Polyvinyl Alcohol
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
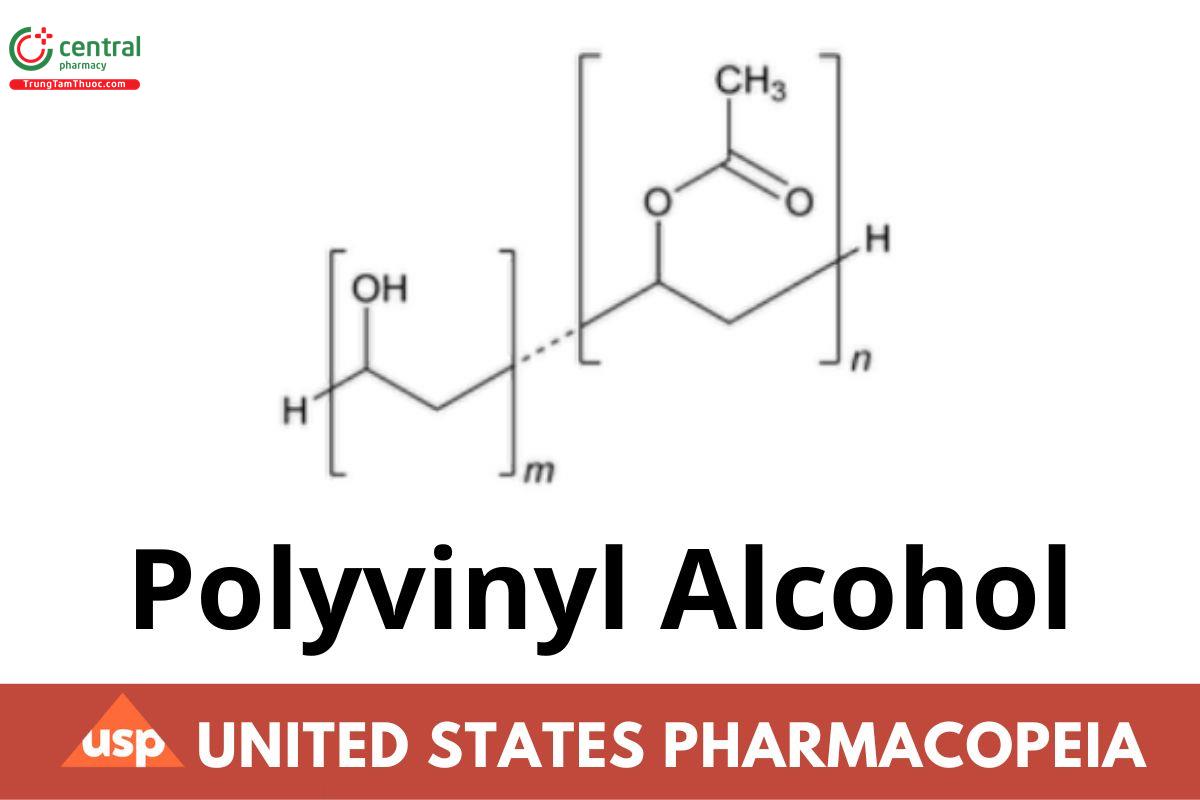
H(C2H4O)m(C4H6O2)nH
Vinyl alcohol and vinyl acetate copolymer (87:13);
A saponied polyvinyl acetate;
Poly(Ethanol)co(vinyl acetate). CAS RN®: 9002-89-5.
1 DEFINITION
Polyvinyl Alcohol is a water-soluble synthetic resin, represented by the formula (C2H4O)m(C4H6O2)n, in which the average value of m+n lies between 444 and 4440. It is prepared by 85%–89% hydrolysis of polyvinyl acetate. The apparent viscosity, in mPa · s, at 20°, of a 4% (w/w) aqueous solution is NLT 85.0% and NMT 115.0% of that stated on the label.
2 IDENTIFICATION
A. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197K
B. It meets the requirements in the test for Viscosity—Capillary Methods 〈911〉, Viscosity—Rotational Methods 〈912〉, or Viscosity—Rolling Ball Method 〈913〉.
C.
Sample solution: Dissolve 0.5 g of Polyvinyl Alcohol in 10 mL of water, with heat if necessary, and let the solution cool to room temperature. Analysis 1: Transfer 5 mL of the Sample solution to a test tube, add 1 drop of iodine TS, mix, and allow to stand. Acceptance criteria 1: A dark red to blue color is produced.
Analysis 2: Transfer 2 mL of the remaining Sample solution to a test tube, add 10 mL of Alcohol, and mix.
Acceptance criteria 2: A white, turbid, or flocculent precipitate is formed.
3 IMPURITIES
Residue on Ignition 〈281〉: NMT 1.0%
Water-Insoluble Substances
Analysis: Wash the tared 100-mesh screen used in the test for Viscosity immediately after with two 25-mL portions of water, and dry at 110° for 1 h.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 6.4 mg of water-insoluble substances are found (corresponding to NMT 0.1%).
Change to read:
Limit of Methanol (Methyl Alcohol) and Methyl Acetate
Diluent: Water
Blank: Transfer 4.0 mL of Diluent to a 20-mL headspace vial and cap.
Standard stock solution: 20 mg/mL each of methanol (methyl alcohol) and methyl acetate prepared as follows. Prepare by transferring 1 g of USP Methyl Alcohol RS and 1 g of USP Methyl Acetate RS to a 50-mL volumetric flask containing Diluent. Dilute with Diluent to volume and mix.
Standard solution A: 0.20 mg/mL each of methanol (methyl alcohol) and methyl acetate prepared as follows. Transfer 2.5 mL of the Standard stock solution into a 250-mL volumetric flask containing Diluent. Dilute with Diluent to volume and mix. [Note—The stability of the Standard solution is 174 h, when stored at ambient room temperature conditions.]
Standard solution B: 0.01 mg/mL each of methanol (methyl alcohol) and methyl acetate prepared as follows. Transfer 5.0 mL of Standard solution A into a 100-mL volumetric flask containing Diluent. Dilute with Diluent to volume and mix.
Sample solution: 20 mg/mL of Polyvinyl Alcohol prepared as follows. Transfer 2 g of Polyvinyl Alcohol into a 100-mL volumetric ask. Pipet 100 mL of Diluent into the volumetric ask. Cap and cover with parafilm. Stir at 60° for 2 h. [Note—It is acceptable to have a few akes of undissolved Polyvinyl Alcohol after extraction stirring.] Allow the sample to cool to room temperature. Pipet 4.0 mL of the solution into a 20- mL headspace vial and cap. [Note—The stability of the Sample solution is 167 h, when stored at ambient room temperature conditions.]
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: GC, equipped with a headspace injector
Detector: Flame ionization
Column: 30-m × 0.32-mm; coated with a 1.8-μm phase G43
Temperatures
Injection port: 140°
Detector: 250°
Column: See Table 1.
Table 1
Initial Temperature (°) | Temperature Ramp(°/min) | Final Temperature (°) | Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
40 | — | 40 | 5 |
40 | 8 | 220 | 5 |
Carrier gas: Helium Flow rate: 2 mL/min
Injection type: Split, split ratio 2.5: 1
Autosampler
Temperatures
Oven: 80°
Needle: 85°
Transfer line: 90°
Times
Injection: 0.04 min
Thermostating: 30.0 min
Needle withdrawal time: 0.2 min
Pressurization: 2.0 min
Column pressure: 29 psi
[Note—These GC conditions (oven temperature program and gas flow) should be optimized according to the instruments used.] System suitability
Samples: Standard solution A and Standard solution B
Suitability requirements
Tailing factor: NMT 2.0, Standard solution A
Relative standard deviation: NMT 15.0%, Standard solution A
Signal-to-noise ratio: NLT 40, Standard solution B
[Note—The relative retention times (RRT) for methyl alcohol and methyl acetate may be around 0.55 and 1.0, respectively. These values are given for informational purposes only. RRT values may vary as per the chromatographic conditions.]
Analysis
Samples: Blank, Standard solution A, and Sample solution
Separately inject equal amounts (about 0.04 min) of the gaseous phase from the headspace vials containing 4.0 mL each of the Blank, Standard solution A, and Sample solution into the chromatographic system. Record the chromatograms and the peak response for each peak.
Calculate the percentages of methanol and methyl acetate in the portion of Polyvinyl Alcohol taken:
Result = (rU /rS ) × (CS /CU ) × 100
rU = peak response of methanol (methyl alcohol) or methyl acetate peak from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of methanol (methyl alcohol) or methyl acetate peak from Standard solution A
CS = concentration of methanol (methyl alcohol) or methyl acetate in Standard solution A (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Polyvinyl Alcohol (ERR 1-Aug-2023) in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria
Methanol (methyl alcohol): NMT 1.0%
Methyl acetate: NMT 1.0%
4 SPECIFIC TESTS
4.1 Loss on Drying 〈731〉
Analysis: Dry at 110° to constant weight.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 5.0%
4.2 Viscosity—Capillary Methods 〈911〉, Viscosity—Rotational Methods 〈912〉, or Viscosity—Rolling Ball Method 〈913〉
Sample: After performing Loss on Drying, weigh undried Polyvinyl Alcohol, equivalent to 6.00 g on the dried basis.
Analysis: Over a period of seconds, transfer the Sample with continuous slow stirring to 140 mL of water contained in a suitable tared flask. When the specimen is well wetted, increase the rate of stirring, avoiding mixing in excess air. Heat the mixture to 90°, and maintain the temperature at 90° for about 5 min. Discontinue heating, and continue stirring for 1 h. Add water to make the mixture weigh 150 g. Resume stirring to obtain a homogeneous solution. Filter the solution through a tared 100-mesh screen into a 250-mL conical flask, cool the filtrate to 15°, mix, and proceed as directed in the chapter. Determine its viscosity at 20 ± 0.1°, using an appropriate viscometer. Acceptance criteria: 85.0%–115.0% of the labeled value
4.3 pH 〈791〉
Sample solution: 40 mg/mL
Acceptance criteria: 5.0–8.0
4.4 Degree of Hydrolysis
Sample: 1 g of Polyvinyl Alcohol, previously dried at 110° to constant weight
Analysis: Transfer the Sample to a wide-mouth, 250-mL conical flask fitted by means of a suitable glass joint to a reflux condenser. Add 35 mL of dilute methanol (3 in 5), and mix gently to ensure complete wetting of the solid. Add 3 drops of phenolphthalein TS, and add 0.2 N hydrochloric acid or 0.2 N sodium hydroxide if necessary, to neutralize. Add 25.0 mL of 0.2 N sodium hydroxide VS, and reflux gently on a hot plate for 1 h. Wash the condenser with 10 mL of water, collecting the washings in the flask, cool, and titrate with 0.2 N hydrochloric acid VS. Concomitantly perform a blank determination in the same manner, using the same quantity of 0.2 N sodium hydroxide VS.
Calculation of saponification value: Calculate the saponification value:
Result = [(VB − VS ) × N × Mr ]/W
VB = volume of 0.2 N hydrochloric acid VS consumed in the titration of the blank (mL)
VS = volume of 0.2 N hydrochloric acid VS consumed in the titration of the Sample solution (mL)
N = actual normality of hydrochloric acid VS
Mr = molecular weight of potassium hydroxide, 56.11
W = weight of the portion of Polyvinyl Alcohol taken (g)
Calculation of degree of hydrolysis: Calculate the degree of hydrolysis, expressed as a percentage of hydrolysis of polyvinyl acetate:
Result = 100 − [7.84 × S/(100 − 0.075 × S)]
S = saponification value of the Polyvinyl Alcohol
Acceptance criteria: 85%–89%
4.5 Acid Value
Sample: 10.0 g
Analysis: Add 200 mL of water to a borosilicate round-bottom flask attached to a reflux condenser. Heat the water on a water bath with constant stirring. Add the Sample to the water, and continue heating for 30 min with continuous stirring. Remove the flask from the water bath, and continue stirring until room temperature is reached. Quantitatively transfer this solution to a 250-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Add 0.5 mL of phenolphthalein TS to 50 mL of this solution, and titrate with 0.05 N potassium hydroxide VS until the pink color persists for 15 s.
Calculate the acid value:
Result = D × Mr × [(N × V)/W]
D = dilution factor
Mr = molecular weight of potassium hydroxide, 56.11
N = normality of potassium hydroxide VS used
V = volume of 0.05 N potassium hydroxide used (mL)
W = weight of the Sample (g)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 3.0
5 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in well-closed containers, and store at room temperature in a dry place.
Labeling: Label it to indicate the viscosity, giving the viscosity measurement parameters, the concentration of the solution, and the type of equipment used.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Methyl Acetate RS
USP Methyl Alcohol RS
USP Polyvinyl Alcohol RS


