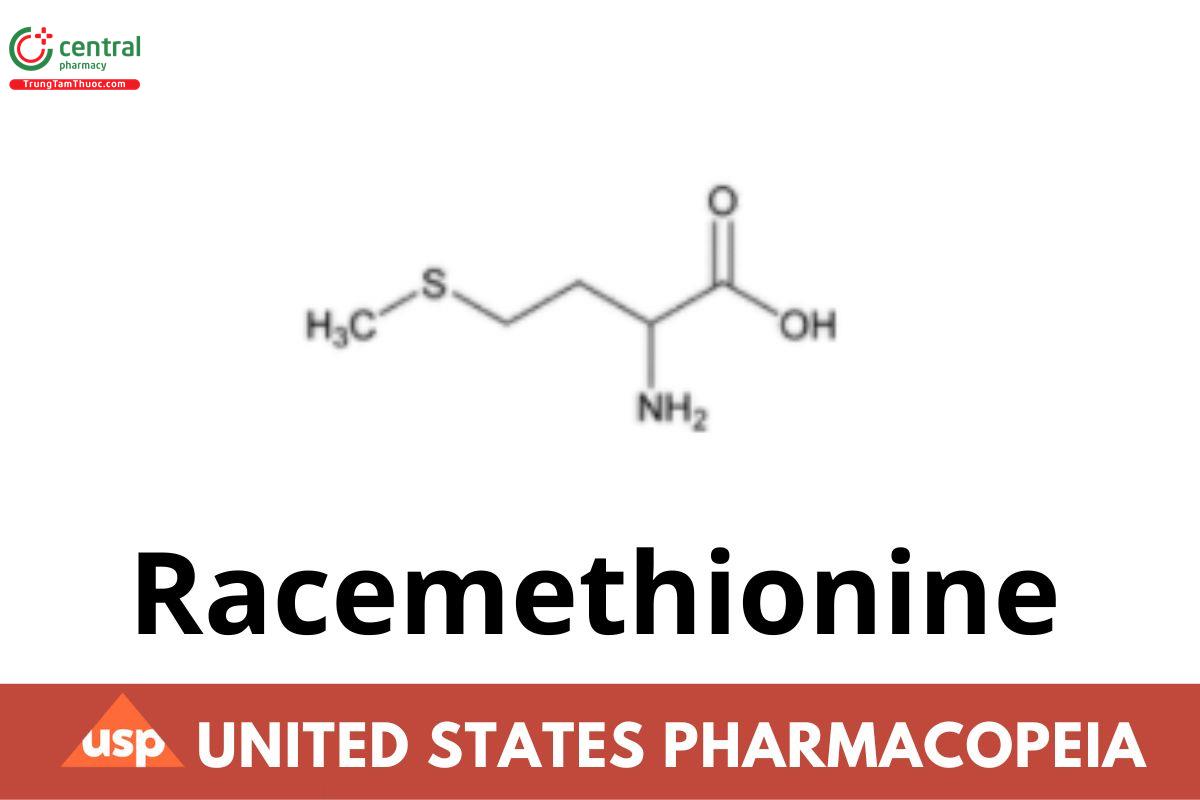
Racemethionine
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
DOWNLOAD PDF HERE
1 DEFINITION
Racemethionine contains NLT 99.0% and NMT 101.0% of C5H11NO2S, as DL-Methionine, calculated on the dried basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
Change to read:
A. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197K (CN 1-May-2020)
Sample: Dry the substances at 105°.
Acceptance criteria: Meets the requirements
B. The principal spot from Sample solution B is similar in size, color, and position to the principal spot from Standard solution A, as obtained in the test for Organic Impurities, Related Substances.
C. Optical Rotation, Angular Rotation〈781A〉
Sample: 50 mg/mL in 1 M hydrochloric acid
Acceptance criteria: −0.05° to +0.05°
D. Procedure
Analysis: Dissolve 0.1 g of Racemethionine and 0.1 g of glycine in 4.5 mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution (85 mg/mL). Add 1 mL of sodium nitroferricyanide solution (25 mg/mL). Heat to 40° for 10 min. Allow to cool, and add 2 mL of a mixture of hydrochloric acid and phosphoric acid (90:10).
Acceptance criteria: A deep red color develops.
3 ASSAY
Procedure
Sample: 140 mg of Racemethionine
Analysis: Dissolve the Sample in a mixture of 3 mL of formic acid and 50 mL of glacial acetic acid. Titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary corrections (see Titrimetry 〈541〉).
Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 14.92 mg of C H NO S.
Acceptance criteria: 99.0%–101.0% on the dried basis
4 IMPURITIES
Inorganic Impurities
Residue on Ignition 〈281〉: NMT 0.1%, determined on 1.0 g
Chloride and Sulfate, Chloride〈221〉: [Note—Prepare the Sample solution and the Standard solution at the same time.]
Chloride standard solution (5 ppm Cl): 0.824 mg/mL of NaCl. Just before use, dilute 1 mL of this solution with water to 100 mL.
Standard solution: To 10 mL of Chloride standard solution add 10 mL of 0.1 N silver nitrate and 25 mL of water, and mix.
Sample solution: Dissolve 0.25 g in 35 mL of water. Add 5 mL of dilute nitric acid and 10 mL of 0.1 N silver nitrate. Allow to stand protected from light for 5 min.
Analysis: Examine the Sample solution and Standard solution laterally against a black background.
Acceptance criteria: Any opalescence in the Sample solution is not more intense than that in the Standard solution (200 ppm).
Chloride and Sulfate, Sulfate〈221〉: [Note—Prepare the Sample solution and the Control solution at the same time.]
Barium chloride solution: 250 mg/mL
Sulfate standard solution (10 ppm SO ): 1.81 mg/mL of potassium sulfate in 30% alcohol (v/v). Just before use, dilute 1 mL of this solution with 30% alcohol (v/v) to 100 mL.
Standard solution: Mix 3 mL of the Barium chloride solution and 4.5 mL of the Sulfate standard solution, and allow to stand for 1 min.
Sample stock solution: 50.0 mg/mL, heated to 60°. Cool to 10°, and filter.
Sample solution: To 2.5 mL of the Standard solution add 15 mL of the Sample stock solution and 0.5 mL of 5 N acetic acid.
Control solution: To 2.5 mL of the Standard solution add 15 mL of the Sulfate standard solution and 0.5 mL of 5 N acetic acid.
Analysis
Samples: Sample solution and Control solution
Acceptance criteria: After 5 min, any opalescence in the Sample solution is not more intense than that in the Control solution (200 ppm).
Limit of Iron
Standard stock solution (125 ppm): Dissolve 1.727 g of ferric ammonium sulfate [FeNH (SO ) · 12H O] in water. Add 50 mL of 10% hydrochloric acid, dilute with water to 1000 mL, and mix. Dilute 1 mL of this solution with water to 40 mL. Pipet 5 mL of this solution into a 200-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Standard solution: Transfer 2 mL of the Standard stock solution to a 25-mL volumetric flask. Add 5 mL of 16% hydrochloric acid, 50 mg of ammonium persulfate, and 3 mL of 30% ammonium thiocyanate, and dilute with water to volume.
Sample solution: Transfer 1 g of Racemethionine to a 25-mL volumetric flask. Add 5 mL of 16% hydrochloric acid, and dissolve. Add 50 mg of ammonium persulfate and 3 mL of 30% ammonium thiocyanate, and dilute with water to volume.
Blank: Transfer 5 mL of 16% hydrochloric acid to a 25-mL volumetric flask. Add 50 mg of ammonium persulfate and 3 mL of 30% ammonium thiocyanate, and dilute with water to volume.
Spectrometric conditions
(See Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy 〈857〉.)
Mode: UV-Vis
Analytical wavelength: 475 nm
Cell: 1 cm
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution, Sample solution, and Blank
Without delay, concomitantly determine the absorbances of each sample, correcting for the Blank.
Acceptance criteria: The absorbance of the Sample solution is NMT that of the Standard solution (NMT 10 ppm).
Limit of Ammonium
Standard solution A: 0.297 mg/mL of USP Ammonium Chloride RS. This solution contains 0.1 mg/mL or 100 ppm of NH4+.
Standard solution B: 0.297 μg/mL of USP Ammonium Chloride RS. This solution contains 0.1 μg/mL or 0.1 ppm of NH4+.
Standard solution C: 2.97 μg/mL of USP Ammonium Chloride RS. This solution contains 1.0 μg/mL or 1 ppm of NH4+.
Standard solution D: 29.7 μg/mL of USP Ammonium Chloride RS. This solution contains 10 μg/mL or 10 ppm of NH4+.
Sample solution: 10 mg/mL of Racemethionine
Electrode system: Use an ammonia-specific,1ion-indicating electrode connected to a pH meter capable of measuring potentials (see pH〈791〉).
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution A, Standard solution B, Standard solution C, Standard solution D, and Sample solution
Add 100 mL of water to a 150-mL beaker, place the electrode in the beaker, stir, and measure the potential. Add 1 mL of 10 N sodium hydroxide. Stir, and measure the potential after stabilization. [Note—It may take about 5 min.] The potential difference must be less than 20 mV.
Add 100.0 mL each of Standard solutions A, B, C, and D to four different 150-mL beakers. To each beaker, add 1 mL of 10 N sodium hydroxide. Place the ammonia electrode in the beaker, stir, and concomitantly measure the potential after stabilization. [Note—It may take about 5 min.] Draw a calibration curve of the potential, in mV, versus, the quantity of ammonium (NH4+), in mg.
Add 100.0 mL of the Sample solution to a 150-mL beaker. Add 1 mL of 10 N sodium hydroxide. Adjust the pH, if necessary, with 10 N sodium hydroxide to a pH of NLT 11. Place the ammonia electrode in the beaker, stir, and measure the potential after stabilization. [Note—It may take about 5 min.] Obtain the quantity of NH4+, in mg, in the 100 mL of the Sample solution based on the calibration curve.
Calculate the percentage of ammonium (NH4+), in the portion of Racemethionine taken:
Result = (C/W) × F
C = quantity of ammonium in the Sample solution from the standard curve (mg)
W = weight of Racemethionine taken to prepare the Sample solution (mg)
F = conversion factor to μg/g (ppm), 1 × 106
Acceptance criteria: NMT 200 ppm
Organic Impurities
Procedure: Related Substances
Standard solution A: 0.40 mg/mL of USP Racemethionine RS
Standard solution B: 40 μg/mL of USP Racemethionine RS
Sample solution A: 20 mg/mL of Racemethionine
Sample solution B: 0.40 mg/mL of Racemethionine
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, Thin-Layer Chromatography.)
Mode: TLC
Adsorbent: 0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel mixture
Application volume: 5 μL
Developing solvent system: Butyl alcohol, glacial acetic acid, and water (3:1:1)
Spray reagent: 2 mg/mL of ninhydrin in a mixture of butyl alcohol and 2 N acetic acid (95:5)
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution A, Standard solution B, Sample solution A, and Sample solution B
Develop over a path of 10 cm using the Developing solvent system. After air-drying the plate, spray with Spray reagent, and heat between 100° and 105° for 15 min. Examine the plate under white light.
Acceptance criteria: Any spot obtained from Sample solution A, apart from the principal spot, is not more intense than the spot obtained from Standard solution B (NMT 0.2%).
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
pH 〈791〉: 5.4–6.1, in a 20 mg/mL solution
Loss on Drying 〈731〉: Dry a sample at 105° for 3 h: it loses NMT 0.5% of its weight, determined on 1.000 g.
Transmittance
Sample solution: 10% of Racemethionine in 2 N hydrochloric acid, prepared by sonication
Analysis: Determine the transmittance in a 1-cm cell at 430 nm with a suitable spectrophotometer.
Acceptance criteria: Transmittance of NLT 0.98, corresponding to an absorbance of NMT about 0.009
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in well-closed containers, protected from light.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Ammonium Chloride RS
USP Racemethionine RS


