Polysorbate 40
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
1 DEFINITION
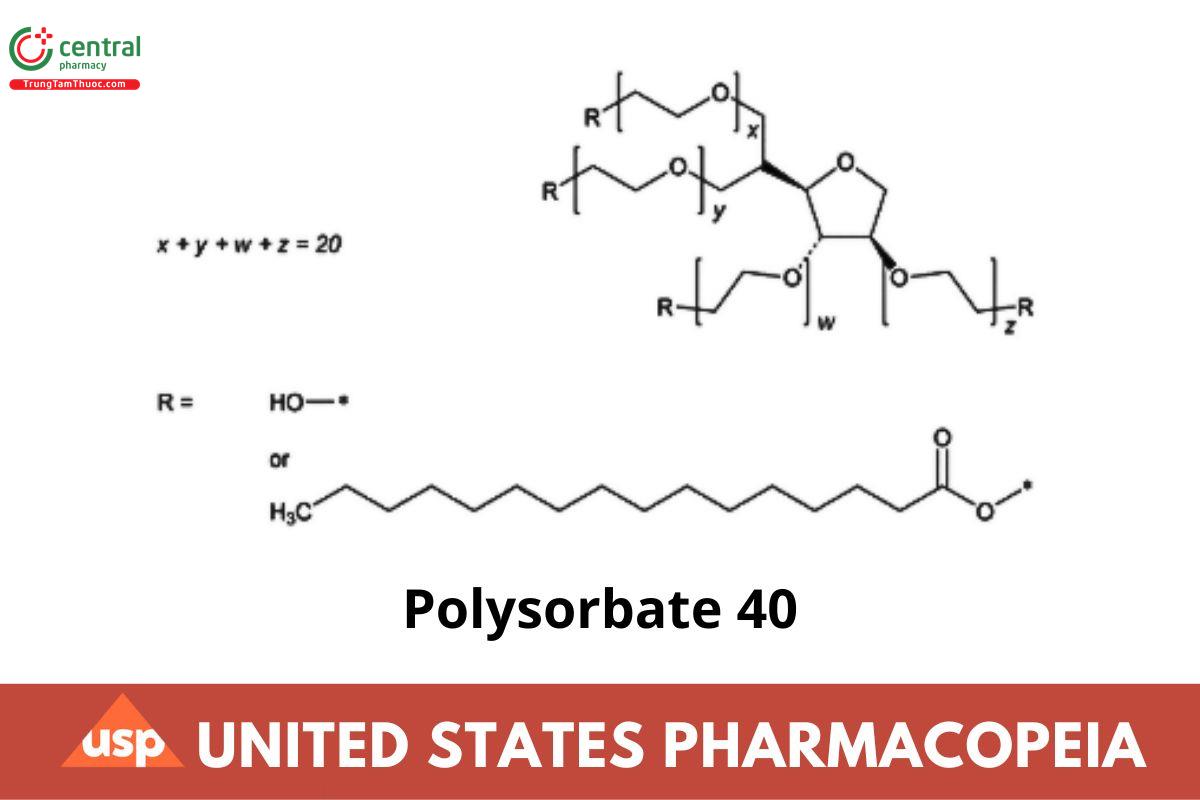
Polysorbate 40 is a palmitate ester of Sorbitol and its anhydrides copolymerized with about 20 moles of ethylene oxide for each mole of sorbitol and sorbitol anhydrides. The fatty acids may be of vegetable, animal, or synthetic origin.
2 IDENTIFICATION
Change to read:
A. ▲Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197F ▲ (CN 1-May-2020)
B. It meets the requirements in the Assay for Composition of Fatty Acids.
3 ASSAY
Composition of Fatty Acids
Polysorbate 40 exhibits the composition profiles of fatty acids shown in Table 1, as determined in Fats and Fixed Oils 〈401〉, Fatty Acid Composition.
Table 1
| Carbon-Chain Length | Number of Double Bonds | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 16 | 0 | ≥92.0 |
4 IMPURITIES
Residue on Ignition 〈281〉: NMT 0.25%
Ethylene Oxide and Dioxane, Method II 〈228〉
Acceptance criteria
Ethylene oxide: NMT 1 ppm
Dioxane: NMT 10 ppm
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
Bacterial Endotoxins Test 〈85〉
For Polysorbate 40 intended for use in the manufacture of injectable dosage forms: The level of bacterial endotoxins is such that the requirement in the relevant dosage form monograph(s) in which Polysorbate 40 is used can be met. Where the label states that Polysorbate 40 must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms, the level of bacterial endotoxins is such that the requirement in the relevant dosage form monograph(s) in which Polysorbate 40 is used can be met.
Fats and Fixed Oils, Acid Value 〈401〉
Sample: 10.0 g
Analysis: Transfer the Sample to a wide-mouth, 250-mL conical flask, and add 50 mL of neutralized alcohol. Heat on a steam bath nearly to boiling, shaking thoroughly occasionally while heating. Invert a beaker over the mouth of the flask, cool under running water, and add 5 drops of phenolphthalein TS. Titrate with 0.1 N sodium hydroxide VS. Calculate the acid value as directed in the chapter.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 2.0
Fats and Fixed Oils, Hydroxyl Value 〈401〉: 89–105
Fats and Fixed Oils, Peroxide Value 〈401〉
Sample: 10.0 g
Saturated potassium iodide solution: Prepare a saturated solution of potassium iodide in carbon dioxide-free water. Make sure the solution remains saturated as indicated by the presence of undissolved crystals.
Analysis: Introduce the Sample into a 100-mL beaker, and dissolve with 20 mL of glacial acetic acid. Add 1 mL of Saturated potassium iodide solution, mix, and allow to stand for 1 min. Add 50 mL of carbon dioxide-free water and a magnetic stirring bar. Titrate with 0.01 M sodium thiosulfate VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically (see Titrimetry 〈541〉). Perform a blank titration. Calculate the peroxide value as directed in the chapter.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 10.0
For Polysorbate 40 intended for use in the manufacture of injectable dosage forms: NMT 5.0
Fats and Fixed Oils, Saponification Value 〈401〉: 41–52
Water Determination, Method I 〈921〉: NMT 3.0%
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in tight containers, protected from light and moisture. Store at room temperature.
Labeling: Label it to indicate whether the fatty acids are derived from animal, vegetable, or synthetic sources. Where Polysorbate 40 is intended for use in the manufacture of injectable dosage forms, it is so labeled.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Polysorbate 40 RS


