Pyridoxine Hydrochloride
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
1 DEFINITION
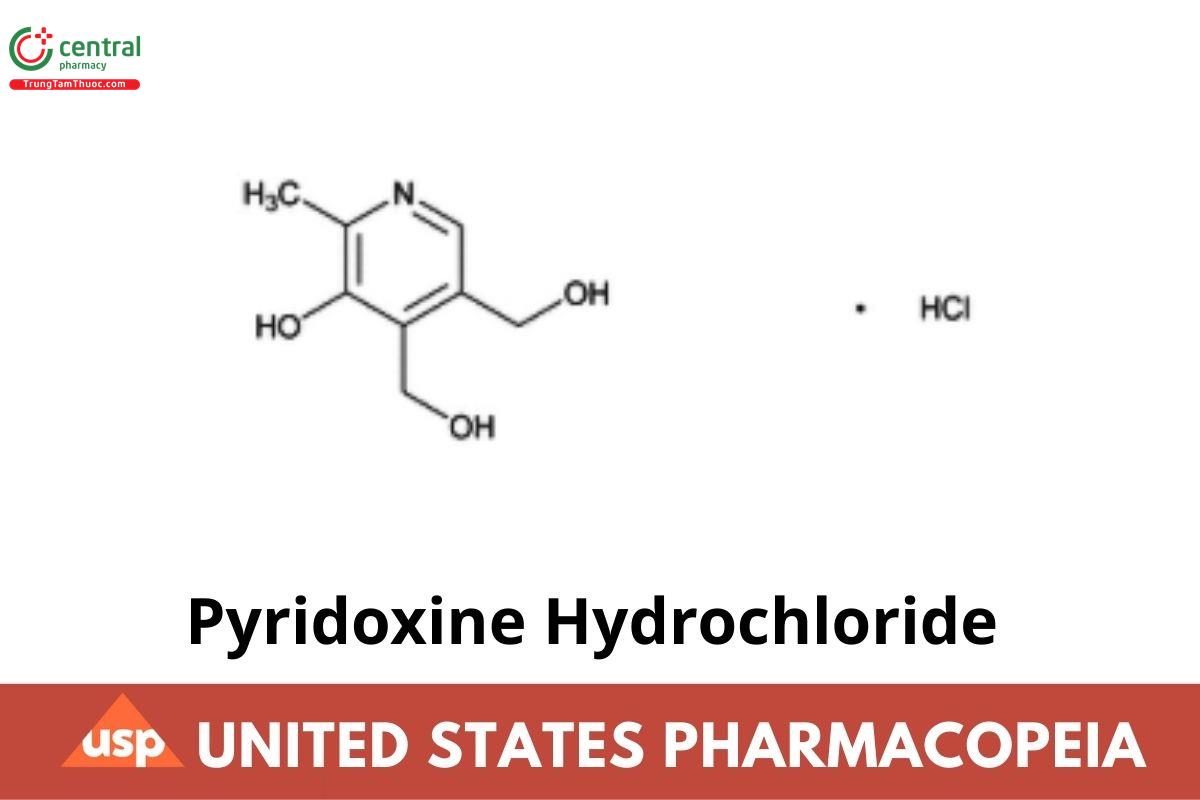
Pyridoxine Hydrochloride contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of pyridoxine hydrochloride (C₈H₁₁NO₃ · HCl), calculated on the dried basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
Change to read:
A. ▲Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197M▲ (CN 1-May-2020)
B. Identification Tests—General, Chloride 〈191〉: Meets the requirements
3 ASSAY
Procedure
Mobile phase: Mix 10 mL of glacial acetic acid, 0.6 g of sodium 1-hexanesulfonate, and 700 mL of water in a 1000-mL volumetric flask. Adjust with glacial acetic acid or 1 N sodium hydroxide to a pH of 3.0. Add 235 mL of methanol, and dilute with water to volume.
Internal standard solution: 5 mg/mL of p-hydroxybenzoic acid in Mobile phase
Standard solution: Prepare a 0.5-mg/mL solution of USP Pyridoxine Hydrochloride RS in Mobile phase. Transfer 10.0 mL of this solution and 1.0 mL of Internal standard solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with Mobile phase to volume.
Sample solution: Prepare a 0.5-mg/mL solution of Pyridoxine Hydrochloride in Mobile phase. Transfer 10.0 mL of this solution and 1.0 mL of Internal standard solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with Mobile phase to volume.
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 280 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; packing L1
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min
Injection size: 20 µL
System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
[Note—The relative retention times for pyridoxine and p-hydroxybenzoic acid are about 0.7 and 1.0, respectively.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 2.5 between pyridoxine and p-hydroxybenzoic acid
Relative standard deviation: NMT 3.0% for the ratios of the pyridoxine peak area response to the internal standard peak area response
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of pyridoxine hydrochloride (C₈H₁₁NO₃ · HCl) in the portion of Pyridoxine Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (Rᵤ/Rₛ) × (Cₛ/Cᵤ) × 100
Rᵤ = internal standard ratio (peak response of pyridoxine/peak response of the internal standard) from the Sample solution
Rₛ = internal standard ratio (peak response of pyridoxine/peak response of the internal standard) from the Standard solution
Cₛ = concentration of USP Pyridoxine Hydrochloride RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
Cᵤ = concentration of Pyridoxine Hydrochloride in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: 98.0%–102.0% on the dried basis
4 IMPURITIES
Residue on Ignition 〈281〉: NMT 0.1%
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
Content of Chloride
Sample: 500 mg of Pyridoxine Hydrochloride
Blank: 50 mL of methanol
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry 〈541〉.)
Mode: Direct titration
Titrant: 0.1 N silver nitrate VS
Endpoint detection: Visual
Analysis: Dissolve the Sample in 50 mL of methanol. Add 5 mL of glacial acetic acid and 2–3 drops of eosin Y TS. Titrate with the Titrant. Perform a Blank determination.
Calculate the percentage of chloride (Cl) in the Sample taken:
Result = {[(V − Vᵦ) × N × F]/W} × 100
V = Titrant volume consumed by the Sample (mL)
Vᵦ = Titrant volume consumed by the Blank (mL)
N = actual normality of the Titrant (mEq/mL)
F = equivalency factor, 35.45 mg/mEq
W = Sample weight (mg)
Acceptance criteria: 16.9%–17.6% on the dried basis
Loss on Drying 〈731〉: Dry a sample in vacuum over silica gel for 4 h: it loses NMT 0.5% of its weight.
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Pyridoxine Hydrochloride RS


