Potassium Gluconate
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
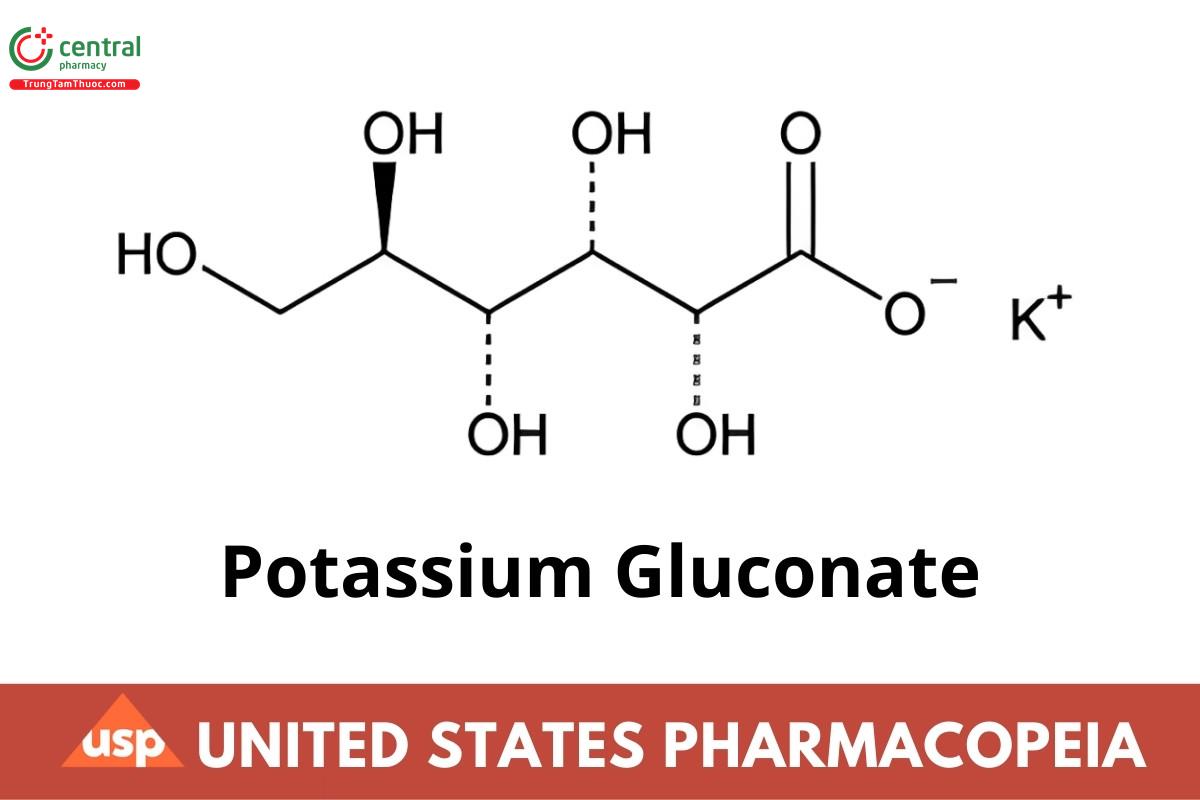
C6H11KO7 234.25
C6H11KO7·H2O 252.26
D-Gluconic acid, monopotassium salt;
Monopotassium D-gluconate.
Anhydrous CAS RN®: 299-27-4; UNII: 12H3K5QKN9.
Monohydrate CAS RN®: 35398-15-3; UNII: 8UXL786OWP.
1 DEFINITION
Potassium Gluconate is anhydrous or contains one molecule of water of hydration. It contains NLT 97.0% and NMT 103.0% of anhydrous potassium gluconate (C6H11KO7), calculated on the dried basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
A. SPECTROSCOPIC IDENTIFICATION TESTS (197), Infrared Spectroscopy: 197M
B. Potassium Gluconate imparts a violet color to a nonluminous flame. Because the presence of small quantities of sodium masks the color, screen out the yellow color produced by sodium by viewing through a blue filter that blocks emission at 589 nm (sodium) but is transparent to emission at 404 nm (potassium). [NOTE-Traditionally, cobalt glass has been used, but other suitable filters are commercially available.]
C. THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY
Standard solution: 10 mg/mL of USP Potassium Gluconate RS
Sample solution: 10 mg/mL of Potassium Gluconate
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography (621), Thin-Layer Chromatography.)
Mode: TLC
Adsorbent: 0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel
Application volume: 5 µL
Developing solvent system: Alcohol, ethyl acetate, ammonium hydroxide, and water (50:10:10:30)
Spray reagent: Dissolve 2.5 g of ammonium molybdate in 50 mL of 2N sulfuric acid in a 100-mL volumetric flask, add 1.0 g of ceric sulfate, swirl to dissolve, and dilute with 2 N sulfuric acid to volume.
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Develop the chromatogram until the solvent front has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate from the chamber, and dry at 110° for 20 min. Allow to cool, and spray with the Spray reagent. Heat the plate at 110° for about 10 min.
Acceptance criteria: The principal spot of the Sample solution corresponds in color, size, and RF to that of the Standard solution.
3 ASSAY
3.1 PROCEDURE
Standard stock solution: Transfer 190.7 mg of potassium chloride, previously dried at 105° for 2 h, to a 1000-mL volumetric flask, add sufficient water to dissolve, and dilute with water to volume. Transfer 100.0 mL of this solution to a 1000-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. This solution contains 10 µg/mL of potassium (equivalent to 19.07 µg/mL of potassium chloride).
Standard solutions: Transfer 10.0, 15.0, and 20.0 mL of Standard stock solution to separate 100-mL volumetric flasks. Add 2.0 mL of a 200-mg/mL sodium chloride solution and 1.0 mL of hydrochloric acid to each flask. Dilute with water to volume and mix. The Standard solutions contain 1.0, 1.5, and 2.0 µg/mL of potassium, respectively.
Sample stock solution: 0.18 mg/mL of Potassium Gluconate in water. Filter the solution.
Sample solution: Transfer 5.0 mL of the filtrate from the Sample stock solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add 2.0 mL of a 200-mg/mL sodium chloride solution and 1.0 mL of hydrochloric acid, and dilute with water to volume.
Blank: Water
Instrumental conditions
(See Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (852).)
Mode: Atomic absorption spectrophotometry
Analytical wavelength: 766.5 nm
Lamp: Potassium hollow-cathode
Flame: Air-acetylene
3.2 Analysis
Samples: Standard solutions and Sample solution
Determine the absorbances of the Standard solutions and the Sample solution. Plot the absorbances of the Standard solutions versus their concentrations, in µg/mL, of potassium, and draw the straight line best fitting the three plotted points. From the graph so obtained, determine the concentration, CK, in µg/mL, of potassium in the Sample solution.
Calculate the percentage of potassium gluconate (C6H11KO7) in the portion of Potassium Gluconate taken:
Result = (CK/CU) x (Mr/Ar) x 100
CK = determined concentration of potassium in the Sample solution (µg/mL)
CU = concentration of Potassium Gluconate in the Sample solution (µg/mL)
Mr = molecular weight of potassium gluconate, 234.25
Ar = atomic weight of potassium, 39.10
Acceptance criteria: 97.0%-103.0% on the dried basis
4 IMPURITIES
Change to read:
REDUCING SUBSTANCES
Sample: 1.0 g of Potassium Gluconate
Blank: 10 mL of water
Titrimetric system (See Titrimetry (541).)
Mode: Residual titration
Titrant: 0.1 N lodine VSA (ERR 1-Sep-2022)
Back-titrant: 0.1 N Sodium Thiosulfate VSA (ERR 1-Sep-2022)
Endpoint detection: Visual
Analysis: Transfer the Sample to a 250-mL conical flask, dissolve in 10 mL of water, and add 25 mL of alkaline cupric citrate TS. Cover the flask, boil gently for 5 min, accurately timed, and cool rapidly to room temperature. Add 25 mL of 0.6 N acetic acid, 10.0 mL of Titrant, and 10 mL of 3 N hydrochloric acid, and titrate with Back-titrant, adding 3 mL of starch TS as the endpoint is approached. Perform the blank determination.
Calculate the percentage of reducing substances (as dextrose) in the portion of the Sample taken:
Result = {[(VB - VS) x NA x F]/W} x 100
VB = Back-titrant volume consumed by the Blank (mL)
VS = Back-titrant volume consumed by the Sample (mL)
NA = actual Back-titrant normality (mEq/mL)
F = equivalency factor, 27 mg/mEq
W = Sample weight (mg)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 1.0%
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
LOSS ON DRYING (731)
Analysis: Dry under vacuum at 105° for 4 h.
Acceptance criteria
Anhydrous: NMT 3.0%
Monohydrate: 6.0%-7.5%
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
6.1 PACKAGING AND STORAGE
Preserve in tight containers.
6.2 LABELING
Label it to indicate whether it is the anhydrous or the monohydrate form.
6.3 USP REFERENCE STANDARDS (11)
USP Potassium Gluconate RS


