Saccharin Sodium
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
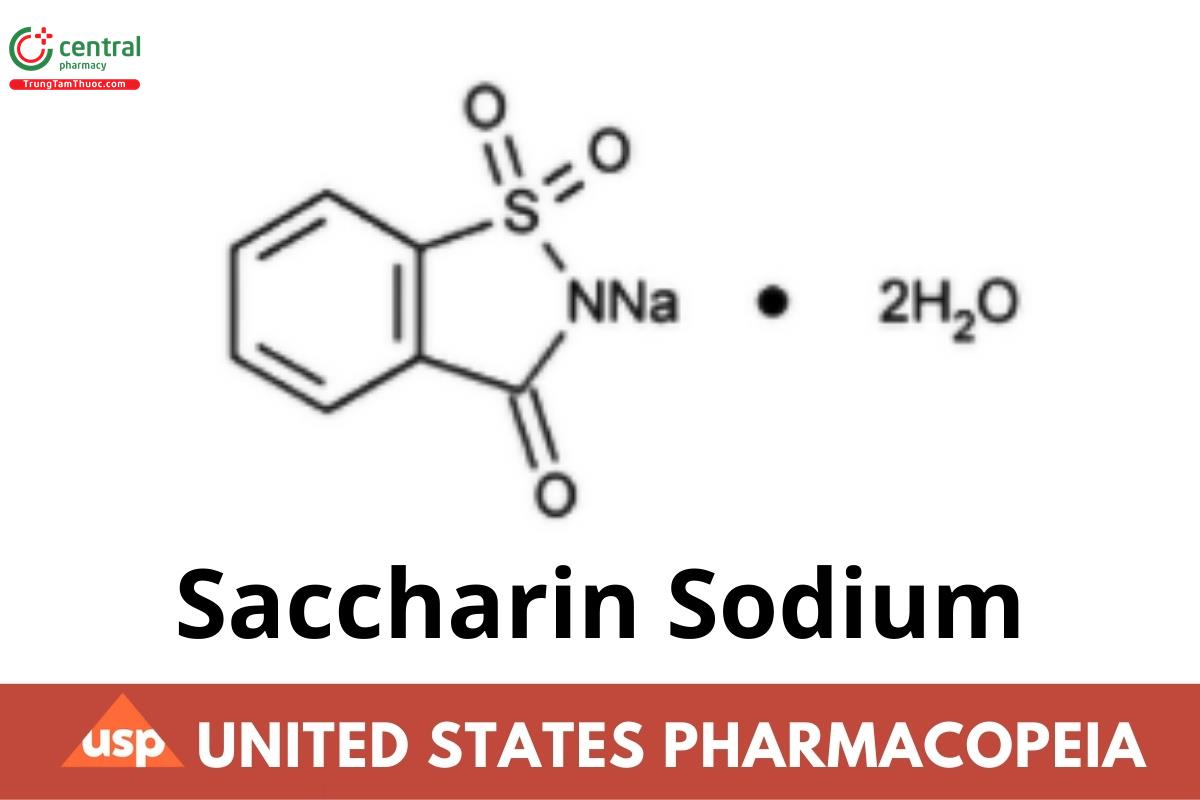
C7H4NNaO3S · 2H2O 241.20
C7H4NNaO3S 205.17
1,2-Benzisothiazol-3(2H)-one, 1,1-dioxide, sodium salt, dihydrate;
1,2-Benzisothiazolin-3-one 1,1-dioxide sodium salt dihydrate CAS RN®: 6155-57-3.
Anhydrous CAS RN®: 128-44-9.
1 DEFINITION
Saccharin Sodium contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of saccharin sodium (C7H4NNaO3S), calculated on the anhydrous basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
Change to read:
2.1 A. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197K (CN 1-May-2020)
Sample: Dry at 105° to constant weight.
Acceptance criteria: Meets the requirements
2.2 B.
Sample solution: 100 mg/mL
Potassium pyroantimonate solution: Dissolve 2 g of potassium pyroantimonate in 95 mL of hot water. Cool quickly, and add 50 mL of a potassium hydroxide solution (50 mg/mL) and 1 mL of sodium hydroxide solution (8.5 in 100). Allow to stand for 24 h, filter, and dilute with water to 150 mL.
Analysis: To 10 mL of the Sample solution add 2 mL of 15% potassium carbonate, and heat to boiling. No precipitate is formed. Add 4 mL of Potassium pyroantimonate solution, and heat to boiling. Allow to cool in ice water and, if necessary, rub the inside of the test tube with a glass rod.
Acceptance criteria: A dense precipitate is formed.
2.3 C. Sodium salts impart an intense yellow color to a nonluminous flame.
3 ASSAY
3.1 Procedure
Solution A: 50 mM dibasic potassium phosphate (K₂HPO₄) buffer in 0.1% (v/v) phosphoric acid solution
Solution B: Methanol
Mobile phase: See Table 1.
Table 1
| Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) |
| 0.0 | 90 | 10 |
| 7.0 | 90 | 10 |
| 8.0 | 5 | 95 |
| 10.0 | 5 | 95 |
| 10.1 | 90 | 10 |
| 15.0 | 90 | 10 |
Diluent: Methanol and water (50:50 v/v)
System suitability solution: 0.1 mg/mL of phthalic anhydride and 0.1 mg/mL of USP Saccharin Sodium RS in Diluent
Standard solution: 0.1 mg/mL of USP Saccharin Sodium RS in Diluent
Sample solution: 0.1 mg/mL of Saccharin Sodium in Diluent
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 230 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 15-cm; 3.5-µm packing L1
Column temperature: 20 ± 5°
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min
Injection volume: 10 µL
Run time: 15 min
System suitability
Samples: System suitability solution and Standard solution
[Note—The retention times for phthalic anhydride and saccharin sodium are about 6.3 and 7.3 min, respectively. Phthalic anhydride is a potential impurity.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 1.5 between the phthalic anhydride and saccharin sodium peaks
Tailing factor: NMT 1.5
Relative standard deviation: NMT 0.73% for five replicate injections
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of saccharin sodium in the portion of Saccharin Sodium taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
rU = peak area of saccharin sodium from the Sample solution
rS = peak area of saccharin sodium from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Saccharin Sodium RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Saccharin Sodium in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: 98.0%–102.0% on the anhydrous basis
4 IMPURITIES
4.1 Limit of Toluenesulfonamides
Internal standard solution: 0.25 mg/mL of caffeine in methylene chloride
Standard stock solution: 20.0 µg/mL of USP o-Toluenesulfonamide RS and 20.0 µg/mL of USP p-Toluenesulfonamide RS in methylene chloride
Standard solution: Evaporate 5.0 mL of Standard stock solution to dryness in a stream of nitrogen. Dissolve the residue in 1.0 mL of the Internal standard solution.
Sample stock solution: 200 mg/mL in water. If necessary, adjust with 1 N sodium hydroxide or 1 N hydrochloric acid to a pH of 7–8 before final dilution.
Sample solution: Shake 50 mL of the Sample stock solution with four quantities each of 50 mL of methylene chloride. Combine the lower layers, dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and filter. Wash the filter and the sodium sulfate with 10 mL of methylene chloride. Combine the solution and the washings, and evaporate almost to dryness in a water bath at a temperature not exceeding 40°. Using a small quantity of methylene chloride, quantitatively transfer the residue into a suitable 10-mL tube, evaporate to dryness in a stream of nitrogen, and dissolve the residue in 1.0 mL of the Internal standard solution.
Blank solution: Evaporate 200 mL of methylene chloride to dryness in a water bath at a temperature not exceeding 40°. Dissolve the residue in 1 mL of methylene chloride.
Chromatographic system
Mode: GC
Detector: Flame ionization
Column: 0.53-mm × 10-m fused silica; coated with a 2-µm film of phase G3
Temperatures
Injection port: 250°
Column: 180°
Detector: 250°
Carrier gas: Nitrogen
Flow rate: 10 mL/min
Injection volume: 1 µL
Injection type: Split ratio, 2:1
System suitability
[Note—The substances are eluted in the following order: o-toluenesulfonamide, p-toluenesulfonamide, and caffeine.]
Acceptance criteria: See Table 2.
Table 2
| Name | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (ppm) |
| o-Toluenesulfonamide | 10 |
| p-Toluenesulfonamide | 10 |
4.2 Limit of Benzoate and Salicylate
Sample solution: 50 mg/mL
Analysis: To 10 mL of the Sample solution add 5 drops of 6 N acetic acid, and then add 3 drops of ferric chloride TS.
Acceptance criteria: No precipitate or violet color appears.
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
5.1 Water Determination 〈921〉, Method I: NMT 15.0%
Change to read:
5.2 Readily Carbonizable Substances Test 〈271〉
Matching fluid A: Cobaltous chloride CS, ferric chloride CS, (ERR 1-May-2020) cupric sulfate CS, and water (0.1:0.4:0.1:4.4)
Sample solution: 40 mg/mL in sulfuric acid maintained at 48°–50° for 10 min
Acceptance criteria: The Sample solution has no more color than Matching fluid A, when viewed against a white background.
5.3 Acidity or Alkalinity
Sample solution: 100 mg/mL in carbon dioxide-free water
Analysis: To 10 mL of the Sample solution add 1 drop of phenolphthalein TS.
Acceptance criteria: No red or pink color is produced. Then add 1 drop of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide: a red or pink color is produced.
5.4 Clarity of Solution
[Note—The Sample solution is to be compared to Reference suspension A in diffused daylight 5 min after preparation of Reference suspension A.]
Hydrazine solution: 10.0 mg/mL of hydrazine sulfate in water. [Note—Allow to stand for 4–6 h.]
Methenamine solution: Transfer 2.5 g of methenamine to a 100-mL glass-stoppered flask, add 25.0 mL of water, insert the glass stopper, and mix to dissolve.
Primary opalescent suspension: Transfer 25.0 mL of Hydrazine solution to the Methenamine solution in the 100-mL glass-stoppered flask. Mix, and allow to stand for 24 h. [Note—This suspension is stable for 2 months, provided it is stored in a glass container free from surface defects. The suspension must not adhere to the glass and must be well mixed before use.]
Opalescence standard: Transfer 15.0 mL of the Primary opalescent suspension, dilute with water to 1000 mL, and mix. [Note—This suspension should not be used beyond 24 h after preparation.]
Reference suspension A: Opalescence standard and water (1 in 20)
Reference suspension B: Opalescence standard and water (1 in 10)
Sample solution: 200 mg/mL in water
Analysis
Samples: Reference suspension A, Reference suspension B, Sample solution, and water
Transfer a sufficient portion of the Sample solution to a test tube of colorless, transparent, neutral glass with a flat base and an internal diameter of 15–25 mm to obtain a depth of 40 mm. Similarly transfer portions of Reference suspension A, Reference suspension B, and water to separate matching test tubes. Compare solutions in diffused daylight, viewing vertically against a black background (see Visual Comparison 〈630〉).
[Note—The diffusion of light must be such that Reference suspension A can readily be distinguished from water, and that Reference suspension B can readily be distinguished from Reference suspension A.]
Acceptance criteria: The Sample solution shows the same clarity as that of water, or its opalescence is NMT that of Reference suspension A.
5.5 Color of Solution
Diluent: 10-g/L solution of hydrochloric acid
Standard stock solution: Ferric chloride CS, cobaltous chloride CS, cupric sulfate CS, and Diluent (3.0:3.0:2.4:1.6)
Standard solution: Standard stock solution and Diluent (1 in 100). [Note—Prepare the Standard stock solution and Standard solution immediately before use.]
Sample solution: Use the Sample solution from the test for Clarity of Solution.
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution, Sample solution, and water
Transfer a sufficient portion of the Sample solution to a test tube of colorless, transparent, neutral glass with a flat base and an internal diameter of 15–25 mm to obtain a depth of 40 mm. Similarly transfer portions of the Standard solution and water to separate, matching test tubes. Compare the solutions in diffused daylight, viewing vertically against a white background (see Visual Comparison 〈630〉).
Acceptance criteria: The Sample solution has the appearance of water or is not more intensely colored than the Standard solution.
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in well-closed containers. Store at room temperature.
Labeling: Where the quantity of saccharin sodium is indicated in the labeling of any preparation containing Saccharin Sodium, this shall be expressed in terms of saccharin (C7H5NO3S).
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Saccharin Sodium RS
USP o-Toluenesulfonamide RS
USP p-Toluenesulfonamide RS


