Procaine Hydrochloride
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
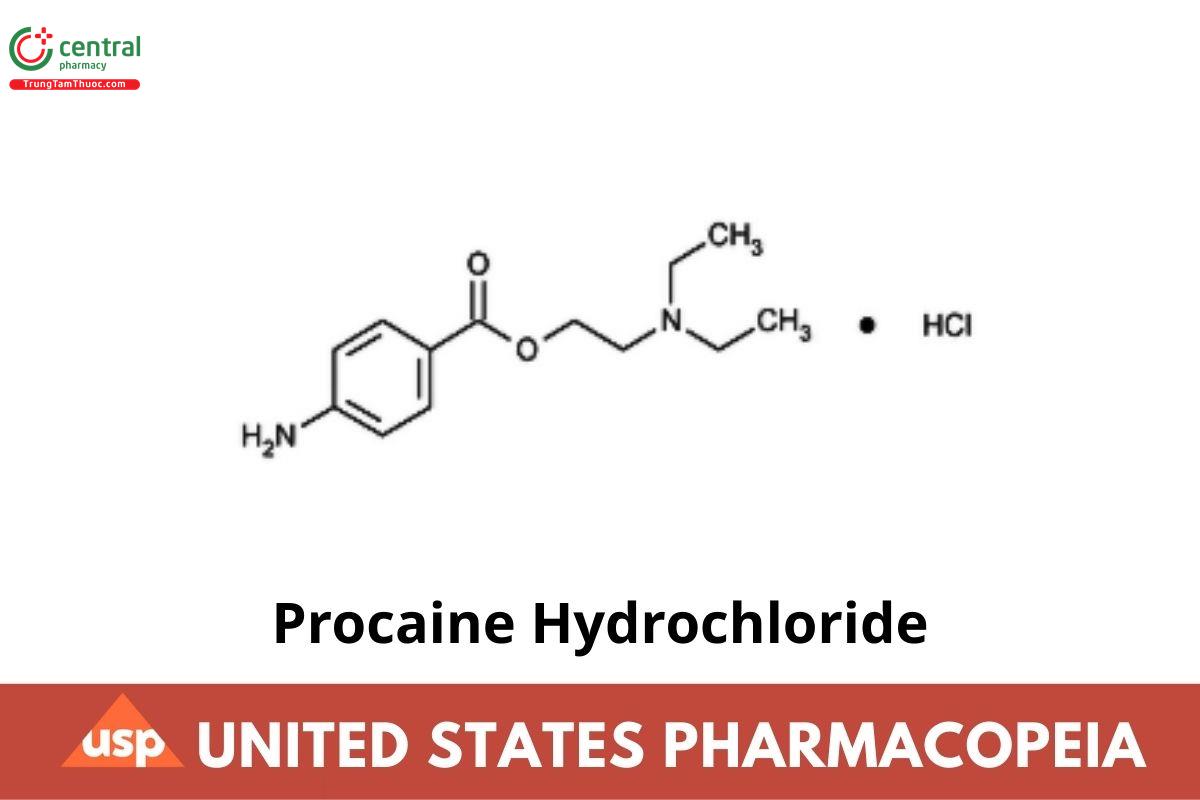
» Procaine Hydrochloride contains not less than 99.0 percent and not more than 101.0 percent of C₁₃H₂₀N₂O₂ · HCl, calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in well-closed containers.
1 Labeling—
Where it is intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms, the label states that it is sterile or must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms.
USP Reference standards 〈11〉—
USP Procaine Hydrochloride RS
2 Identification—
Change to read:
A: ▲Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197K▲ (CN 1-May-2020).
B: Dissolve 10 mg in 1 mL of water, add 1 drop each of hydrochloric acid and sodium nitrite solution (1 in 10), then add 1 mL of a solution prepared by dissolving 0.2 g of 2-naphthol in 10 mL of sodium hydroxide solution (1 in 10), and shake: a scarlet-red precipitate is formed.
C: It responds to the tests for Chloride 〈191〉.
Melting range 〈741〉—
between 153° and 158°.
Bacterial Endotoxins Test 〈85〉—
Where the label states that Procaine Hydrochloride is sterile or must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms, it contains not more than 0.6 USP Endotoxin Unit per mg of procaine hydrochloride.
Sterility Tests 〈71〉—
It meets the requirements when tested as directed for Membrane Filtration under Test for Sterility of the Product to be Examined.
Acidity—
To a solution of 1.0 g in 25 mL of water add 1 drop of methyl red TS, and titrate with 0.020 N sodium hydroxide: not more than 0.50 mL is required for neutralization.
Loss on drying 〈731〉—
Dry it over silica gel for 18 hours: it loses not more than 1.0% of its weight.
Residue on ignition 〈281〉—
not more than 0.15%.
Chromatographic purity—
Solvent— Prepare a mixture of methanol and trichloroethane (7:3).
Standard preparations— Prepare a solution of USP Procaine Hydrochloride RS in Solvent containing 1.6 mg per mL. Dilute quantitatively with Solvent to obtain Standard preparations having the following compositions:
| Standard preparation | Dilution | Concentration (mg RS per mL) | Percentage (% for comparison with test specimen) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2.5 in 10 | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| B | 2.0 in 10 | 0.32 | 0.4 |
| C | 1.0 in 10 | 0.16 | 0.2 |
| D | 0.5 in 10 | 0.08 | 0.1 |
Test preparation— Transfer 1.6 g of Procaine Hydrochloride, accurately weighed, to a suitable capped container, add 20 mL of Solvent, close the container, and sonicate for 2 minutes. Use this solution as the Test preparation.
Procedure— Apply separately 10 µL of the Test preparation and 10 µL of each Standard preparation to a suitable thin-layer chromatographic plate (see Chromatography 〈621〉) coated with a 0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel mixture, prewashed with methanol and allowed to dry. Use a double-trough chromatographic chamber. Fill one trough with ammonium hydroxide, and allow the chamber to equilibrate for 1 hour. Position the plate in the other trough, and develop the chromatogram in a solvent system consisting of a mixture of methylene chloride and methanol (95:6) until the solvent front has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate from the developing chamber, mark the solvent front, and allow the solvent to evaporate. Examine the plate under short-wavelength UV light. Compare the intensities of any secondary spots observed in the chromatogram of the Test preparation with those of the principal spots in the chromatograms of the Standard preparations: no secondary spot is more intense than the principal spot obtained from Standard (0.5%), and the sum of the intensities of all secondary spots obtained from the Test preparation does not exceed 1.0%.
3 Assay—
Transfer about 0.5 g of Procaine Hydrochloride, accurately weighed, to a beaker, add 100 mL of cold water, 5 mL of hydrochloric acid, and 100 mg of potassium bromide, and stir until dissolved. Proceed as directed under Nitrite Titration 〈451〉, beginning with “cool to about 15°.” Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 M sodium nitrite is equivalent to 27.28 mg of C₁₃H₂₀N₂O₂ · HCl.


