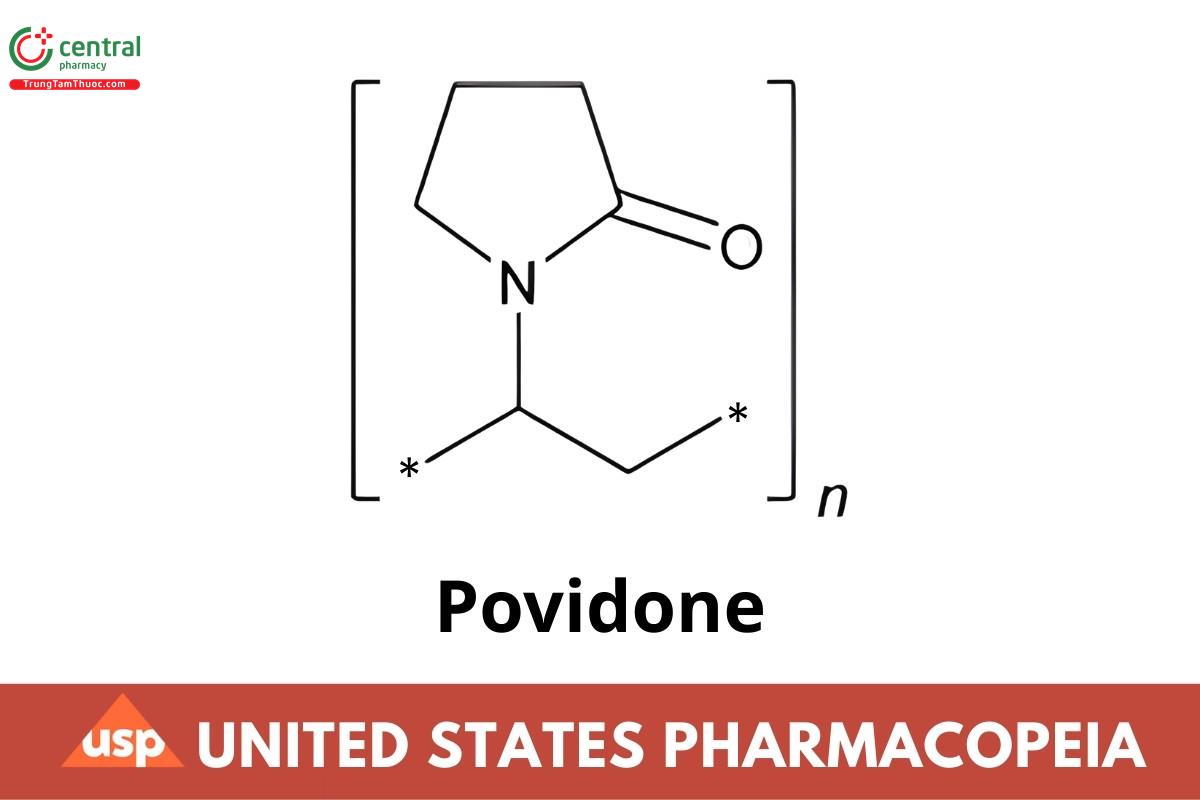
Povidone
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
Portions of the monograph text that are national USP text, and are not part of the harmonized text, are marked with symbols (◆◆) to specify this fact.
(C6H9NO)n
2-Pyrrolidinone, 1-ethenyl-, homopolymer;
1-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone polymer,
Poly [(2-oxo-1-pyrrolidinyl)ethylene]
CAS RN®: 9003-39-8.
1 DEFINITION
Povidone is a chain polymer of 1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone. It contains NLT 11.5% and NMT 12.8% of nitrogen (N: 14.01), calculated on the anhydrous basis. It has the nominal K-value of NLT 10 and NMT 120. The nominal K-value is shown on the label.
2 IDENTIFICATION
A. SPECTROSCOPIC IDENTIFICATION TESTS (197), Infrared Spectroscopy: 197K
Sample: Dry at 105° for 6 h.
Acceptance criteria: Meets the requirements
◆B.
Sample solution: 20 mg/mL of Povidone
Analysis: To 10 mL of the Sample solution, add 20 mL of 1 N hydrochloric acid VS and 5 mL of potassium dichromate TS.
Acceptance criteria: An orange-yellow precipitate is formed.◆
◆C.
Solution A: Dissolve 75 mg of cobalt nitrate and 300 mg of ammonium thiocyanate in 2 mL of water.
Sample solution: 20 mg/mL of Povidone
Analysis: Combine Solution A and 5 mL of the Sample solution, and render the resulting solution acidic by the addition of 3 N hydrochloric acid.
Acceptance criteria: A pale blue precipitate is formed.◆
◆D.
Sample solution: 5 mg/mL of Povidone
Analysis: To 5 mL of the Sample solution, add a few drops of iodine TS.
Acceptance criteria: A deep red color is produced.◆
Ε.
Sample solution: 50 mg/mL of Povidone in water
Acceptance criteria: The substance dissolves.
3 ASSAY
NITROGEN DETERMINATION
Sample: 0.1 g of Povidone
Analysis: Weigh the Sample accurately and place in a Kjeldahl flask. Add 5 g of a powdered mixture of 33 g of potassium sulfate, 1 g of cupric sulfate, and 1 g of titanium dioxide. Wash down any adhering sample from the neck of the flask with a small amount of water. Add 7 mL of sulfuric acid allowing it to flow down the inside wall of the flask. Heat the flask gradually until the solution has a clear, yellow-green color and the inside wall of the flask is free from any carbonized material and then heat for an additional 45 min. After cooling, cautiously add 20 mL of water, and connect the flask to the distillation apparatus previously washed by passing steam through it. To the absorption flask add 30 mL of a solution of boric acid (1 in 25), 3 drops of bromocresol green-methyl red TS, and sufficient water to immerse the lower end of the condenser tube. Add 30 mL of a solution of sodium hydroxide (2 in 5) through the funnel, rinse the funnel cautiously with 10 mL of water, immediately close the clamp attached to the rubber tube, and then start the distillation with steam to obtain 80-100 mL of the distillate. Remove the absorption flask from the lower end of the condenser tube, rinsing the end part with a small quantity of water, and titrate the distillate with 0.025 mol/L sulfuric acid VS until the color of the solution changes from green through pale grayish blue to pale grayish red-purple. Perform a blank determination in the same manner, and make any necessary correction.
Each milliliter of 0.025 mol/L sulfuric acid VS equals 0.700 mg of nitrogen.
Acceptance criteria: 11.5%-12.8% on the anhydrous basis
4 IMPURITIES
4.1 RESIDUE ON IGNITION (281)
NMT 0.1%
Change to read:
4.2 ◆LEAD (251), Procedures, Procedure 1 (CN 1-JUN-2023)
Test preparation: 1.0 g in 25 mL of water
Acceptance criteria: NMT 10 ppm◆
4.3 LIMIT OF ALDEHYDES
Solution A: Transfer 8.3 g of potassium pyrophosphate to a 500-mL volumetric flask and dissolve in 400 mL of water. Adjust, if necessary, with 1 N hydrochloric acid VS to a pH of 9.0, and dilute with water to volume.
Solution B: Transfer a quantity of lyophilized aldehyde dehydrogenase, equivalent to 70 units, to a glass vial, and dissolve in 10.0 mL of water. [NOTE-This solution is stable for 8 h at 4°.]
Solution C: Transfer 40 mg of Nicotinamide Adenine dinucleotide to a glass vial, and dissolve in 10.0 mL of Solution A. [NOTE-This solution is stable for four weeks at 4°.]
Standard solution: Dissolve 0.140 g of acetaldehyde ammonia trimer trihydrate in water to make 200.0 mL. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution with Solution A to 100.0 mL.
Sample solution: 10 mg/mL of Povidone in Solution A. Insert a stopper into the flask, heat at 60° for 1 h, and cool to room temperature.
Instrumental conditions
(See Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy (857).)
Mode: UV
Analytical wavelength: 340 nm
Cell: 1 cm
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution, Sample solution, and water
Pipet 0.5 mL each of the Standard solution, Sample solution, and water (used for blank test) into separate cells. Add 2.5 mL of Solution A and 0.2 mL of Solution C to each cell. Cover the cells to exclude oxygen. Mix by inversion and allow to stand for 2-3 min at 22 ± 2°. Determine the absorbances of the solutions using the water as the reference. Add 0.05 mL of Solution B to each cell. Cover the cells to exclude oxygen. Mix by inversion and allow to stand for 5 min at 22 ± 2°. Determine the absorbances of the solutions, using the water as the reference.
Calculate the percentage of aldehydes, expressed as acetaldehyde, in the portion of Povidone taken:
Result = 100 x (CS/CU) x {[(AU2 - ΑU1) - (AB2 - AB1)]/[(AS2 - AS2) - (AB2 - AB1)]}
CS = concentration of acetaldehyde in the Standard solution, calculated from the weight of the acetaldehyde ammonia trimer trihydrate with the factor 0.72 (mg/mL).
[NOTE-The molar mass of acetaldehyde is 44.05 g/mol, and the molar mass of acetaldehyde ammonia trimer trihydrate is 183.26 g/mol. (44.05 x 3)/183.26 = 0.72]
CU = concentration of the Sample solution (mg/mL), calculated on the anhydrous basis
AU2 = absorbance of the solution from the Sample solution, after addition of Solution B
ΑU1 = absorbance of the solution from the Sample solution, before addition of Solution B
AB2 = absorbance of the solution from the blank, after addition of Solution B
AB1 = absorbance of the solution from the blank, before addition of Solution B
AS2 = absorbance of the solution from the Standard solution, after addition of Solution B
AS2 = absorbance of the solution from the Standard solution, before addition of Solution B
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.05%
4.4 LIMIT OF HYDRAZINE
Standard solution: 9 µg/mL of salicylaldazine in toluene
Sample solution: Transfer 2.5 g to a 50-mL centrifuge tube, add 25 mL of water, and mix to dissolve. Add 500 µL of a solution (1 in 20) of salicylaldehyde in methanol. Swirl and heat in a water bath at 60° for 15 min. Allow to cool and add 2.0 mL of toluene. Insert a stopper in the tube, shake vigorously for 2 min, and centrifuge. Use the clear upper toluene layer in the centrifuge tube as the Sample solution.
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography (621), General Procedures, Thin-Layer Chromatography.)
Mode: TLC
Adsorbent: 0.25-mm layer of dimethylsilanized chromatographic silica gel with fluorescent indicator
Application volume: 10 µL
Developing solvent system: Methanol and water (2:1)
Analytical wavelength: UV 365 nm
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Proceed as directed in the chapter. Allow the spots to dry, and develop the chromatogram with the Developing solvent system until the solvent front has moved three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate from the chamber, mark the solvent front, and allow the solvent to evaporate. Locate the spots on the plate by examination under UV light.
Acceptance criteria: Salicylaldazine appears as a fluorescent spot having an RF value of 0.3; and the fluorescence of any salicylaldazine spot from the Sample solution is not more intense than that produced by the spot from the Standard solution (NMT 1 ppm of hydrazine).
4.5 VINYLPYRROLIDINONE
Mobile phase: Water and acetonitrile (90:10)
System suitability solution: Transfer 10 mg of vinylpyrrolidinone and 500 mg of vinyl acetate to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in and dilute with methanol to volume. Transfer 1.0 mL of this solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with Mobile phase to volume.
Standard stock solution: 5 µg/mL of vinylpyrrolidinone in Mobile phase
Standard solution: 0.25 µg/mL of vinylpyrrolidinone diluted from the Standard stock solution in Mobile phase
Sample solution: 25 mg/mL of Povidone in Mobile phase
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography (621), System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 235 nm
Columns
Guard: 4.0-mm x 1.0-cm; packing L1
Analytical: 4.6-mm x 15-cm; 5-um packing L1
Column temperature: 40°
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min
Injection volume: 20 µL
System suitability
Samples: System suitability solution and Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 2.0 between vinylpyrrolidinone and vinyl acetate, in this elution order, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation: NMT 2.0% of vinylpyrrolidinone for six injections, Standard solution
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Record the chromatograms and measure the responses for the vinylpyrrolidinone peak.
Calculate the percentage of vinylpyrrolidinone in the sample taken:
Result = (rU/rS) x (CS/CU) x 100
rU = peak response of vinylpyrrolidinone from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of vinylpyrrolidinone from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of vinylpyrrolidinone in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Povidone in the Sample solution (mg/mL), calculated on the anhydrous basis
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.001%
4.6 2-PYRROLIDONE
Mobile phase: Water and methanol (19:1)
Standard solution: 30 µg/mL of 2-pyrrolidinone in Mobile phase
Sample solution: 5 mg/mL of Povidone in Mobile phase
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography (621), System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 205 nm
Columns
Guard: 4.0-mm x 1.0-cm; packing L1
Analytical: 4.6-mm x 15-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Column temperature: 40°
Flow rate: 0.8 mL/min
[NOTE-The retention time of 2-pyrrolidinone is about 7 min.]
Injection volume: 50 µL
System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Column efficiency: NLT 5000 theoretical plates for the 2-pyrrolidinone peak
Symmetry factor: NMT 1.5 for the 2-pyrrolidinone peak
Relative standard deviation: NMT 2.0% of 2-pyrrolidinone for six injections
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Record the chromatograms and measure the responses for the 2-pyrrolidinone peak.
Calculate the percentage of 2-pyrrolidinone in the sample taken:
Result = (rU/rS) x (CS/CU) x 100
rU = peak response of 2-pyrrolidinone from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of 2-pyrrolidinone from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of 2-pyrrolidinone in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Povidone in the Sample solution (mg/mL), calculated on the anhydrous basis
Acceptance criteria: NMT 3.0%
4.7 PEROXIDES
Sample solution: 40 mg/mL of Povidone in water, calculated on the anhydrous basis
Blank: To 25 mL of the Sample solution, add 2 mL of 13% sulfuric acid.
Instrumental conditions
(See Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy (857).)
Mode: UV-Vis
Analytical wavelength: 405 nm
Cell: 1 cm
Analysis
Sample: Sample solution
To 25 mL of the Sample solution, add 2 mL of titanium trichloride-sulfuric acid TS, and allow to stand for 30 min. Measure the absorbance of a portion of this solution against the Blank.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.35, corresponding to NMT 400 ppm, expressed as H2O2
4.8 FORMIC ACID
Mobile phase: Diluted perchloric acid (1 in 700)
Standard solution: 10 µg/mL of formic acid in water
Sample stock solution: 20 mg/mL of Povidone in water
Sample solution: Transfer a suspension of strongly acidic ion-exchange resin (use the hydrogen form of ion-exchange resin) in water to a column of about 8 mm in inside diameter to give a packing depth of about 20 mm in length. Keep the strongly acidic ion-exchange resin layer constantly immersed in water. Pour 5 mL of water and adjust the flow rate so that water drops at a rate of about 1 mL/min. When the level of the water is near the top of the strongly acidic ion-exchange resin layer, introduce 100 mL of the Sample stock solution into the column. Disregard the first 2 mL of the eluate, then collect 1.5 mL of the solution, and use this as the Sample solution.
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography (621), System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 210 nm
Column: 7.9-mm x 30-cm; 10-µm packing L17
Column temperature: 35°
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min
[NOTE-The retention time of formic acid is about 8 min.]
Injection volume: 50 µL
System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Column efficiency: NLT 1000 theoretical plates for the formic acid peak
Symmetry factor: 0.5-1.5 for the formic acid peak
Relative standard deviation: NMT 2.0% of formic acid for six injections
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Record the chromatograms and measure the responses for the formic acid peak.
Calculate the percentage of formic acid in the sample taken:
Result = (rU/rS) x (CS/CU) x 100
rU = peak response of formic acid from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of formic acid from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of formic acid in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Povidone in the Sample solution (mg/mL), calculated on the anhydrous basis
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.5%
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
5.1 PH (791)
Sample solution: 50 mg/mL in water
Acceptance criteria: 3.0-5.0 for Povidone having a nominal K-value of 30 or less; 4.0-7.0 for Povidone having a nominal K-value greater than 30
5.2 WATER DETERMINATION (921), Method I
NMT 5.0%
5.3 K-VALUE
Sample solution: Weigh a quantity of undried Povidone, equivalent on the anhydrous basis, to the amount specified in Table 1.
Table 1
| Nominal K-value | Quantity (g) |
| ≤18 | 5.00 |
| >18 to ≤95 | 1.00 |
| >95 | 0.10 |
Dissolve it in 50 mL of water in a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute to volume. Allow to stand for 1 h.
Analysis
Samples: Sample solution and water
Determine the viscosity of the Sample solution and the water, using a capillary-tube viscometer (see Viscosity-Capillary Methods (911)), at 25 ± 0.2°.
Calculate the K-value of Povidone:
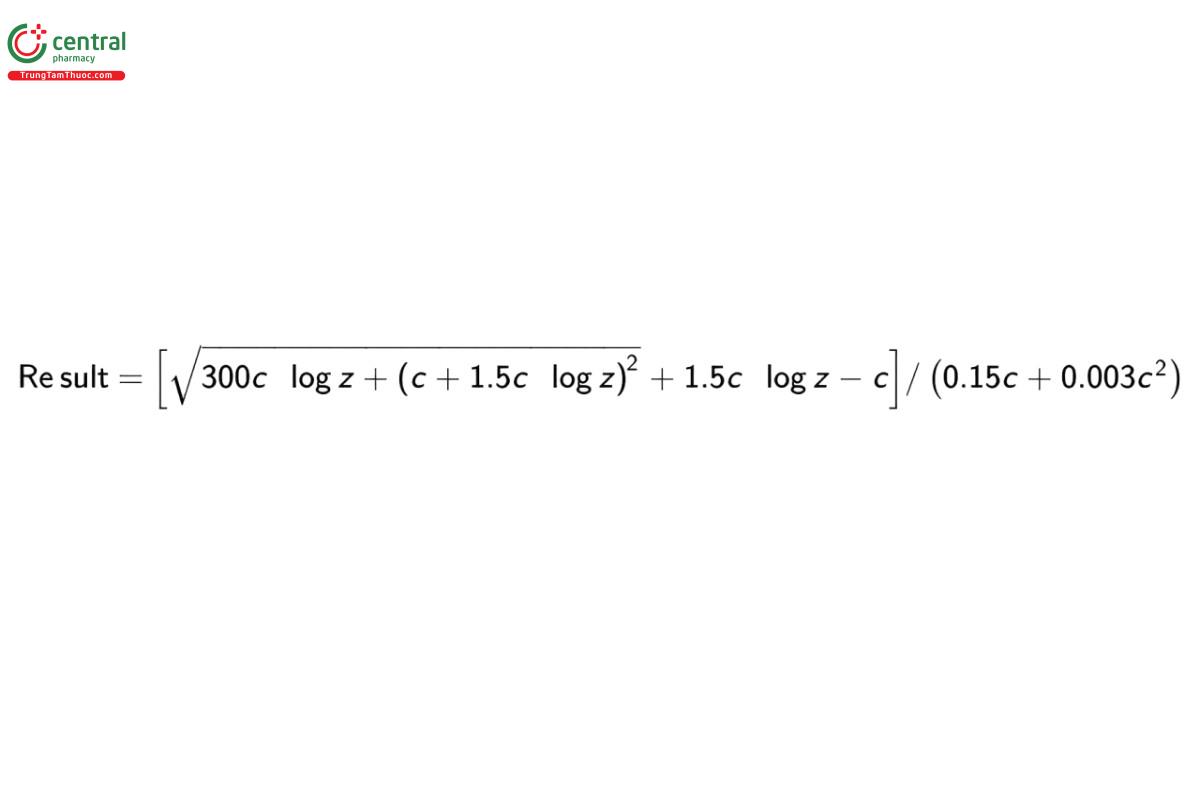
c = weight, on the anhydrous basis, of the specimen tested in each 100.0 mL of solution (g)
z = viscosity of the Sample solution relative to that of water
Acceptance criteria
K-value of Povidone having a stated (nominal) K-value of NMT 15: 85.0%-115.0% of the stated values
K-value of Povidone having a stated K-value or a stated K-value range with an average of more than 15: 90.0%-108.0% of the stated value or of the average of the stated range
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
6.1 ◆PACKAGING AND STORAGE
Preserve in tight containers.◆
6.2 LABELING
Label it to state, as part of the official title, the K-value or K-value range of Povidone.
6.3 ◆USP REFERENCE STANDARDS (11)
USP Povidone RS◆


