Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
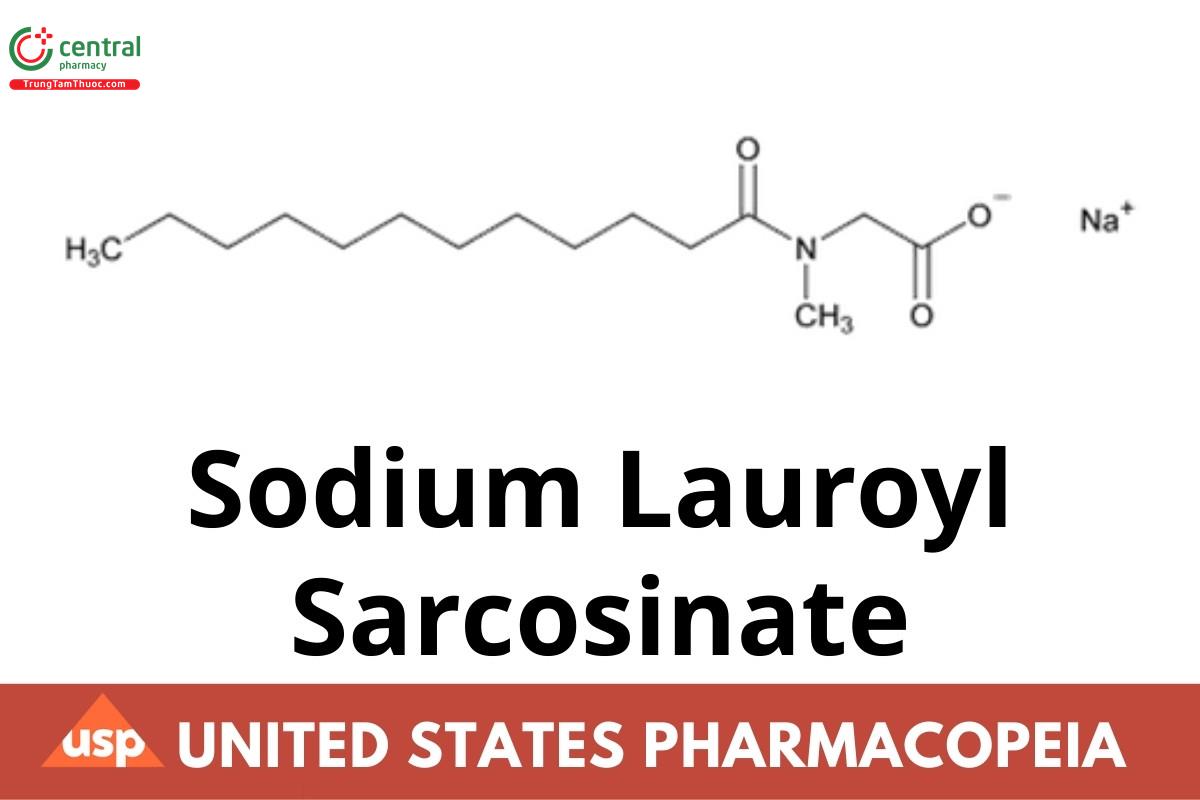
1 DEFINITION
Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate is a mixture of sodium N-acyl-N-methylglycinates, mainly consisting of NLT 92.0% and NMT 102.0% of sodium N- lauroyl-N-methylglycinate (sodium [dodecanoyl(methyl)amino]acetate) calculated on the anhydrous basis. It may contain a chelating agent.
2 IDENTIFICATION
A. SPECTROSCOPIC IDENTIFICATION TESTS 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197A
B. CHROMATOGRAPHIC IDENTITY
Analysis: Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Acceptance criteria: The retention time of the major peak of the Sample solution corresponds to that of the Standard solution.
C. PRESENCE OF SODIUM
Sample solution: Transfer 0.5 g of Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate in a silica crucible and ignite in a muffle furnace at 600 ± 25° for 1 h. Allow to cool to room temperature. Dissolve the residue in 10 mL of water. Use 0.5 mL of the solution so obtained as a Sample solution.
Methoxyphenylacetic solution: Dissolve 2.7 g of methoxyphenylacetic acid in 6 mL of 10% (w/w) tetramethylammonium hy droxide solution, and add 20 mL of absolute alcohol. Store in a polyethylene container.
Analyses: Perform the following 4 analyses in sequence.
Analysis 1: To the Sample solution add 1.5 mL of Methoxyphenylacetic solution, and cool in ice water for 30 min. Rub the inside of the test tube to initiate precipitation.
Acceptance criteria: A voluminous, white, crystalline precipitate is formed. Analysis 2: Place the test tube in water at 20°, and stir for 5 min.
Acceptance criteria: The precipitate does not disappear.
Analysis 3: To the test tube, add 1 mL of a 100-mg/mL ammonia solution, prepared by diluting 41 g of stronger ammonia water with water to 100 mL.
Acceptance criteria: The precipitate dissolves completely.
Analysis 4: To the test tube, add 1 mL of a 158-mg/mL ammonium carbonate solution, and mix well. Acceptance criteria: No precipitate is observed.
3 ASSAY
PROCEDURE
Solution A: 0.05% phosphoric acid, prepared by dissolving 1.0 mL of phosphoric acid in 2 L of water and mixing well Solution B: Acetonitrile
Diluent: Solution A and Solution B (1:1) Mobile phase: See Table 1.
Table 1
System suitability solution: 0.4 mg/mL of USP Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate RS and 20 µg/mL of USP Sodium Decanoyl Sarcosinate RS in Diluent
Standard solution: 0.4 mg/mL of USP Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate RS in Diluent Sample solution: 0.4 mg/mL of Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate in Diluent
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 205 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 10-cm; 2.7-µm packing L1 Column temperature: 40°
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min Injection volume: 10 µL Run time: NLT 40 min
System suitability
Samples: System suitability solution and Standard solution
[NOTE—The typical retention time for sodium lauroyl sarcosinate is about 7 min. The relative retention times for sodium decanoyl sarcosinate and sodium lauroyl sarcosinate are 0.4 and 1.0, respectively.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 8.0 between sodium lauroyl sarcosinate and sodium decanoyl sarcosinate, System suitability solution Tailing factor: 0.8–1.5, Standard solution
Relative standard deviation: NMT 0.5%, Standard solution Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of sodium lauroyl sarcosinate (C15H28NNaO3) in the portion of Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
rU = peak response of sodium lauroyl sarcosinate from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of sodium lauroyl sarcosinate from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: 92.0%–102.0% on the anhydrous basis IMPURITIES
LIMIT OF SODIUM DECANOYL SARCOSINATE AND SODIUM MYRISTOYL SARCOSINATE
Solution A, Solution B, Diluent, System suitability solution, Sample solution, and Chromatographic system: Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Standard solution: 2 µg/mL of USP Sodium Decanoyl Sarcosinate RS and 6 µg/mL of USP Sodium Myristoyl Sarcosinate RS in Diluent System suitability
Samples: System suitability solution and Standard solution
[NOTE—The relative retention times for sodium decanoyl sarcosinate, sodium lauroyl sarcosinate, and sodium myristoyl sarcosinate are 0.4, 1.0, and 2.7, respectively.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 8.0 between sodium lauroyl sarcosinate and sodium decanoyl sarcosinate, System suitability solution Relative standard deviation: NMT 5%, Standard solution
Signal-to-noise ratio: NLT 40, Standard solution Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Based on the Standard solution, identify the peaks of sodium decanoyl sarcosinate and sodium myristoyl sarcosinate. Compare peak areas of sodium decanoyl sarcosinate and sodium myristoyl sarcosinate in the Standard solution and the Sample solution.
Acceptance criteria
Sodium decanoyl sarcosinate: The peak area of sodium decanoyl sarcosinate in the Sample solution is NMT the peak area of sodium decanoyl sarcosinate in the Standard solution, corresponding to NMT 0.5% of sodium decanoyl sarcosinate in Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate.
Sodium myristoyl sarcosinate: The peak area of sodium myristoyl sarcosinate in the Sample solution is NMT the peak area of sodium myristoyl sarcosinate in the Standard solution, corresponding to NMT 1.5% of sodium myristoyl sarcosinate in Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate.
LIMIT OF SODIUM SARCOSINATE
Solution A: Add 3.0 mL of glacial acetic acid and 1.0 mL of triethylamine to 1 L of water, and mix well. Adjust with 1 M sodium hydroxide solution to a pH of 4.2.
Solution B: Acetonitrile
Borate buffer: Weigh 0.62 g of boric acid and dissolve in 100 mL of water. Adjust with 1 M sodium hydroxide solution to a pH of 9.0. This is a 0.1 M borate buffer.
FMOC-Cl solution: 30 µg/mL of 9-fluorenylmethyl chloroformate (FMOC-Cl) in Solution B Diluent: Solution B and water (2:3)
Mobile phase: See Table 2.
Table 2
System suitability solution A: 1.0 mg/mL of USP Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate RS, 8 µg/mL of sarcosine, and 10 µg/mL of 9-fluorenemethanol in Diluent
System suitability solution B: Add 0.1 mL of Borate buffer and 0.5 mL of FMOC-Cl solution to 0.4 mL of System suitability solution A, and mix well. Use within 24 h.
Standard solution A: 0.8 µg/mL of sarcosine in Diluent
Standard solution B: Add 0.1 mL of Borate buffer and 0.5 mL of FMOC-Cl solution to 0.4 mL of Standard solution A, and mix well. Use within 24 h.
Sample solution A: 1.0 mg/mL of Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate in Diluent
Sample solution B: Add 0.1 mL of Borate buffer and 0.5 mL of FMOC-Cl solution to 0.4 mL of Sample solution A, and mix well. Use within 24 h.
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.) Mode: LC
Detector: UV 260 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 10-cm; 2.7-µm packing L1 Column temperature: 40°
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min Injection volume: 10 µL Run time: NLT 13 min
System suitability
Samples: System suitability solution B and Standard solution B
[NOTE—The relative retention times for the FMOC derivative of sarcosine (FMOC-sarcosine) and 9-fluorenemethanol are 1.0 and 1.8, respectively.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 3 between the FMOC derivative of sarcosine (FMOC-sarcosine) and 9-fluorenemethanol, System suitability solution B Relative standard deviation: NMT 5% for the peak of the FMOC derivative of sarcosine (FMOC-sarcosine), Standard solution B
Signal-to-noise ratio: NLT 10 for the peak of the FMOC derivative of sarcosine (FMOC-sarcosine), Standard solution B Analysis
Samples: Standard solution B and Sample solution B
Based on Standard solution B, identify the peak of the FMOC derivative of sarcosine (FMOC-sarcosine). Calculate the percentage of sodium sarcosinate in the portion of Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × (Mr1/Mr2) × 100
rU = peak area of FMOC-sarcosine from Sample solution B
rS = peak area of FMOC-sarcosine from Standard solution B
CS = concentration of FMOC-sarcosine in Standard solution B (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate in Sample solution B (mg/mL)
Mr1 = molecular weight of sodium sarcosinate, 111.08
Mr2 = molecular weight of sarcosine, 89.09
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.2%
LIMIT OF SODIUM LAURATE
Solution A, Solution B, Diluent, System suitability solution, and Chromatographic system: Proceed as directed in the Assay. Standard solution A: 0.072 mg/mL of USP Lauric Acid RS in Diluent
Standard solution B: 0.36 mg/mL of USP Lauric Acid RS in Diluent Sample solution: 8.0 mg/mL of Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate in Diluent System suitability
Samples: System suitability solution, Standard solution A, and Standard solution B
[NOTE—The relative retention times for sodium decanoyl sarcosinate, sodium lauroyl sarcosinate, and sodium laurate are 0.4, 1.0, and 1.9, respectively.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 8.0 between sodium lauroyl sarcosinate and sodium decanoyl sarcosinate, System suitability solution Relative standard deviation: NMT 5%, Standard solution B
Signal-to-noise ratio: NLT 10, Standard solution A Analysis
Samples: Standard solution B and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of sodium laurate in the portion of Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × (Mr1/Mr2) × 100
rU = peak area of lauric acid from the Sample solution
rS = peak area of lauric acid from Standard solution B
CS = concentration of USP Lauric Acid RS in Standard solution B (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Mr1 = molecular weight of sodium laurate, 222.30
Mr2 = molecular weight of lauric acid, 200.32
Acceptance criteria: NMT 5.0%
LIMIT OF SODIUM CHLORIDE
Sample: 500 mg of Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate
Analysis: Dissolve the Sample in 50 mL of a mixture of equal volumes of alcohol and water. Add 10 mL of nitric acid and titrate with 0.005 M silver nitrate, determining the endpoint potentiometrically.1
Calculate the percentage of sodium chloride in the portion of Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate taken:
Result = [(M × V × Mr)/W] × 100
M = molarity of the silver nitrate solution (mmol/mL)
V = volume of 0.005 M silver nitrate used (mL)
Mr = molecular weight of sodium chloride, 58.44 mg/mmol
W = weight of the Sample (mg) Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.5%
LIMIT OF SODIUM SULFATE
Sample: 300 mg of Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate
Buffer solution: Add 60.0 mL of 2-propanol to 15.0 mL of acetic acid (300 mg/mL of glacial acetic acid in water). Adjust with stronger ammonia water to a pH of 3.7, and dilute with water to 100.0 mL.
Barium perchlorate solution: Dilute 10.0 mL of 0.05 M barium perchlorate solution with Buffer solution to 100 mL. The concentration is 0.005 M.
Analysis: In a 150-mL borosilicate-glass beaker dissolve the Sample in 20 mL of water. Add 0.3 mL of a 1-mg/mL naphtharson solution, 1.0 mL of perchloric acid, and 70.0 mL of 2-propanol.
Degas the solution under vacuum for 30 s or use an ultrasonic bath for 2 min and then titrate with Barium perchlorate solution.
Determine the endpoint using a suitable autotitrator equipped with an optrode or phototrode at about 520 nm and at 25°.2 Use a breakpoint to define the end of the titration. Adjust the stirrer speed to avoid the formation of bubbles.
Calculate the percentage of sodium sulfate in the portion of Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate taken:
Result = [(M × V × Mr)/W] × 100
M = molarity of the Barium perchlorate solution (mmol/mL)
V = volume of Barium perchlorate solution used (mL)
Mr = molecular weight of sodium sulfate, 142.04 mg/mmol
W = weight of the Sample (mg) Acceptance criteria: NMT 1.5%
4 SPECIFIC TESTS
PH 〈791〉
Sample solution: Dissolve 3.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water and dilute with water to 100 mL. Acceptance criteria: 7.5–8.5
WATER DETERMINATION 〈921〉 , Method I: NMT 5.0%
5 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
PACKAGING AND STORAGE: Preserve in tight containers. Store at room temperature.
LABELING: Label to indicate the name and amount of any added chelating agent.
USP REFERENCE STANDARDS 〈11〉
USP Lauric Acid RS
USP Sodium Decanoyl Sarcosinate RS
USP Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate RS
USP Sodium Myristoyl Sarcosinate RS (NF 1-Dec-2021)


