Potassium Alginate
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
(C6H7KO6)n+2
Alginic acid, potassium salt;
Potassium alginate
CAS RN®: 9005-36-1.
1 DEFINITION
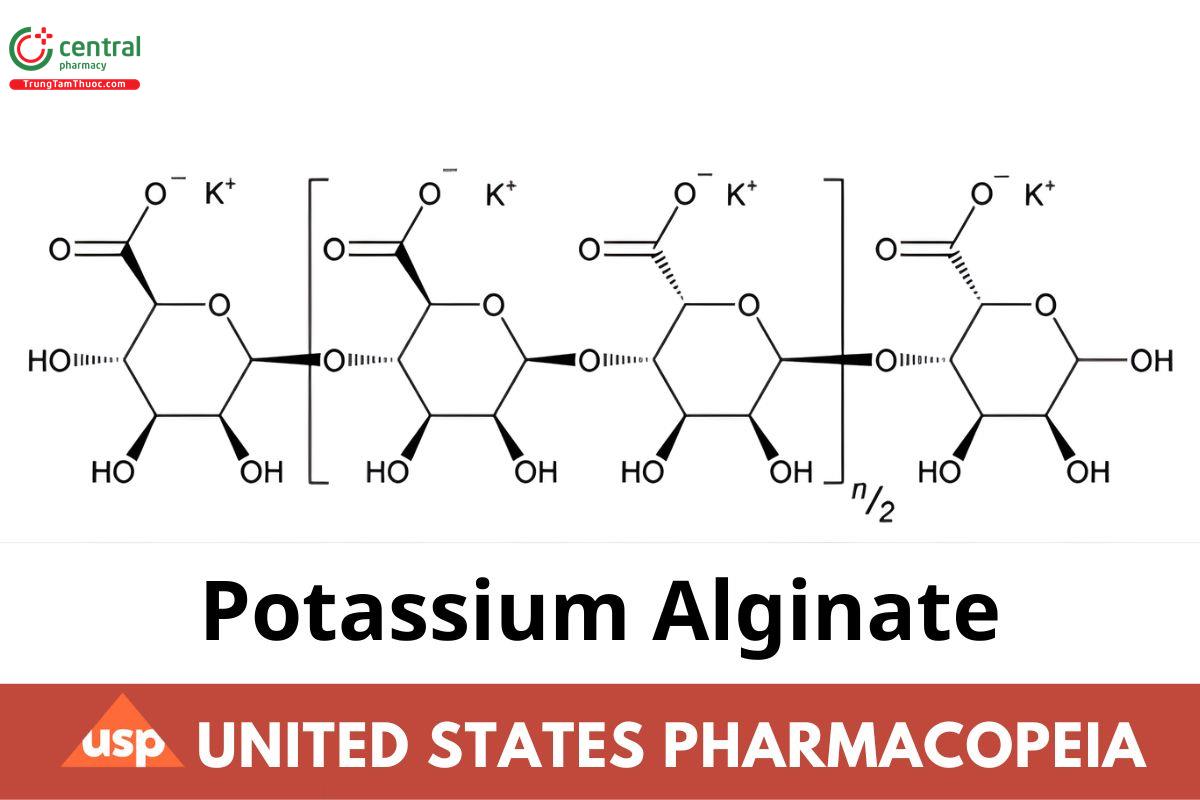
Potassium Alginate is the purified carbohydrate product extracted from various species of brown seaweeds by the use of dilute alkali. It consists chiefly of the potassium salt of Alginic Acid, a linear, unbranched copolymer of β-d-mannuronic acid (M) and α-l-guluronic acid (G) linked to each other by 1→4 glycosidic bonds. The M and G units in the alginates may be randomly or non-randomly arrayed as heterogeneous or homogeneous sequences. It yields NLT 16.5% and NMT 19.5% of carbon dioxide (CO ), equivalent to NLT 89.2% and NMT 105.5% of potassium alginate, calculated on the dried basis. Typical average molecular weight is in the range of 10,000–600,000 g/mol.
2 IDENTIFICATION
A. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197K or 197A
B.
Analysis 1: To 5 mL of a 1-in-100 solution in 0.1 N sodium hydroxide add 1 mL of calcium chloride TS.
Acceptance criteria 1: A voluminous, gelatinous precipitate is formed.
Analysis 2: To 10 mL of a 1-in-100 solution in 0.1 N sodium hydroxide add 1 mL of 2 N sulfuric acid.
Acceptance criteria 2: A heavy, gelatinous precipitate is formed.
C.
Analysis: To 5 mg in a test tube add 5 mL of water, 1 mL of a freshly prepared 1-in-100 solution of 1,3-naphthalenediol in alcohol, and 5 mL of hydrochloric acid. Heat the mixture to boiling, boil gently for 3 min, then cool to 15°. Transfer the contents of the test tube to a 30-mL separator with the aid of 5 mL of water, and extract with 15 mL of isopropyl ether.
Acceptance criteria: The isopropyl ether extract exhibits a deeper purplish hue than that from a blank, similarly prepared.
D. Identification Tests—General 〈191〉, Chemical Identification Tests, Potassium
Sample solution: 5 mg/mL of Potassium Alginate
Analysis 1: Transfer 1 mL of the Sample solution into a test tube, add 1 mL of sodium bitartrate TS, stir the inside of the test tube with a glass rod, and add 0.5 mL of alcohol.
Acceptance criteria 1: A white crystalline precipitate is formed.
Analysis 2: To the test tube from Analysis 1 add 3 mL of 6 N ammonium hydroxide.
Acceptance criteria 2: The white crystalline precipitate is dissolved.
3 ASSAY
Alginates Assay 〈311〉: 16.5%–19.5% of carbon dioxide (CO2 ), equivalent to 89.2%–105.5% of potassium alginate on the dried basis
4 IMPURITIES
Delete the following:
Arsenic 〈211〉, Procedures, Method II (NF 1-May-2023)
Delete the following:
Lead 〈251〉 (NF 1-May-2023)
Add the following:
Limit of Lead and Arsenic
[Note—When water is specified as the diluent, use deionized ultra- filtered water. Use of glass volumetric flasks is discouraged.]
Diluent: Weigh around 3.5 g of sodium nitrate in a 1000-mL volumetric flask. Add 500 mL of water to dissolve. Add 170 mL of nitric acid, ultratrace, and mix. Cool to room temperature and dilute with water to volume.
Standard stock solution: Into a 10-mL volumetric flask, transfer 100 μL of a standard solution containing 1000 mg/L of arsenic1 and 500 μL of a standard solution containing 1000 mg/L of lead.2
Add 1–2 drops of nitric acid, ultratrace. Dilute with water to volume.
Internal standard solution: Transfer 1.0 mL of a standard solution containing 10,000 mg/L of yttrium3 to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add 1–2 drops of nitric acid, ultratrace, and dilute with water to volume. [Note—The concentration of the Internal standard solution can be adjusted if a high number of signal counts from the Internal standard solution causes an artifact.]
Calibration standard solution A: Into a separate 100-mL volumetric flask, prepare a solution containing 0.01 μg/mL of arsenic and 0.05 μg/mL of lead from the Standard stock solution. To each flask, add 100 μL of the Internal standard solution and 20 μL of a standard solution containing 1000 mg/L of gold.4
Dilute with Diluent to volume.
Calibration standard solution B: Into a separate 100-mL volumetric flask, prepare a solution containing 0.02 μg/mL of arsenic and 0.1 μg/mL of lead from the Standard stock solution. To each flask, add 100 μL of the Internal standard solution and 20 μL of a standard solution
containing 1000 mg/L of gold. Dilute with Diluent to volume.
Calibration standard solution C: Into a separate 100-mL volumetric flask, prepare a solution containing 0.04 μg/mL of arsenic and 0.2 μg/mL of lead from the Standard stock solution. To each flask, add 100 μL of the Internal standard solution and 20 μL of a standard solution containing 1000 mg/L of gold. Dilute with Diluent to volume.
Blank solution: In a 100-mL volumetric flask, add 100 μL of the Internal standard solution. Add 20 μL of a standard solution containing 1000 mg/L of gold to the same flask. Dilute with Diluent to volume, and mix well.
Sample solution: Weigh about 0.50 g of Potassium Alginate in a Teflon pressure vessel. Add 10 mL of nitric acid, ultratrace. Add 10 μL of a standard solution containing 1000 mg/L of gold. Screw the cap of the pressure vessel and commence digestion in a microwave digester per the program given in Table 1.
Table 1
| Sequence | Temperature (°) | Power (W) | Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ramp to | 80 | 400 | 5 |
| Hold at | 80 | 400 | 5 |
| Ramp to | 150 | 800 | 10 |
| Hold at | 150 | 800 | 10 |
| Ramp to | 170 | 800 | 10 |
| Hold at | 170 | 800 | 10 |
| Cool | – | 0 | – |
Once completed, allow it to cool. Rinse the vessel using water and transfer the rinsate to a separate 50-mL volumetric flask. Add 50 μL of the Internal standard solution. Dilute with water to volume, and mix well.
Instrumental conditions
(See Plasma Spectrochemistry 〈730〉.)
Mode: ICP–OES
Emission wavelengths: 189.042 nm for arsenic, 220.353 nm for lead, and 224.306 nm for yttrium. Set the sample read time and other instrument parameters as appropriate or as recommended by the instrument manufacturer.
System suitability
Samples: Calibration standard solutions A–C, Blank solution, and Sample solution
Suitability requirements
[Note—Instrument performance must be verfied to conform to the manufacturer's specifications for resolution and sensitivity. Before analyzing samples, the instrument must pass a suitable performance check. Additional system suitability parameters can be used per the instrument manufacturer's recommendations, along with the internal quality requirements.]
Correlation coeficient: NLT 0.999, determined from the Calibration curve constructed in the Analysis
Analysis
Samples: Calibration standard solutions A–C, Blank solution, and Sample solution. [Note—The following analysis is described for one type of ICP–OES instrument. If a different ICP–OES instrument is used, follow the instrument manufacturer's recommendations for operation.]
Take 3 replicate scans with the integration set as recommended by the instrument manufacturer. Follow the instrument manufacturer's recommendations for delivering the sample. Flush the samples through the system before analysis. Program a read delay into the sampling routine to allow for fluid flow equilibration after the high-speed flush, before the first analytical read of the sample. Between samples, wash the pumping system by flushing the Blank solution. Analyze the Sample solution on the ICP.
Calibration curve: Generate the calibration curve using the Blank solution and Calibration standard solutions A–C as follows. Scan the Internal standard solution while running the Blank solution to measure the intensity of the yttrium emission. Hold this value constant throughout the remainder of the test. Separately scan the Blank solution, Calibration standard solutions A–C, and Internal standard solution. Normalize the yttrium intensity to the value of the Internal standard solution. Apply this normalization factor to the intensity of the respective elements, which is then referred to as the corrected intensity. Obtain the concentration of arsenic and lead (C), in μg/mL, in the Sample solution through the calibration curve. Plot the corrected intensity versus the known concentrations, in μg/mL, of arsenic and lead.
Calculate the content in μg/g (ppm) of arsenic and lead in the portion of Potassium Alginate taken:
Result = (C × V)/W
C = concentration of arsenic/lead in the Sample solution obtained from the Calibration curve (μg/mL)
V = volume of the Sample solution (mL)
W = weight of Potassium Alginate taken to prepare the Sample solution (g)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 1.5 μg/g of arsenic and 10 μg/g of lead (NF 1-May-2023)
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
Articles of Botanical Origin 〈561〉, Methods of Analysis, Total Ash
Analysis: Proceed as directed in the chapter, carefully igniting 3 g in a tared platinum dish until the residue is thoroughly carbonized (5 min), and then igniting in a muffle furnace at a temperature of 800 ± 25° until the carbon is completely burned off (approximately 75 min).
Acceptance criteria: 24.0%–32.0% of ash is found, calculated on the as-is basis.
Microbial Enumeration Tests 〈61〉 and Tests for Specified Microorganisms 〈62〉: The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 103 cfu/g, and the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 102 cfu/g.
Loss on Drying 〈731〉
Analysis: Dry at 105° for 4 h.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 15%
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in well-closed containers. No storage requirements specified.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Potassium Alginate RS
1 Arsenic ICP standard solutions are commercially available. A suitable ICP standard is available from LGC (www.lgcstandards.com) or Millipore Sigma (www.sigmaaldrich.com).
2 Lead ICP standard solutions are commercially available. A suitable ICP standard is available from LGC (www.lgcstandards.com) or Millipore Sigma (www.sigmaaldrich.com).
3 Yttrium ICP standard solutions are commercially available. A suitable ICP standard is available from LGC (www.lgcstandards.com) or Millipore Sigma (www.sigmaaldrich.com).
4 Gold standard solutions are commercially available. A suitable ICP standard is available from LGC (www.lgcstandards.com) or Millipore Sigma (www.sigmaaldrich.com).


