Secobarbital Sodium
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
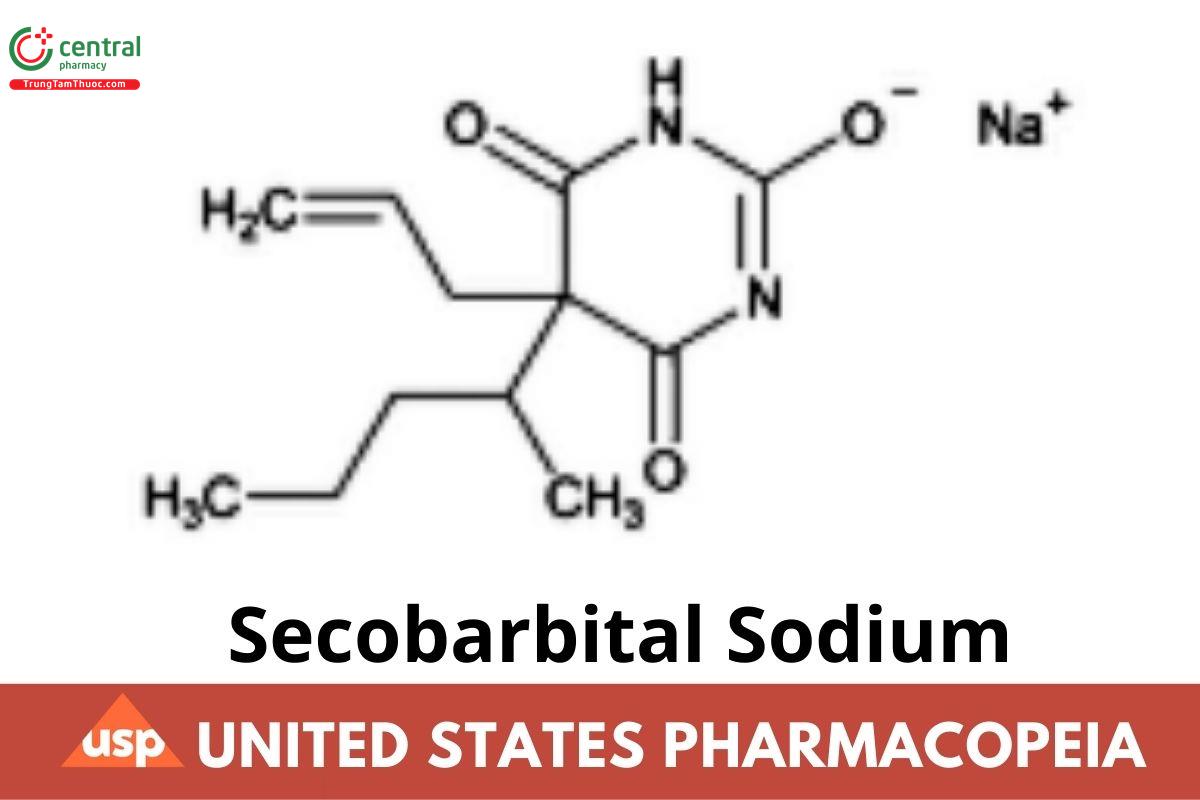
C12H17N2NaO3 260.26
2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-Pyrimidinetrione, 5-(1-methylbutyl)-5-(2-propenyl)-, monosodium salt.
Sodium 5-allyl-5-(1-methylbutyl)barbiturate CAS RN®: 309-43-3; UNII: XBP604F6UM.
Secobarbital Sodium contains not less than 98.0 percent and not more than 102.0 percent of C12H17N2NaO3, calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—Preserve in tight containers.
Labeling—Where it is intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms, the label states that it is sterile or must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms.
USP Reference standards 〈11〉—
USP Secobarbital RS
Completeness of solution—Mix 1.0 g with 10 mL of carbon dioxide-free water: after 1 minute, the solution is clear and free from undissolved solid.
Identification—
A: Spectroscopic Identication Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197M—
Test specimen: Dissolve about 500 mg of Secobarbital Sodium, accurately weighed, in 15 mL of water in a separator. To the solution, add 2 mL of hydrochloric acid, shake, and extract the liberated secobarbital with eight 25-mL portions of dichloro methane. Test for completeness of extraction by extracting with an additional 10-mL portion of dichloromethane and evaporating the solvent: not more than 0.5 mg of residue remains. Filter the extracts into a tared beaker, and finally rinse the separator and the filter with several small portions of dichloromethane. Evaporate the combined filtrate and washings on a steam bath with the aid of a current of air just to dryness. Dissolve the residue in 2 mL of dehydrated alcohol, and evaporate to dryness. Repeat the dissolution and evaporation with 2 mL of dehydrated alcohol, and dry the residue at 100° for 2 hours. Use a suitable amount of the residue for examination.
B: Ignite about 500 mg: the residue effervesces with acids, and meets the requirements of the tests for Sodium 〈191〉. C: The retention time of the major peak in the chromatogram of the Assay preparation corresponds to that in the chromatogram of the Standard preparation, as obtained in the Assay.
pH 〈791〉: between 9.7 and 10.5, in the solution prepared in the test for Completeness of solution.
Loss on drying 〈731〉—Dry it at 80° for 5 hours: it loses not more than 3.0% of its weight.
Related compounds—
Buffer, Mobile phase, and Standard preparation—Prepare as directed in the Assay.
Standard solution—Quantitatively dilute with Mobile phase a suitable volume of the Standard preparation to obtain a nal solution having a known concentration of about 5 µg per mL of USP Secobarbital RS.
Test solution—Use the Assay stock preparation.
Chromatographic system—Prepare as directed for Assay. Chromatograph the Standard solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the tailing factor for secobarbital is not more than 2.0; and the relative standard deviation for ve replicate injections for secobarbital is not more than 6.0%.
Procedure—Separately inject a volume (about 10 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, and record the chromatograms. Identify the peaks due to the impurities using the relative retention times given in Table 1. Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Secobarbital Sodium taken by the formula:
100(r/rS)(CS/CU)(1/F)
in which r is the response of the impurity peak obtained from the Test solution; rS is the response of secobarbital obtained from the Standard solution; CS is the concentration of USP Secobarbital RS, in mg per mL, in the Standard solution; CU is the nominal concentration ofSecobarbital Sodium, in mg per mL, in the Test solution; and F is the relative response factor given in Table 1. The impurities meet the limits given in Table 1.
Table 1
Compound | Relative Retention Time (RRT) | Relative Response Factor (F) | Limit (%) |
Imino impurity1 | 0.33 | 1.7 | NMT 1.0 |
2-Hydroxy propyl impurity2 | 0.38 | 0.95 | NMT 0.25 |
Secobarbital | 1.0 | 1.0 | — |
MIBK impurity3 | 1.61 | 0.96 | NMT 0.55 |
Any individual unspecified impurity | — | 1.0 | NMT 0.10 |
Total impurities | — | — | NMT 1.5 |
1 5-Allyl-4-imino-5-(1-methylbutyl) barbituric acid.
2 5-(2-Hydroxypropyl)-5-(1-methylbutyl) barbituric acid.
3 5-Allyl-5-(1-3-dimethylbutyl) barbituric acid.
Change to read:
Other requirements—Where the label states that Secobarbital Sodium is sterile, it meets the requirements for Sterility Tests 〈71〉 and the level of bacterial endotoxins is not more than 0.9 USP Endotoxin Units per mg of secobarbital sodium tested per Bacterial Endotoxins Test 〈85〉. Where the label states that Secobarbital Sodium must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms, the level of bacterial endotoxins is not more than 0.9 USP Endotoxin Units per mg of secobarbital sodium tested per Bacterial Endotoxins Test 〈85〉.
Assay—
Buffer—Dissolve 1.36 g of monobasic potassium phosphate in 1000 mL of water.
Diluted phosphoric acid—Dilute orthophosphoric acid with water (4:1).
Mobile phase—Prepare a mixture of Buffer and acetonitrile (13:7). Adjust with Diluted phosphoric acid to a pH of 3.5. Standard preparation—In a suitable volumetric flask, dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Secobarbital RS in Mobile phase to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.4 mg per mL of secobarbital.
Assay stock preparation—Transfer about 100 mg of Secobarbital Sodium into a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add 60 mL of Mobile phase, and sonicate to dissolve. Dilute with Mobile phase to volume, and mix.
Assay preparation—Quantitatively dilute with Mobile phase the Assay stock preparation to obtain a nominal concentration of 0.4 mg per mL of secobarbital sodium.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography 〈621〉)—The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 215-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 15.0-cm column containing 3.5-µm packing L1. The ow rate is about 1 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the tailing factor for secobarbital is not more than 2.0; and the relative standard deviation from replicate injections for secobarbital is not more than 2.0%.
Procedure—Separately inject a volume (about 10 µL) of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph, and record the chromatograms. Identify the peaks due to the impurities using the relative retention times given in Table 1. Calculate the percentage of C12H17N2NaO3, in the portion of Secobarbital Sodium taken by the formula:
100(CS/CU)(rU/rS)(Mr1/Mr2)
in which CS is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Secobarbital RS in the Standard preparation;CU is the nominal concentration ofSecobarbital Sodium, in mg per mL, in the Assay preparation; rS is the response of secobarbital peak obtained from the Assay preparation; rS is the response of secobarbital peak obtained from the Standard preparation; Mr1 is the molecular weight of secobarbital sodium, 260.27; and Mr2 is the molecular weight of secobarbital, 238.28.


