Sodium Gluconate
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
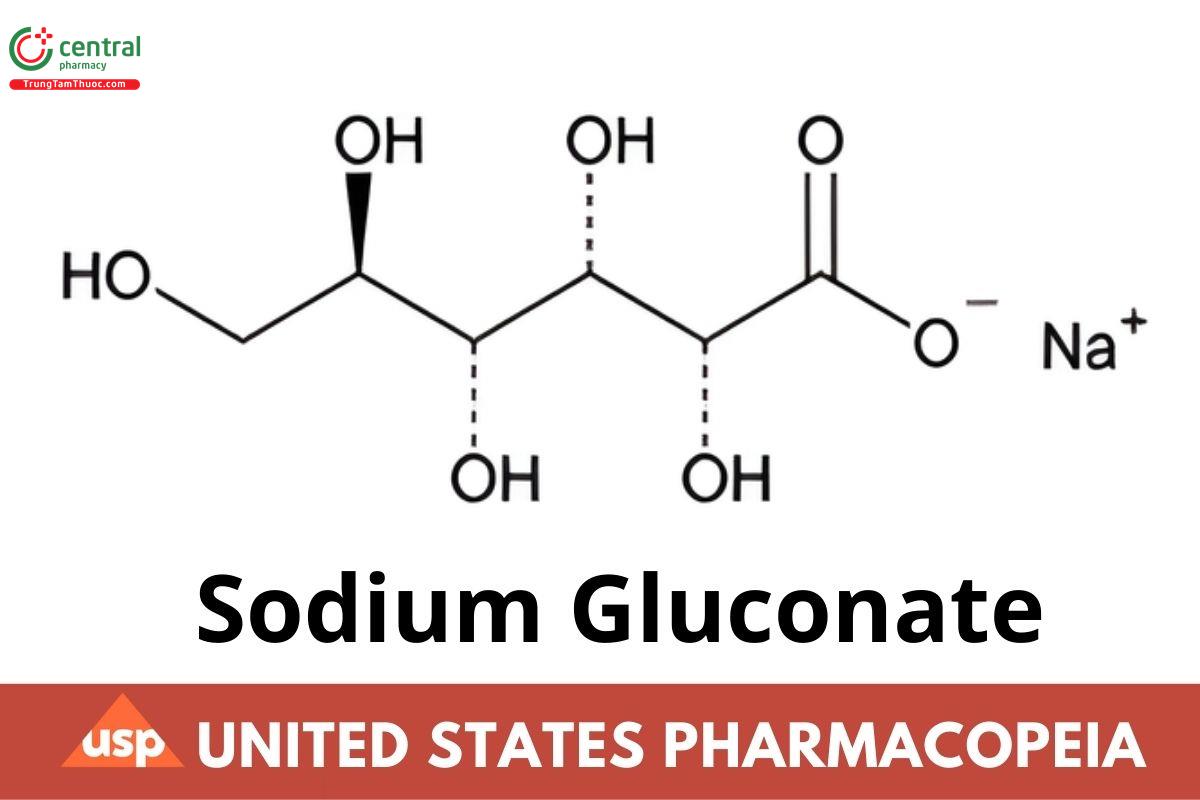
d-Gluconic acid, monosodium salt;
Monosodium d-gluconate CAS RN®: 527-07-1; UNII: R6Q3791S76.
1 DEFINITION
Sodium Gluconate contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of sodium gluconate (C6H11NaO7).
2 IDENTIFICATION
A. Identification Tests—General 〈191〉, Chemical Identification Tests, Sodium
Sample solution: 1 in 20
Acceptance criteria: Meets the requirements
B. Thin-Layer Chromatography
Standard solution: 10 mg/mL of USP Potassium Gluconate RS in water. [Note—Heat in a water bath at 60° to dissolve, if necessary.]
Sample solution: 10 mg/mL of Sodium Gluconate in water. [Note—Heat in a water bath at 60° to dissolve, if necessary.]
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, Thin-Layer Chromatography.)
Mode: TLC
Adsorbent: 0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel
Application volume: 5 μL
Developing solvent system: Alcohol, ethyl acetate, ammonium hydroxide, and water (50:10:10:30)
Spray reagent: Dissolve 2.5 g of ammonium molybdate in 50 mL of 2 N sulfuric acid in a 100-mL volumetric flask, add 1.0 g of ceric sulfate, swirl to dissolve, and dilute with 2 N sulfuric acid to volume.
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Develop in the Developing solvent system until the solvent front has moved three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate from the chamber, and dry at 110° for 20 min. Allow to cool and spray with the Spray reagent. Heat the plate at 110° for 10 min.
Acceptance criteria: The color, size, and R value of the principal spot from the Sample solution corresponds to that from the Standardsolution.
3 ASSAY
Procedure
Sample: 150 mg
Analysis: Transfer the Sample to a suitable conical flask and dissolve in 75 mL of glacial acetic acid, warming to dissolve, if necessary. Cool, add quinaldine red TS, and titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS to a colorless endpoint. Each milliliter of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent. to 21.81 mg of sodium gluconate (C6H11NaO7 ).
Acceptance criteria: 98.0%–102.0%
4 IMPURITIES
Change to read:
Chloride and Sulfate 〈221〉, Chloride
Sample: 1.0 g
Acceptance criteria: The turbidity produced in the Sample does not exceed that produced in (USP 1-May-2022) 1 mL of 0.02 N hydrochloric acid (NMT 0.07%).
Change to read:
Chloride and Sulfate 〈221〉, Sulfate
Sample: 2.0 g, dissolved in boiling water
Acceptance criteria: The turbidity produced in the Sample does not exceed that produced in (USP 1-May-2022) 1 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid (NMT 0.05%).
Delete the following:
Lead 〈251〉
Test preparation: 1.0 g in 25 mL of water
Acceptance criteria: NMT 10 ppm (USP 1-May-2022)
Reducing Substances
Sample: 1.0 g
Analysis: Transfer the Sample to a 250-mL conical flask, dissolve in 10 mL of water, and add 25 mL of alkaline cupric citrate TS. Cover the flask; boil gently for 5 min, accurately timed; and cool rapidly to room temperature. Add 25 mL of 0.6 N acetic acid, 10.0 mL of 0.1 N iodine VS, and 10 mL of 3 N hydrochloric acid, and then titrate with 0.1 N sodium thiosulfate VS, adding 3 mL of starch TS as the endpoint is approached. Perform a blank determination, omitting the specimen, and note the difference in volumes required (see Titrimetry 〈541〉). Each milliliter of the difference in volume of 0.1 N sodium thiosulfate consumed is equivalent to 2.7 mg of reducing substances (as dextrose).
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.5%
5 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in well-closed containers.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Potassium Gluconate RS


