Quinine Sulfate
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
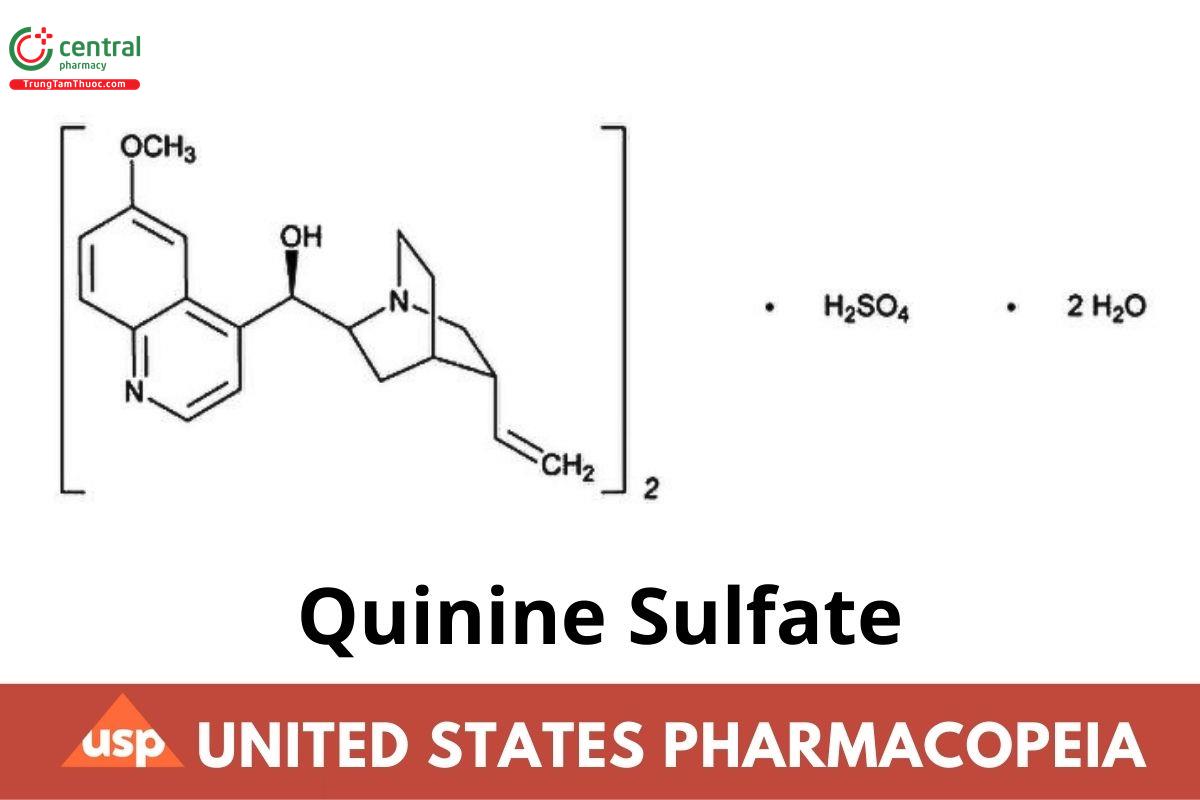
(C20H24N2O2)2 · H2SO4 · 2H2O 782.94
Cinchonan-9-ol, 6′-methoxy-, (8α,9R)-, sulfate (2:1) (salt), dihydrate;
Quinine sulfate (2:1) (salt) dihydrate CAS RN®: 207671-44-1
Anhydrous 746.93 CAS RN®: 804-63-7; UNII: M4XCR57IWG.
1 DEFINITION
Quinine Sulfate is the sulfate of an alkaloid obtained from the bark of species of Cinchona. It contains NLT 99.0% and NMT 101.0% of total alkaloid salt, calculated as (C20H24N2O2)2 · H2SO4, on the anhydrous basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
2.1 A.
A 0.5-mg/mL solution in dilute sulfuric acid (1 in 350) exhibits a vivid blue fluorescence. On the addition of a few drops of hydrochloric acid, the fluorescence disappears.
2.2 B.
The R value of the principal spot of the Sample solution corresponds to that of the Standard stock solution, as obtained in the test for Organic Impurities.
2.3 C. Identification Tests-General, Sulfate 〈191〉
Sample solution: 20-mg/mL solution made with the aid of a few drops of hydrochloric acid
Acceptance criteria: Meets the requirements
3 ASSAY
3.1 Procedure
Sample: 200 mg of Quinine Sulfate
Analysis: Dissolve the Sample in 20 mL of acetic anhydride, and add 4 drops of p-naphtholbenzein TS. Titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS from a 10-mL microburet to a green endpoint. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 24.90 mg of total alkaloid salt, calculated as quinine sulfate [(C20H24N2O2)2 · H2SO4].
Acceptance criteria: 99.0%–101.0% on the anhydrous basis
4 IMPURITIES
4.1 Residue on Ignition 〈281〉
NMT 0.1%
4.2 Chloroform–Alcohol-Insoluble Substances
Sample: 2 g
Analysis: Warm the Sample with 15 mL of a mixture of chloroform and dehydrated alcohol (2:1) at 50° for 10 min. Pass through a tared, sintered-glass filter, using gentle suction. Wash the filter with five 10-mL portions of the chloroform–alcohol mixture, dry at 105° for 1 h, and weigh.
Acceptance criteria: The weight of the residue is NMT 2 mg (0.1%).
4.3 Organic Impurities
Standard stock solution: 6 mg/mL of USP Quinine Sulfate RS, in diluted alcohol
Standard solution A: 0.06 mg/mL of USP Quinine Sulfate RS from the Standard stock solution, in diluted alcohol
Standard solution B: 0.05 mg/mL of USP Quininone RS (corresponding to 0.06 mg/mL of the sulfate), and 0.10 mg/mL of cinchonidine (corresponding to 0.12 mg/mL of the sulfate), in diluted alcohol
Sample solution: 6 mg/mL of Quinine Sulfate, in diluted alcohol
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, Thin-Layer Chromatography.)
Mode: TLC
Adsorbent: 0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel mixture
Application volume: 10 µL
Developing solvent system: Chloroform, acetone, and diethylamine (5:4:1). [Note-The solvent chamber being used without previous equilibration.]
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution A, Standard solution B, and Sample solution
Proceed as directed for Chromatography 〈621〉, Thin-Layer Chromatography. Allow the spots to dry, and develop the chromatogram in a solvent system until the solvent front has moved 15 cm. Remove the plate from the developing chamber, mark the solvent front, and allow the solvent to evaporate. Locate the spots on the plate by spraying with glacial acetic acid, and examine under long-wavelength UV light.
Acceptance criteria: Any spot produced by the Sample solution at the R value of a spot produced by Standard solution B is not greater in size or intensity than that corresponding spot. Apart from these spots and from the spot appearing at the R value of quinine, any additional fluorescent spot is not greater in size or intensity than the spot of Standard solution A. Spray the plate with potassium iodoplatinate TS. Any spot produced by the Sample solution is not greater in size or intensity than a corresponding spot from Standard solution B.
4.4 Dihydroquinine Sulfate
Solution A: Add 35.0 mL of methanesulfonic acid to 20.0 mL of glacial acetic acid, and dilute with water to 500 mL.
Solution B: Dissolve 10.0 mL of diethylamine in water to obtain 100 mL of solution.
Mobile phase: Acetonitrile, Solution A, Solution B, and water (100:20:20:860). Adjust with Solution B to a pH of 2.6 if found to be lower.
System suitability solution: 0.2 mg/mL of USP Quinine Sulfate RS and 0.2 mg/mL dihydroquinine prepared as follows. Dissolve in methanol using 5% of the final volume, and dilute with Mobile phase to volume.
Sample solution: 0.2 mg/mL of Quinine Sulfate in Mobile phase
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: 235 nm
Column: 3.9-mm × 30-cm; packing L1
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Injection size: 50 µL
System suitability
Sample: System suitability solution
[Note-The relative retention times for quinine and dihydroquinine are 1 and 1.5, respectively.]
Suitability requirements:
Resolution: NLT 1.2 between quinine and dihydroquinine
Relative standard deviation: NMT 2.0% for the quinine peak
Analysis
Sample: Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of dihydroquinine in the portion of Quinine Sulfate taken:
Result = rU/(rU + rS) × 100
rU = peak response of dihydroquinine from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of quinine from the Sample solution
Acceptance criteria: NMT 10.0% of dihydroquinine
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
5.1 Optical Rotation, Specific Rotation 〈781S〉
Sample solution: 20 mg/mL, in 0.1 N hydrochloric acid
Acceptance criteria: −235° to −245°
5.2 Water Determination, Method I 〈921〉: 4.0%–5.5%
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in well-closed, light-resistant containers.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Quinine Sulfate RS
USP Quininone RS
Cinchonan-9-one, 6′-methoxy-, (8α)-.
C20H22N2O2 322.40


