Pectin
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
CAS RN®: 9000-69-5.
1 DEFINITION
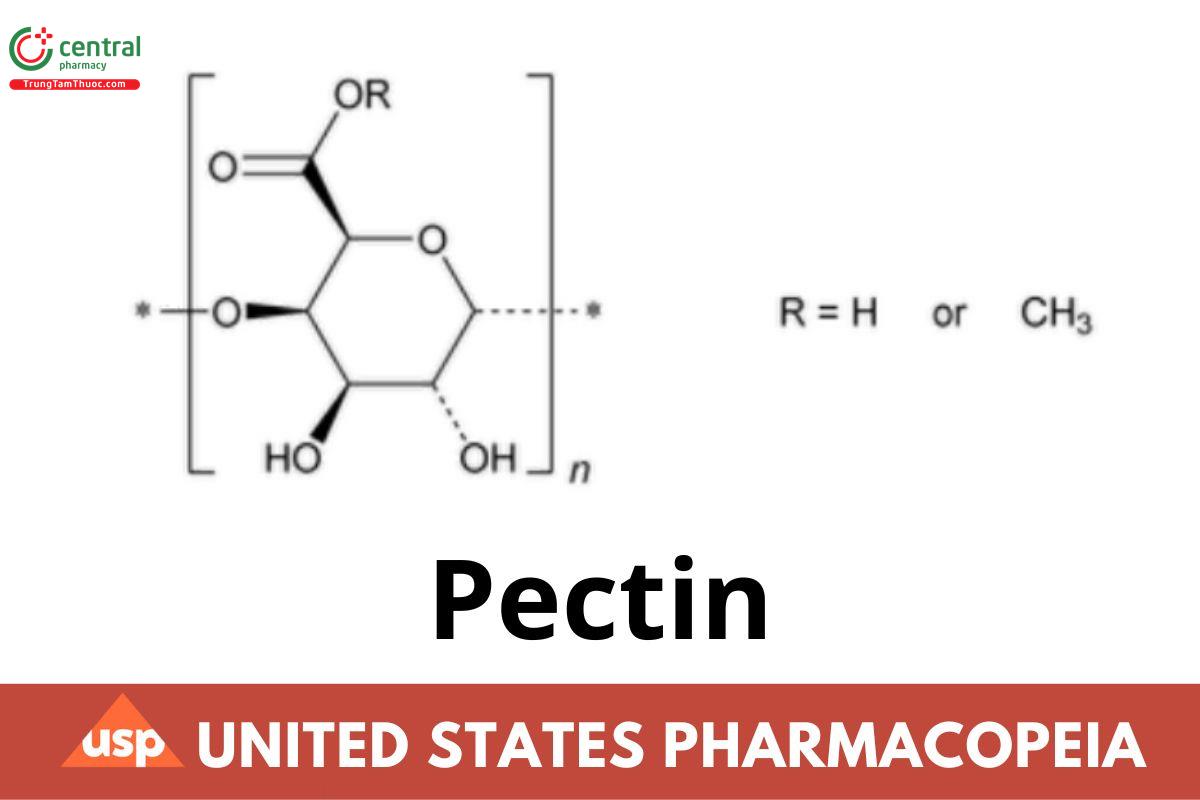
Pectin is a purified carbohydrate polymer consisting mainly of a linear backbone of partially methoxylated alpha (1-4) linked d-galacturonic acid. It is obtained from the dilute acid extract of the rind of citrus fruits or from apple pomace. No organic solvents other than methanol, ethanol, and isopropanol are used during its production. Pectin yields NLT 74.0% of galacturonic acid (C6H10O7), calculated on the dried basis.
[Note—Commercial pectin for the production of jellied food products is standardized to the convenient “150 jelly grade” by addition of dextrose or other sugars, and sometimes contains sodium citrate or other buffer salts. This monograph refers to the pectin to which no such additions have been made.]
2 IDENTIFICATION
Procedure
Sample stock solution: Transfer a quantity of Pectin, equivalent to 0.05 g on the dried basis, to a suitable container, and moisten with 250 µL of 2-propanol. Add 50 mL of water to the container, and mix the solution using a magnetic stirrer. Use 0.5 N sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH of the solution to 12, stop the stirrer, and allow the solution to stand undisturbed at room temperature for 15 min. Adjust with 0.5 N hydrochloric acid to a pH of 7.0, and dilute with water to 100 mL.
Tris buffer solution: Transfer 6.055 g of tris(hydroxylmethyl)aminomethane and 0.147 g of calcium chloride (CaCl2 · 2H2O) to a 1000-mL volumetric flask containing 950 mL of water. Adjust with 1 N hydrochloric acid to a pH of 7.0, and dilute with water to volume. Enzyme solution: Mix pectate lyase 1 with Tris buffer solution to make a solution (1 in 100).
Sample blank: Mix 0.5 mL of Tris buffer solution, 1.0 mL of Sample stock solution, and 1.0 mL of water in a quartz cuvette. Enzyme blank: Mix 0.5 mL of Tris buffer solution, 1.5 mL of water, and 0.5 mL of Enzyme solution in a quartz cuvette.
Sample solution: Mix 0.5 mL of Tris buffer solution, 1.0 mL of Sample stock solution, 0.5 mL of water, and 0.5 mL of Enzyme solution in a quartz cuvette.
Analysis
Samples: Sample blank, Enzyme blank, and Sample solution
Perform the test with the Samples using a suitable UV/visible spectrophotometer (see Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy 〈857〉) and using water as a blank. Measure the absorbance at 235 nm immediately after mixing the solutions well, and record the value at time 0 for the Enzyme blank, A0-EB ; for the Sample blank, A0-TB ; and for the Sample solution, A0-TS. After incubation at room temperature for 10 min, determine the absorbance again at 235 nm for the Enzyme blank, A10-EB; for the Sample blank, A10-TB; and for the Sample solution, A10-TS.
Calculate the corrected absorbance A0- at time 0 and the corrected absorbance A10 at 10 min:
A0 = A0-TS − (A0-EB + AA0-TB )
A10 = A10-TS − (A10-EB + A10-TB )
Calculate the quantity of unsaturated product produced:
Result = (A10− A0)/(ε235× L)
ε235 = molar extinction coefficient of the reaction product (4600 M-1 · cm-1)
L = path length of the reaction cuvette, 1 cm
Acceptance criteria: The amount of unsaturated product is NLT 0.5 × 10-5 M.
3 ASSAY
3.1 Degree of Esterification
Sample: 5.0 g
Analysis: Transfer the Sample to a suitable beaker, and stir for 10 min with a mixture of 5 mL of hydrochloric acid and 100 mL of 60% alcohol. Transfer to a sintered-glass filter (30- to 60-mL crucible or Büchner type, coarse), and wash with six 15-mL portions of the hydrochloric acid–60% alcohol mixture, followed by 60% alcohol until the filtrate is free from chlorides. Finally wash with 20 mL of alcohol, dry for 1 h at 105°, cool, and weigh. Transfer exactly one-tenth of the total net weight of the dried Sample (representing 500 mg of the original unwashed Sample) to a 250-mL conical flask, and moisten with 2 mL of alcohol. Add 100 mL of carbon dioxide-free water, insert the stopper, and swirl occasionally until the Pectin is completely dissolved. Add 5 drops of phenolphthalein TS, and titrate with 0.1 N sodium hydroxide VS. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Record the results as the initial titer, VI (mL). Add 20.0 mL of 0.5 N sodium hydroxide VS, insert the stopper, shake vigorously, and allow to stand for 15 min. Add 20.0 mL of 0.5 N hydrochloric acid VS, and shake until the pink color disappears. Add phenolphthalein TS, and titrate with 0.1 N sodium hydroxide VS to a faint pink color that persists after vigorous shaking. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Record this value as the saponification titer, VS (mL). Calculate the degree of esterification:
Result = [VS /(VI+ VS )] × 100
VS = saponification titer (mL)
VI= initial titer (mL)
Acceptance criteria: The value for Degree of Esterification is within the range stated on the label.
3.2 Galacturonic Acid
Each mL of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide used in the total titration (the initial titer added to the saponification titer) in the Assay for Degree of Esterification is equivalent to 19.41 mg of C6H10O7. Calculate the percentage of galacturonic acid in the portion of Pectin taken:
Result = 19.41 × [(VI + VS )/W] × 100
VI = initial titer (mL)
VS = saponification titer (mL)
W = weight of the original unwashed and dried Pectin taken to prepare the solution for titration (mg)
Acceptance criteria: NLT 74.0%
3.3 Methoxy Groups
Each mL of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide used in the saponification titer in the Assay for Degree of Esterification is equivalent to 3.10 mg of –OCH3. Calculate the percentage of methoxy groups in the portion of Pectin taken:
Result = 3.10 × (VS /W) × 100
VS = saponification titer (mL)
W = weight of the original unwashed and dried Pectin taken to prepare the solution for titration (mg)
Acceptance criteria: The percentage of methoxy groups is within the range stated on the label.
4 IMPURITIES
Change to read:
Arsenic 〈211〉, Procedures, Procedure 2 (CN 1-Jun-2023) : NMT 3 ppm
4.1 Lead
Standard stock solution: 1000 µg/mL of lead. [Note—Use a commercially available certified solution.]
Standard solution: 2 µg/mL of lead, prepared immediately before use by pipetting 0.10 mL of Standard stock solution into a 50-mL volumetric flask containing 30 mL of water, 4 mL of 20% hydrochloric acid, and 4 mL of 0.1 M EDTA. Dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Reference solution: 0.4 µg/mL of lead, prepared by pipetting 5.0 mL of the Standard solution into a 25-mL volumetric ask containing 10 mL of water, 2 mL of 20% hydrochloric acid, and 2 mL of 0.1 M EDTA. Dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Sample solution: Transfer 2.0 g of Pectin to a clean, 100-mL glass beaker, add 25 mL of 70% nitric acid, cover with a watch glass, and heat at low to moderate heat on a hot plate in a fume hood for 2 h. Remove the watch glass, and continue to heat until the sample is dry with no visible fumes. Add 0.5 mL of 70% nitric acid, and heat to dryness. Cool to room temperature, and add 2 mL of 20% hydrochloric acid and 2 mL of 0.1 M EDTA. Quantitatively transfer the solution to a 25-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Blank solution: Add 30 mL of water, 4 mL of 20% hydrochloric acid, and 4 mL of 0.1 M EDTA into a 50-mL volumetric ask. Dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Analysis: Lead is determined using an inductively coupled plasma–atomic emission spectrometer (ICP–AES) (see Plasma Spectrochemistry 〈730〉) by measuring the emission at 220.35 nm with the settings optimized as directed by the manufacturer. Instrument performance must be verified to conform to the manufacturer's specifications for resolution and sensitivity. Before analyzing samples, the instrument must pass a suitable performance check. Calibrate the instrument with the Blank solution and the Standard solution. Then analyze the Reference solution and the Sample solution.
Acceptance criteria: The concentration in the Sample solution is NMT that in the Reference solution, corresponding to NMT 5 ppm of lead.
4.2 Sulfur Dioxide, Method V〈525〉
Sample: 100 g
Analysis: Suspend the Sample in 500 mL of methanol, then transfer this mixture to the ask (C). Prepare a mixture of 20 mL of hydrochloric acid and 10 mL of water, and transfer it to the separatory funnel (B). Add 10 mL of Hydrogen peroxide solution to the vessel (G). Perform the refluxing for 2 h before removing the vessel (G).
Acceptance criteria: NMT 50 ppm
4.3 Sugars and Organic Acids
Sample: 1 g
Analysis: Place the Sample in a 500-mL flask, moisten with 3–5 mL of alcohol, rapidly pour in 100 mL of water, shake, and allow to stand until the solution is complete. To this solution add 100 mL of alcohol containing 0.3 mL of hydrochloric acid, mix, and filter rapidly. Measure 25 mL of the filtrate into a tared dish, evaporate the liquid on a steam bath, and dry the residue in a vacuum oven at 50° for 2 h.
Acceptance criteria: The weight of the residue does not exceed 20 mg, corresponding to NMT 16% of sugars and organic acids. • Methanol (Methyl Alcohol), Ethanol (Alcohol), and Isopropanol (2-Propanol)
[Note—Residual alcohols are volatile. They should be stored in a cool and dry place. When preparing the Standard stock solution, Standard solution, and Internal standard stock solution for residual alcohols, mix thoroughly and keep the solutions at 20° when diluting with water to volume.]
Internal standard stock solution: 5000 µg/mL of USP 2-Butanol RS. [Note—This solution can be stored at 5°–8° for 3 months.] Standard stock solution: Use USP Methyl Alcohol RS, USP 2-Propanol RS, and alcohol to prepare a solution having known concentrations of 5000 µg/mL each for methyl alcohol, 2-propanol, and alcohol.
Standard solution: To a 250-mL volumetric flask add 2.5 mL of the Standard stock solution and 2.5 mL of the Internal standard stock solution. Dilute with water to volume, and mix. This solution contains 50 µg/mL each of methyl alcohol, 2-propanol, and alcohol. [Note—This solution can be stored at 5°–8° for 3 months.] Transfer 1.0 g of this solution to a 10-mL headspace vial.
Sample solution: Transfer 1.0 g of Pectin and 5 g of sucrose to a stoppered 100-mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 90 mL of water, add 1.0 mL of the Internal standard stock solution, and dilute with water to 100 mL. Mix the solution using a magnetic stirrer. Continue stirring until all of the Pectin has been completely dissolved; typically it takes about 1–2 h. This solution contains 50 µg/mL of USP 2-Butanol RS. Transfer 1.0 g of this solution to a 10-mL headspace vial.
4.3.1 Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: Headspace GC
Detector: Flame ionization
Column: 0.32-mm × 30-m capillary column; 1.8-µm layer of phase G43. [Note—An alternative column such as a 0.32-mm × 25-m capillary column bonded with a 5-µm layer of phase S3 can be used as long as the system suitability requirements are met.]
Temperatures
Detector: 280°
Column: 70°
Injection port: 200°
Carrier gas: Nitrogen
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min
Make up gas: Nitrogen
Split flow rate: 30 mL/min
Injection volume: 1 mL (the gaseous headspace)
Injection type: Split ratio 20:1
Balanced pressure automatic headspace sampler
Equilibration time: 10 min
Equilibration temperature: 70°
Agitation speed: 500 rpm
Agitation on time: 5 s
Agitation off time: 90 s
Syringe temperature: 80°
Syringe size: 2.5 mL
Fill speed: 100 µL/s
Pull-up delay: 2.0 s
GC run time: 10.5 min
[Note—These GC conditions should be optimized according to the instruments used.]
4.3.2 System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
[Note—See Table 1 for the relative retention times.]
Table 1
Component | Relative Retention Time |
Methanol | 0.5 |
Ethanol | 0.6 |
2-Propanol | 0.7 |
2-Butanol | 1.0 |
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 1.5, between each pair of analytes
Relative standard deviation: NMT 10%, determined from each analyte
4.3.3 Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of methanol, ethanol, and 2-propanol in the portion of Pectin taken:
Result = (RU /RS ) × (CS /W) × F × V × 100
RU = internal standard ratio (peak response of the respective alcohol/peak response of the internal standard) from the Sample solution
RS = internal standard ratio (peak response of the respective alcohol/peak response of the internal standard) from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of the respective residual alcohol (methanol, ethanol, or 2-propanol) in the Standard solution (µg/mL)
W = weight of Pectin taken to prepare the Sample solution (g)
F = conversion factor (10-6 g/µg)
V = volume of the Sample solution, 100 mL
Acceptance criteria: NMT 1% for total methanol, ethanol, and isopropanol
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
Microbial Enumeration Tests 〈61〉andTests for Specified Microorganisms 〈62〉: The total aerobic microbial count is NMT 103 cfu/g, and the total combined molds and yeasts count is NMT 102 cfu/g.
Loss on Drying 〈731〉
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in tight containers. Store in a cool and dry place.
Labeling: Label it to indicate whether it is of apple or of citrus origin. Label it to indicate the range of the degree of esterification and the range of the percentage of methoxy groups. The labeling also indicates the presence of sulfur dioxide if the residual sulfur dioxide concentration is greater than 10 ppm.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP 2-Butanol RS
USP Methyl Alcohol RS
USP 2-Propanol RS
1 A suitable pure enzyme is available from Megazyme International Ireland Ltd., Bray Business Park, Bray, Co. Wicklow, Ireland


