Repository Corticotropin Injection
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here

This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
1 DEFINITION
Repository Corticotropin Injection is Corticotropin in a solution of partially hydrolyzed gelatin. Its potency is NLT 80.0% and NMT 125.0% of the potency stated on the label in USP Corticotropin Units. It may contain a suitable antimicrobial agent.
2 IDENTIFICATION
A. Meets the requirements of the Assay
3 ASSAY
Procedure
Standard solutions: Add gelatin TS to an opened container of USP Corticotropin RS, and mix to obtain a solution having a concentration of 2.0 USP Corticotropin Units/mL. Using gelatin TS as a diluent, prepare three diluted Standard solutions such that the respective concentrations of corticotropin constitute a geometric series such as 1:2:4 or 1:3:9 and such that the quantity of corticotropin in each 0.5 mL lies within the range of 10–300 milliunits.
Sample solutions: In the same manner as the Standard solutions preparation, using the same diluent, dilute the Injection to make three Sample solutions corresponding in concentration to those of the Standard solutions.
The animals: Select healthy rats, of the same but either sex, that have been raised on a diet fully adequate with respect to vitamin and mineral content. Anesthetize the rats and remove the hypophysis from each by application of gentle suction through a fine-tipped tube. Between 16 and 48 h after the operation, select those rats weighing 80–180 g, but restrict the selection so that no rat is more than 30% heavier than the lightest, and the number of rats is an exact multiple of 6. Separate the selected rats into 6 groups, equal in size, of NLT 6 rats each, and assign at random one of the three diluted Standard solutions or one of the three Sample solutions to each group.
Analysis: Inject all rats of each group subcutaneously with the assigned test doses. Three h after the injection, anesthetize the rats, and remove both adrenal glands from each rat, free them from adhering tissue, and promptly weigh each pair on a suitable balance to the nearest 0.2 mg. Place the weighed glands from each rat in suitable vessels each containing 8.0 mL of metaphosphoric acid solution (1 in 40), and pulverize the glands by grinding with a small quantity of washed sand. Cover each vessel, and proceed similarly until all glands have been extracted.
Ascorbic acid determination: Filter the metaphosphoric acid extracts, and pipet 4 mL of each filtrate into suitable vessels each containing 4.0 mL of indophenol–acetate TS. Mix by shaking, and read the absorbance at 520 nm, with a suitable spectrophotometer. From the observed absorbance and the standard curve prepared as directed below, calculate the amount of ascorbic acid in mg/100 g of adrenal gland tissue.
Prepare a standard concentration–absorbance curve, using three ascorbic acid solutions containing, respectively, 6.0, 8.0, and 10.0 µg/mL of USP Ascorbic Acid RS in metaphosphoric acid solution (1 in 40). Pipet into each of three suitable vessels, preferably spectrophotometer cells, 4 mL of indophenol–acetate TS. Add 4.0 mL of one of the three standard ascorbic acid solutions to one of the cells, mix, and promptly read the absorbance from the same instrument and under the same conditions as for the adrenal gland extracts. Repeat the process for the other two standard ascorbic acid solutions, plot the concentration–absorbance values, and draw the straight line best fitting the three plotted points.
Calculation: If there are no missing data (i.e., all groups of rats are the same size, f), then the following may be used. [Note—If there are missing values, then suitable software can be used and standard procedures followed for parallel line bioassays, including assessment of parallelism and linearity.] Tabulate the observed concentration of ascorbic acid in the adrenal glands of each rat, designated by the symbol yjkl, where j = S (Standard) or U (Sample), k = 1, 2, or 3 for the three doses, and l = 1, . . ., f rats. Total the values of the yjkl,s in each group as:

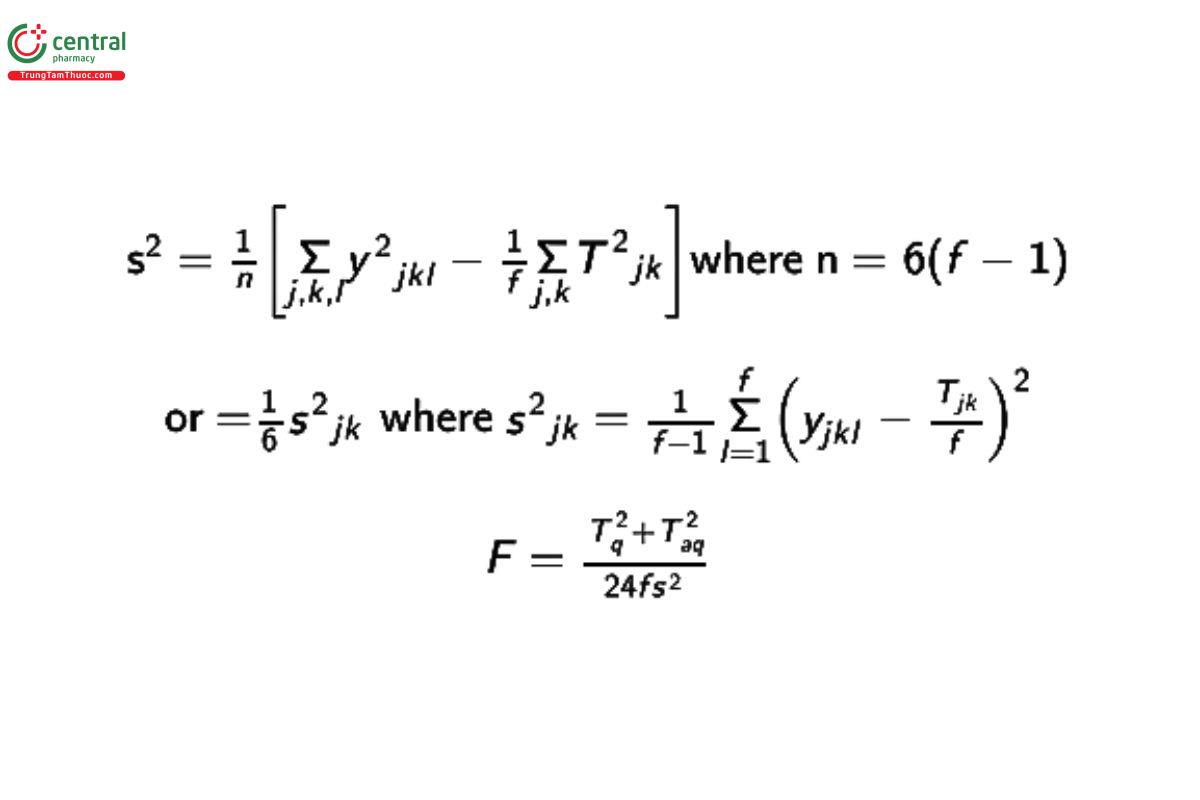
If V ≥ 0.75 and V ≤ 1.33, then the data satisfy parallelism. If F ≤ F0.05,2,n, where F0.05,2,n is the upper 0.05 percentage point of an F distribution with 2 and n degrees of freedom, then the data satisfy linearity. If both conditions are satisfied, determine the logarithm of potency of the Injection, M, taken as:
M = M′ + log R
where
M′ = 4iTa/(3Tb)
i = interval between successive log doses [log(higher dose) − log(lower dose)] of both the Standard solution and the Sample solution
R = vS / vU, the ratio of the high dose of the Standard solution in USP Corticotropin Units (vS) to the high dose of the Sample solution in mL (vU)
Determine the width, L, of the log confidence interval as:
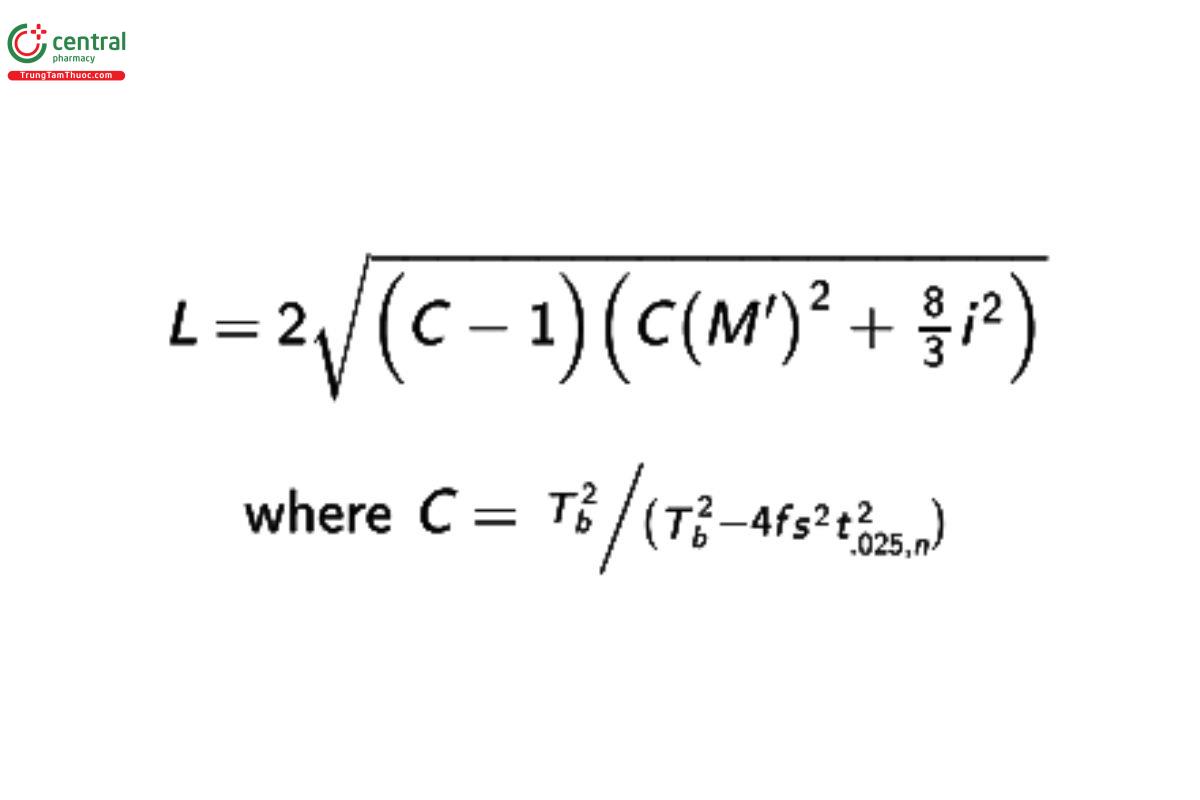
and t0.025,n is the upper one-sided 0.025 percentage point (or two-sided 0.05 percentage point) of a t-distribution with n degrees of freedom.
Replication: Repeat the entire determination at least once. Test the agreement among the two or more independent determinations, and compute the weight for each (see Design and Analysis of Biological Assays 〈111〉, Combination of Independent Assays). Calculate the weighted mean log-potency M and its confidence interval, L (see Design and Analysis of Biological Assays 〈111〉, The Confidence Interval and Limits of Potency). The potency, P, is satisfactory if P = antilog M is 80%–125% of the labeled potency and if the confidence interval does not exceed 0.40.
Acceptance criteria: 80.0%–125.0%
4 IMPURITIES
Vasopressin Activity
Solution A: Dissolve 6.6 g of dibasic ammonium phosphate in about 950 mL of water, and adjust with concentrated phosphoric acid to a pH of 3.0. Dilute with water to 1 L.
Mobile phase: Acetonitrile and Solution A (13:87). Filter and degas.
[Note—The retention time of the vasopressin peak is very sensitive to small changes in the acetonitrile concentration.]
Standard solution: Dissolve the entire contents of a vial of USP Vasopressin RS in a known volume of Solution A, and dilute with Solution A to obtain a final solution containing 0.1 USP Vasopressin Units/mL.
Sample solution: Dissolve the entire contents of a vial of Injection in a known volume of Solution A, and dilute with Solution A to obtain a final solution containing 2.0 USP Corticotropin Units/mL.
Chromatographic system
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 220 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Flow rate: About 1.5 mL/min
Injection volume: 20 µL
System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
Suitability requirements:
Relative standard deviation: NMT 2.0%
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the vasopressin activity in USP Vasopressin Units/USP Corticotropin Unit:
Result = C × [(rU / rS)/2]
C = concentration of the Standard solution (USP Vasopressin Units/mL)
rU = peak response from the Sample solution
rS = peak response from the Standard solution
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.05 USP Vasopressin Units/USP Corticotropin Unit
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
pH 〈791〉: 3.0–7.0
Bacterial Endotoxins Test 〈85〉: NMT 3.1 USP Endotoxin Units/USP Corticotropin Unit
Injections and Implanted Drug Products 〈1〉: Meets the requirements
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in single-dose or multiple-dose containers, preferably of Type I glass.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Ascorbic Acid RS
USP Corticotropin RS
USP Vasopressin RS


