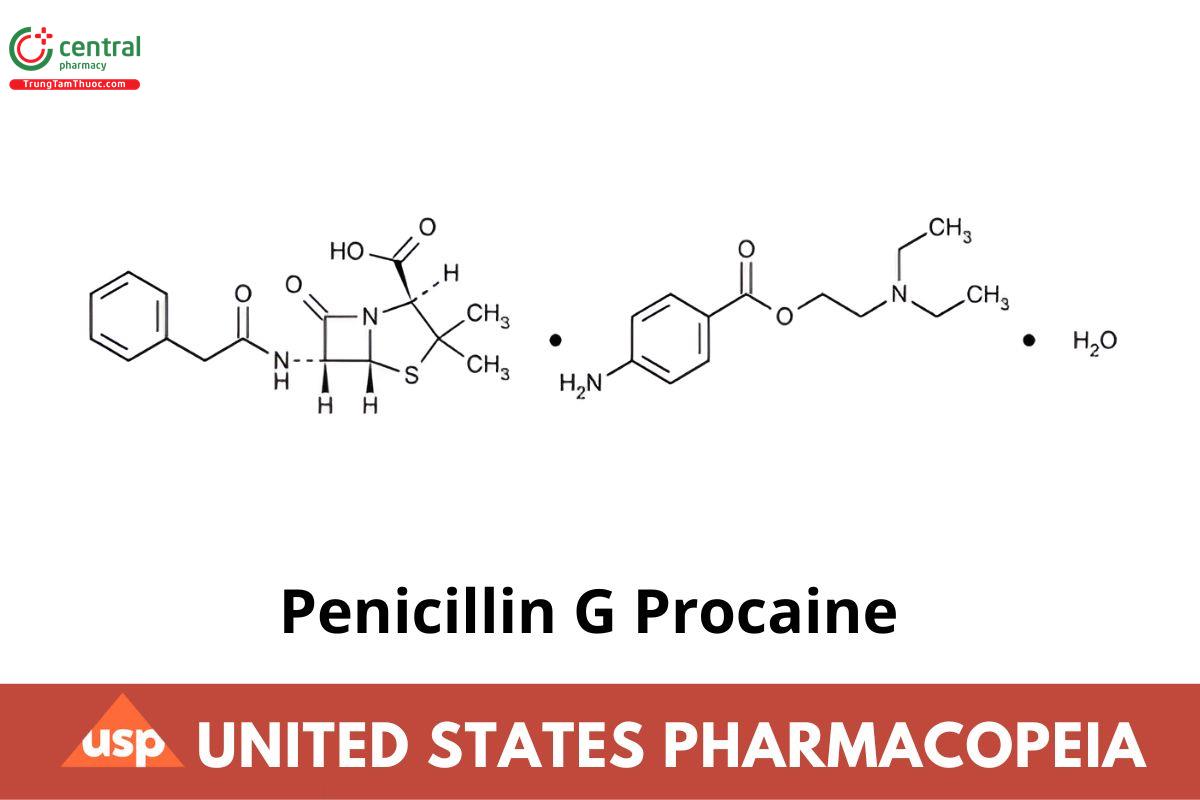
Penicillin G Procaine
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
C16H18N2O4S · C13H20N2O2 · H2O 588.72
C16H18N2O4S · C13H20N2O2 570.71
4-Thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[(phenylacetyl)amino-], 2S-(2α,5α,6β)-, compound with 2-(diethylamino)ethyl 4-aminobenzoate (1:1) monohydrate;
(2S,5R,6R)-3,3-Dimethyl-7-oxo-6-(2-phenylacetamido)-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid compound with 2-(diethylamino)ethyl p-aminobenzoate (1:1) monohydrate CAS RN®: 6130-64-9; UNII: 17R794ESYN.
Anhydrous CAS RN®: 54-35-3; UNII: 1LW5K9CIR1.
1 DEFINITION
Penicillin G Procaine has a potency of NLT 900 Penicillin G Units/mg and NMT 1050 Penicillin G Units/mg.
2 IDENTIFICATION
A. Thin-Layer Chromatography
Solution A: Acetone, 0.1 M citric acid, and 0.1 M sodium citrate (2:1:1)
Standard solution 1: Prepare a solution containing the equivalent of 12,000 Penicillin G Units/mL, from USP Penicillin G Potassium RS in Solution A.
Standard solution 2: 5 mg/mL of USP Procaine Hydrochloride RS in Solution A
Sample solution: Nominally 12,000 Penicillin G Units/mL from Penicillin G Procaine in Solution A
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, Thin-Layer Chromatography.)
Mode: TLC
Adsorbent: 0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel mixture
Application volume: 20 μL
Developing solvent system: Toluene, dioxane, and glacial acetic acid (90:25:4)
Spray reagent 1: Starch TS
Spray reagent 2: Iodine TS diluted 1 in 10 with water
Spray reagent 3: 50 mg/mL of p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde in methanol
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution 1, Standard solution 2, and Sample solution
Proceed as directed in the chapter. Develop the chromatogram until the solvent has moved three-fourths of the length of the plate.
Remove the plate from the chamber, mark the solvent front, and allow to air-dry. Examine the plate under short- and long-wavelength UV light, noting the positions of the spots. Spray the plate with Spray reagent 1 followed by Spray reagent 2. Penicillin G appears as a white spot on a purple background. Spray the location of the spots visualized with UV light with Spray reagent 3. Procaine appears as a bright yellow spot.
Acceptance criteria: The R value of the penicillin G spot from the Sample solution corresponds to that from Standard solution 1. The R value of the procaine spot from the Sample solution corresponds to that from Standard solution 2.
3 ASSAY
Procedure
Standard solution: Prepare as directed in Iodometric Assay - Antibiotics 〈425〉, Standard Preparation, using USP Penicillin G Potassium RS.
Sample solution: Prepare as directed in Iodometric Assay - Antibiotics 〈425〉, Assay Preparation, except dissolve 100 mg of Penicillin G
Procaine in 2.0 mL of methanol, and dilute with Buffer B.1 (see Antibiotics - Microbial Assays 〈81〉) to obtain a solution containing 2000 Penicillin G Units/mL.
Analysis: Pipet 2 mL of the Sample solution into each of two glass-stoppered, 125-mL conical flasks. Use one of these to perform the Blank Determination. Proceed as directed in Iodometric Assay - Antibiotics 〈425〉, Procedure.
Calculate the potency, in Penicillin G Units/mg, of the Penicillin G Procaine taken:
Result = (B − I) × F × 1/(D × V) × 100
B = volume of 0.01 N sodium thiosulfate consumed in the Blank Determination (mL)
I = volume of 0.01 N sodium thiosulfate consumed in the Inactivation and Titration (mL)
F = equivalency factor as calculated in Procedure in the chapter (Penicillin G Units/mL of 0.01 N sodium thiosulfate consumed by the Standard solution)
D = nominal concentration of Penicillin G in the Sample solution (Penicillin G Units/mL)
V = volume of the Sample solution used for the Inactivation and Titration (mL)
Acceptance criteria: 900–1050 Penicillin G Units/mg
4 SPECIFIC TESTS
Content of Penicillin G and Procaine
Solution A: Phosphoric acid diluted 1 in 10 with water
Mobile phase: Dissolve 14 g of monobasic potassium phosphate and 6.5 g of tetrabutylammonium hydroxide, 40% in water, in 700 mL of water. Adjust with 1 N potassium hydroxide to a pH of 7.0, and dilute with water to 1000 mL. Mix 500 mL of this solution, 250 mL of acetonitrile, and 250 mL of water. Adjust with 1 N potassium hydroxide or Solution A to a pH of 7.5 ± 0.05, and pass through a suitable filter.
Standard solution: 0.8 mg/mL of USP Penicillin G Potassium RS and 0.54 mg/mL of USP Procaine Hydrochloride RS in Mobile phase
System suitability solution: 2.4 mg/mL of USP Penicillin V Potassium RS in Mobile phase. Mix the resultant solution with Standard solution (1:3).
Sample solution: Transfer 70 mg of Penicillin G Procaine to a 50-mL volumetric flask. Add 30 mL of Mobile phase, sonicate to dissolve, and dilute with Mobile phase to volume.
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 235 nm
Column: 3.9-mm × 30-cm; 10-μm packing L1
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Injection volume: 10 μL
System suitability
Samples: Standard solution and System suitability solution
[Note - The relative retention times for procaine, penicillin G, and penicillin V are about 0.4, 1.0, and 1.5, respectively.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 2.0 between penicillin G and penicillin V, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation: NMT 3.0% for penicillin G potassium, Standard solution
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of penicillin G (C16H18N2O4S) in the portion of Penicillin G Procaine taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × G
rU = peak response of penicillin G from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of penicillin G from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Penicillin G Potassium RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Penicillin G Procaine in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
G = content of penicillin G in USP Penicillin G Potassium RS (%)
Calculate the percentage of procaine (C13H20N2O2) in the portion of Penicillin G Procaine taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × (Mr1/Mr2) × 100
rU = peak response of procaine from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of procaine from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Procaine Hydrochloride RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Penicillin G Procaine in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Mr1 = molecular weight of procaine, 236.32
Mr2 = molecular weight of procaine hydrochloride, 272.78
Acceptance criteria: See Table 1.
Table 1
| Penicillin G | 51.0% – 59.6% |
| Procaine | 37.5% – 43.0% |
Bacterial Endotoxins Test 〈85〉: Where the label states that Penicillin G Procaine is sterile or that it must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms, it contains NMT 0.01 USP Endotoxin Unit/100 Penicillin G Units.
Sterility Tests 〈71〉: Where the label states that Penicillin G Procaine is sterile, it meets the requirements. If the test for Membrane Filtration is used, perform the procedure as directed in the chapter with the following exceptions. Use Fluid A to which has been added sufficient sterile penicillinase to inactivate the penicillin G, and swirl the vessel until solution is complete before filtering.
Crystallinity 〈695〉: Meets the requirements
pH 〈791〉
Sample solution: A saturated solution containing about 300 mg/mL of Penicillin G Procaine in water
Acceptance criteria: 5.0–7.5
Water Determination 〈921〉, Method I: 2.8%–4.2%
5 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Where it is intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms, preserve as directed in Packaging and Storage Requirements 〈659〉, Injection Packaging, Packaging for constitution.
Labeling: Where it is intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms, the label states that it is sterile or must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Penicillin G Potassium RS
USP Penicillin V Potassium RS
USP Procaine Hydrochloride RS


