solution A and Standard stock solution B.
Sample solution 1: 12.5 mg/mL of Soybean Phospholipids in Diluent
Sample solution 2: 1.25 mg/mL of Soybean Phospholipids in Diluent
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography (621), System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: Evaporative light-scattering
Column: 4-mm x 12.5-cm; 5-µm packing L20
Temperatures
Column: 55°
Detector: 50°
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min with step gradient to 2.0 mL/min. See Table 3.
Injection volume: 20 µL
[NOTE-The Detector temperature and Flow rate can be adjusted as long as system suitability requirements are met.]
System suitability
Samples: Standard solution B5 and System suitability solution
[NOTE-The relative retention times for all of the specified components are listed in Table 6.]
Table 6
| Name | Relative Retention Time |
| N-Acylphosphatidylethanolamine | 0.3 |
| Phosphatidic acid | 0.5 |
| Phosphatidylethanolamine | 0.9 |
| Phosphatidylcholine | 1.0 |
| Phosphatidylinositol | 1.1 |
| Lysophosphatidylcholine | 1.3 |
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 2.0 between any adjacent peak pairs of the specified components, System suitability solution
Tailing factor: NMT 2.0 for the phosphatidylcholine peak, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation: NMT 5.0% for the phosphatidylcholine peak, System suitability solution
Signal-to-noise ratio: NLT 10 for N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidic acid, phosphatidylinositol, and lysophosphatidylcholine peaks, Standard solution B5
Analysis
Samples: Standard solutions A1-A5, Standard solutions B1-B5, Sample solution 1, and Sample solution 2
Measure the phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine peak areas obtained from Standard solutions A1-A5. Measure the N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidic acid, phosphatidylinositol, and lysophosphatidylcholine peak areas obtained from Standard solutions B1-85. Using a least-squares analysis, determine the linear regression line using the logarithms of the relevant responses versus the logarithms of the concentrations, in mg/mL, of each of the components obtained from the corresponding standard solutions. The correlation coefficient for the linear regression line for each phospholipid is NLT 0.995. From the linear regression lines so obtained, determine the concentration, in mg/ml, of each of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine in Sample solution 2, and the concentration, in mg/mL, of each of N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidic acid, phosphatidylinositol, and lysophosphatidylcholine in Sample solution 1.
Calculate the percentage of each phospholipid listed in Table 7 in the portion of Soybean Phospholipids taken:
Result = (CU/CS) × 100
CU = concentration of phosphatidylethanolamine or phosphatidylcholine in Sample solution 2, or each of N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidic acid, phosphatidylinositol, and lysophosphatidylcholine in Sample solution 1 (mg/mL), determined from the calibration curve
CS = concentration of Soybean Phospholipids in Sample solution 2 for the calculation of phosphatidylethanolamine or phosphatidylcholine, or in Sample solution 1 for the calculation of each of N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidic acid, phosphatidylinositol, and lysophosphatidylcholine (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: See Table Z.
Table 7
| Name | Acceptance Criteria (%) |
| N-Acylphosphatidylethanolamine | NMT 6.0 |
| Phosphatidic acid | NMT 3.0 |
| Phosphatidylethanolamine | 6.0–11.0 |
| Phosphatidylcholine | 65.0–89.9 |
| Phosphatidylinositol | NMT 1.5 |
| Lysophosphatidylcholine | NMT 6.0 |
For Soybean Phospholipids intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms
Lysophosphatidylcholine: NMT 3.0%
Other phospholipids: See Table 7.
4 IMPURITIES
LIMIT OF NONPHOSPHATIDYL LIPIDS
Diluent: Ethyl ether
Sample solution: 500 mg of Soybean Phospholipids, dissolved in 15 mL of Diluent, in a 50-mL conical flask
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography (621), General Procedures, Column Chromatography.)
Mode: Column
Chromatographic column: Transfer 1000 g of silica gel having a particle size of 0.05-0.2 mm into a container with well-closing screw caps.
Add 150 g of water, shake well, and allow to stand for 24 h. Suspend 15 g of prepared adsorbent in 50 mL of Diluent, and introduce into a 1-to 2-cm chromatographic column. Drain the Diluent through the column to a level of about 1 cm above the silica gel bed.
Analysis
Sample: Sample solution
Transfer the Sample solution to the Chromatographic column. Rinse the column containing the Sample solution with two 15-mL portions of Diluent, allowing each rinse to pass through the column before adding the next. After rinsing, elute with 105 mL of Diluent. Evaporate the eluate (150 mL) in a tared, round-bottom, 250-mL flask to dryness, using a suitable rotary evaporator. The volatiles are blown out with a stream of nitrogen, and the residue is dried at 105° for 20 min. The weight of the residue gives the oil fraction, determined as nonpolar lipids, in Soybean Phospholipids.
Calculate the percentage of the nonphosphatidyl lipids taken:
Result = WR/WS x 100
WR = weight of the residue (mg)
WS = weight of Soybean Phospholipids taken in the Sample solution (mg)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 4.0%
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
5.1 FATS AND FIXED OILS (401), Procedures. Acid Value
Sample: 2 g of Soybean Phospholipids
Analysis: Transfer the Sample into a 250-mL. Erlenmeyer flask. Add 100 mL of a mixture of equal volumes of alcohol and ethyl ether (which has been previously neutralized to phenolphthalein with 0.1 N potassium hydroxide VS). After the Sample is completely dissolved, add phenolphthalein TS. Titrate with 0.1 N potassium hydroxide VS to a pink endpoint that persists for at least 15 s.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 12
5.2 FATS AND FIXED OILS (401), Procedures, Peroxide Value
Sample: 5 g of Soybean Phospholipids
Analysis: Transfer the Sample into a 250-mL Erlenmeyer flask with a ground-glass stopper, add 35 mL of a mixture of chloroform and acetic acid, glacial (2:3), and mix. Completely dissolve the Sample while shaking gently. Add 0.5 mL of saturated potassium iodide aqueous solution. Shake for exactly 1 min, then add 30 mL of water. Titrate with 0.01 N sodium thiosulfate VS, adding the titrant slowly with continuous vigorous shaking, until the yellow color is almost discharged. Add 10 mL of starch TS and continue the titration, shaking vigorously, until the color is discharged. Perform a blank determination under the same conditions, and make any necessary correction.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 5
For Soybean Phospholipids intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms: NMT 3
5.3 MICROBIAL ENUMERATION TESTS (61) and TESTS FOR SPECIFIED MICROORGANISMS (62)
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 103 cfu/g, and the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 102 cfu/g. It meets the requirements of the tests for absence of Salmonella species and Escherichia coli. For Soybean Phospholipids intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms, which is specified in the labeling, the total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 102 cfu/g.
5.4 BACTERIAL ENDOTOXINS TEST (85)
Where the label states that Soybean Phospholipids must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms, the level of bacterial endotoxins is such that the requirement under the relevant dosage form monograph(s) in which Soybean Phospholipids is used can be met.
5.5 WATER DETERMINATION (921), Method I. Method la
NMT 2.0%
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
PACKAGING AND STORAGE: Preserve in well-closed, light-resistant containers. Store at a temperature between 2° and 8° for use in non-injectable dosage forms. Store at a temperature not exceeding -10° for use in injectable dosage forms. Protect from excess heat and moisture.
LABELING: Label to indicate the name and concentration of any stabilizer. Where Soybean Phospholipids is intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms, it is so labeled. Where Soybean Phospholipids must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms to ensure acceptable levels of bacterial endotoxins, it is so labeled.
USP REFERENCE STANDARDS (11)
USP Lyagphosphatidylcholine (Sov) RS
USP N-Acylphosphatidylethanolamine (Soy) Ammonium RS
USP Phosphatidic Acid (Soy) Monosodium RS
USP Phosphatidylcholine (Soy) RS
USP Phosphatidylethanolamine (Sov) RS
USP Phosphatidylinositol (Sov) Sodium RSA ▲(NF 1-Dec-2024)
1 A standard kit is available from CS Chromatographie Service GmbH (FAME-Test-Mix; item number 192005-3). An equivalent standard kit can also be used.
2 0.5 N sodium methoxide in methanol is available from Sigma-Aldrich, product number 403067. An equivalent reagent can be also used.


