Ranitidine Hydrochloride
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
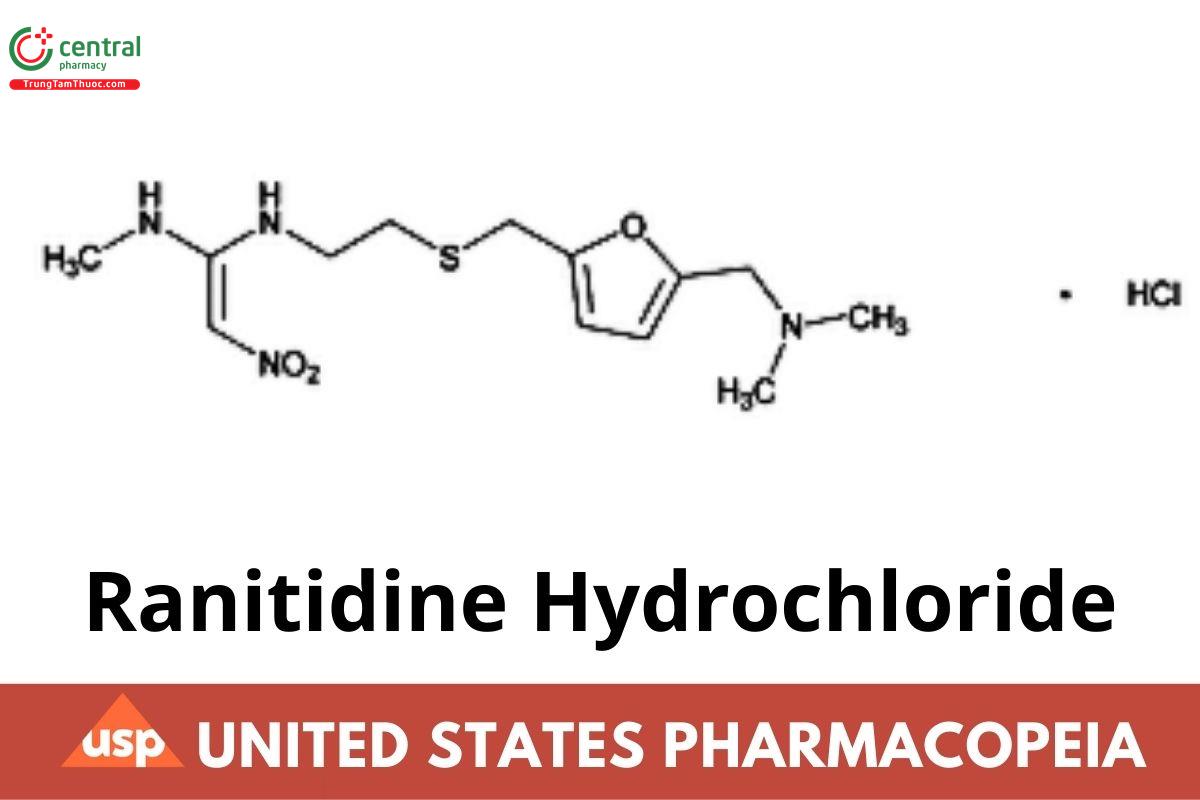
C13H22N4O3S.HCl 350.86
1,1-Ethenediamine, N-[2-[[[5-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-2-furanyl]-methyl]thio]ethyl]-N′-methyl-2-nitro-, monohydrochloride. N-[2-[[[5-[(Dimethylamino)methyl]-2-furanyl]methyl]thio]ethyl]-N′-methyl-2-nitro-1,1-ethenediamine, hydrochloride CAS RN®: 66357-59-3; UNII: BK76465IHM.
Ranitidine Hydrochloride contains not less than 97.5 percent and not more than 102.0 percent of C13H22N4O3S.HCl, calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers.
USP Reference standards 〈11〉—
USP Ranitidine Hydrochloride RS
USP Ranitidine Resolution Mixture RS
It is a mixture of ranitidine hydrochloride and four related impurities: ranitidine-N-oxide, ranitidine complex nitroacetamide, ranitidine diamine hemifumarate, and ranitidine amino alcohol hemifumarate.
Ranitidine-N-oxide: N,N-dimethyl[5-[[[2-[[1-(methylamino)-2-nitroethenyl]amino]ethyl]sulphanyl]meth yl]furan-2-yl]methanamine N-oxide. Ranitidine complex nitroacetamide: N-[2-[[[5-[(dimethyl amino)methyl]furan-2-yl]methyl]sulphanyl]ethyl]-2-nitroacetamide. Ranitidine diamine hemifumarate (related compound A): 5-[[(2-aminoethyl)thio]methyl]-N,N-dimethyl-2-furanmethanamine, hemifumarate salt. Ranitidine amino alcohol hemifumarate: [5-[(dimethylamino)methyl]furan-2-yl]methanol.
Identification—
Change to read:
A: Spectroscopic Identication Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197M (CN 1-May-2020) .
Change to read:
B: Spectroscopic Identication Tests 〈197〉, Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy: 197U (CN 1-May-2020)
Solution: 10 µg per mL.
Medium: water.
Absorptivities at 229 nm and 315 nm, calculated on the dried basis, do not differ by more than 3.0%.
C: A solution of it meets the requirements of the tests for Chloride 〈191〉.
pH 〈791〉: between 4.5 and 6.0, in a solution (1 in 100).
Loss on drying 〈731〉—Dry it in vacuum at 60° for 3 hours: it loses not more than 0.75% of its weight.
Residue on ignition 〈281〉: not more than 0.1%.
Chromatographic purity—
Diluent, Mobile phase, Resolution solution, and Chromatographic system—Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Standard solution—Prepare as directed for Standard preparation in the Assay.
Test solution—Prepare as directed for Assay preparation in the Assay.
Procedure—Separately inject equal volumes (about 10 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and identify the ranitidine peak and the peaks due to impurities and degradation products listed in the table below.
Name | Relative Retention Time |
Ranitidine simple nitroacetamide1 | 0.14 |
Ranitidine oxime2 | 0.21 |
Ranitidine amino alcohol3 | 0.45 |
Ranitidine diamine4 | 0.57 |
Ranitidine S-oxide5 | 0.64 |
Ranitidine N-oxide6 | 0.72 |
Ranitidine complex nitroacetamide7 | 0.84 |
Ranitidine formaldehyde adduct8 | 1.36 |
Ranitidine bis-compound9 | 1.75 |
1 N-Methyl-2-nitroacetamide.
2 3-(Methylamino)-5,6-dihydro-2H-1,4-thiazin-2-one oxime.
3{5-[(Dimethylamino)methyl]furan-2-yl}methanol.
4 5-{[(2-Aminoethyl)thio]methyl}-N,N-dimethyl-2-furanmethanamine (ranitidine related compound A).
5 N-{2-[({5-[(Dimethylamino)methyl]-2-furanyl}methyl)sulnyl]ethyl}-N′-methyl-2-nitro-1,1-ethenediamine (ranitidine related compound C). 6 N,N-Dimethyl(5-{[(2-{[1-(methylamino)-2-nitroethenyl]amino}ethyl) sulphanyl]methyl}furan-2-yl)methanamine N-oxide.
7 N-{2-[({5-[(Dimethylamino)methyl]furan-2-yl}methyl)sulphanyl]ethyl}-2-nitroacetamide.
8 2,2′-Methylenebis(N-{2-[({5-[(dimethylamino)methyl]furan-2-yl}methyl) sulphanyl]ethyl}-N′-methyl-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine).
9 N,N′-bis{2-[({5-[(Dimethylamino)methyl]-2-furanyl}methyl)thio]ethyl}-2-nitro-1,1-ethenediamine (ranitidine related compound B).
Measure the responses for the major peaks, and calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Ranitidine Hydrochloride taken by the formula:
100CV/W(ri/rs)
in which C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of ranitidine hydrochloride in the Standard solution; V is the volume, in mL, of the Test solution; W is the weight, in mg, of Ranitidine Hydrochloride taken to prepare the Test solution; ri is the peak response for each impurity obtained from the Test solution; and rs is the ranitidine peak response obtained from the Standard solution: not more than 0.3% of ranitidine bis-compound is found, not more than 0.1% of any other single impurity is found, and not more than 0.5% of total impurities is found. The reporting level for impurities is 0.05%.
Assay—
Phosphate buffer—Place approximately 1900 mL of water in a 2.0-L volumetric flask, accurately add 6.8 mL of phosphoric acid, and mix. Accurately add 8.6 mL of 50% sodium hydroxide solution, and dilute with water to volume. If necessary, adjust with 50% sodium hydroxide solution or phosphoric acid to a pH of 7.1, and filter.
Solution A—Prepare a mixture of Phosphate buffer and acetonitrile (98:2).
Solution B—Prepare a mixture of Phosphate buffer and acetonitrile (78:22).
Mobile phase—Use variable mixtures of Solution A and Solution B as directed for Chromatographic system. Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography 〈621〉).
Diluent—Use Solution A.
Standard preparation—Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Ranitidine Hydrochloride RS in Diluent to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.125 mg of ranitidine hydrochloride per mL.
Resolution solution—Transfer about 1.3 mg of USP Ranitidine Resolution Mixture RS to a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in and dilute with Diluent to volume.
[Note—USP Ranitidine Resolution Mixture RS contains ranitidine hydrochloride and four related impurities: ranitidine amino alcohol hemifumarate, ranitidine diamine hemifumarate, ranitidine N-oxide, and ranitidine complex nitroacetamide.]
Assay preparation—Transfer about 25 mg of Ranitidine Hydrochloride, accurately weighed, to a 200-mL volumetric flask. Dissolve in and dilute with Diluent to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography 〈621〉)—The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 230-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 10-cm column containing 3.5-µm packing L1 that is stable from pH 1 to 12. The flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute. The column temperature is maintained at 35°. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
Time (minutes) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) | Elution |
0–10 | 100→0 | 0→100 | linear gradient |
10–15 | 0 | 100 | isocratic |
15–16 | 0→100 | 100→0 | linear gradient |
16–20 | 100 | 0 | re-equilibration |
Chromatograph the Resolution solution, and identify the peaks using the table of impurities and degradation products (found above): the resolution, R, between the peaks for ranitidine N-oxide and ranitidine complex nitroacetamide is not less than 1.5. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 1.0%.
Procedure—Separately inject equal volumes (about 10 µL) of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the areas for the major peaks. Calculate the percentage of C13H22N4O3S.HCl in the portion of Ranitidine Hydrochloride taken by the formula:
100(CU/CS)(rS/rU)
in which CU and CS are the concentrations, in mg per mL, of ranitidine hydrochloride in the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation, respectively; and rU and rS are the peak responses obtained from the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation, respectively.


