Paroxetine Hydrochloride
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
Change to read:
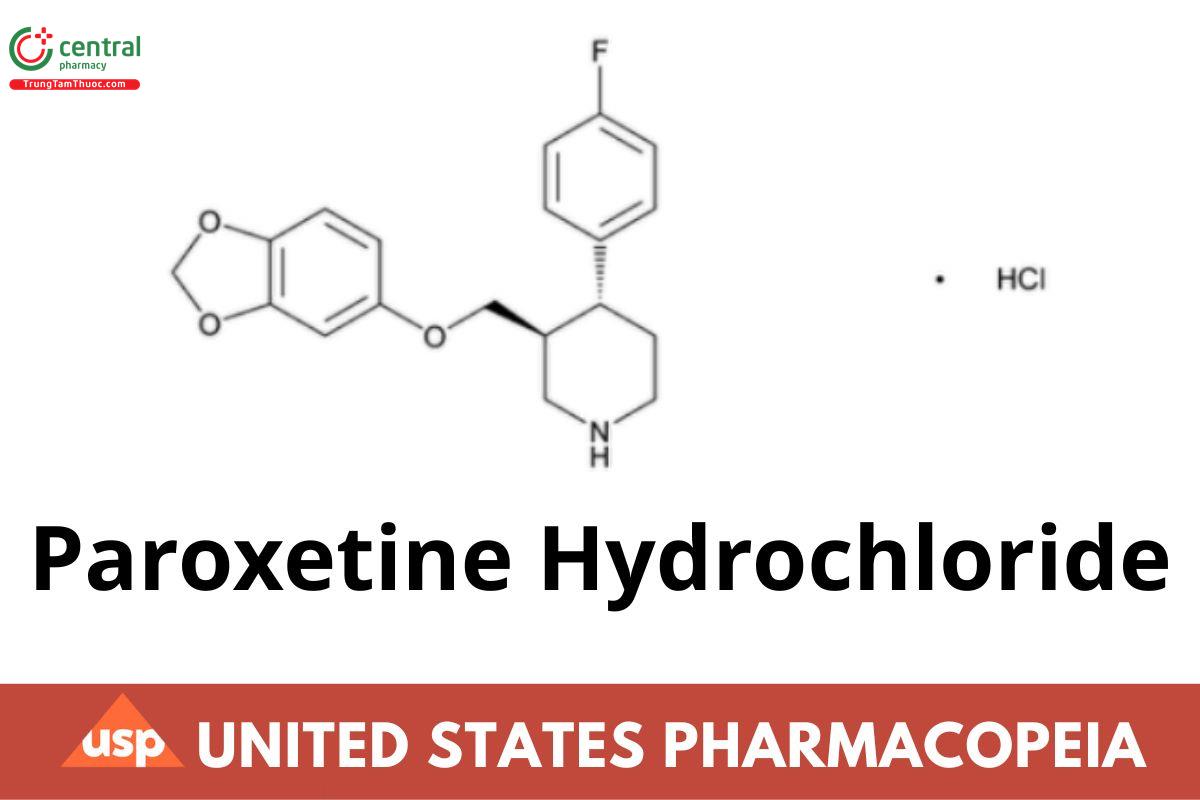
C19H20FNO3 · HCl 365.83
C19H20FNO3 · HCl · ½H O 374.83
Piperidine, 3-[(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yloxy)methyl]-4-(4-uorophenyl)-, hydrochloride, (3S-trans)-;
(−)-(3S,4R)-4-(p-Fluorophenyl)-3-[[ (ERR 1-Nov-2021) (3,4-methylenedioxy)phenoxy]methyl]piperidine hydrochloride; (3S,4R)-3-[(Benzodioxol-5-yloxy)methyl]-4-(4-uorophenyl)piperidine hydrochloride.
Anhydrous CAS RN®: 78246-49-8; UNII: 3I3T11UD2S.
Hemihydrate CAS RN®: 110429-35-1; UNII: X2ELS050D8.
1 DEFINITION
Paroxetine Hydrochloride is anhydrous or contains one-half molecule of water of hydration. It contains NLT 98.5% and NMT 102.0% of paroxetine hydrochloride (C19H20FNO3 · HCl), calculated on the anhydrous and solvent-free basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
A. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197M, 197K, or 197A
Standard: Dissolve USP Paroxetine Hydrochloride RS in a mixture of water and isopropyl alcohol (1 in 10). Heat to 70° to dissolve, recrystallize, and dry the residue under vacuum at 50° for 3 h.
Sample: Dissolve Paroxetine Hydrochloride in a mixture of water and isopropyl alcohol (1 in 10). Heat to 70° to dissolve, recrystallize, and dry the residue under vacuum at 50° for 3 h.
Acceptance criteria: Meets the requirements
B. Identification Tests—General 〈191〉, Chemical Identification Tests, Chloride
Sample solution: 10 mg/mL of Paroxetine Hydrochloride in methanol and water (50:50)
Acceptance criteria: Meets the requirements
C. The retention time of the major peak of the Sample solution corresponds to that of the Standard solution as obtained in the Assay.
3 ASSAY
Procedure
Buffer: 0.05 M ammonium acetate in water. Adjust with glacial acetic acid to a pH of 4.5.
Mobile phase: Acetonitrile, Buffer, and triethylamine (30:70:1). [Note—The ratio for acetonitrile, Buffer, and triethylamine may be varied between 25:75:1 and 40:70:1 to meet system suitability requirements.] Adjust with glacial acetic acid to a pH of 5.5.
System suitability solution: 0.5 mg/mL each of USP Paroxetine Hydrochloride RS and USP Paroxetine Related Compound B RS in water Standard solution: 0.5 mg/mL of USP Paroxetine Hydrochloride RS in water
Sample solution: 0.5 mg/mL of Paroxetine Hydrochloride in water
3.1 Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 295 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L13
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Injection volume: 10 µL
Run time: NLT 1.5 times the retention time of paroxetine
3.2 System suitability
Sample: System suitability solution
[Note—The approximate relative retention times for paroxetine related compound B and paroxetine are about 0.9 and 1.0, respectively.] Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 2.0 between paroxetine related compound B and paroxetine
Tailing factor: NMT 2.0 for paroxetine
Relative standard deviation: NMT 0.73% for paroxetine
3.3 Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of paroxetine hydrochloride (C19H20FNO3 · HCl) in the portion of Paroxetine Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rU /rS ) × (CS /CU) × 100
rU= peak response of paroxetine from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of paroxetine from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Paroxetine Hydrochloride RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU= concentration of Paroxetine Hydrochloride in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: 98.5%–102.0% on the anhydrous and solvent-free basis
4 IMPURITIES
Residue on Ignition 〈281〉: NMT 0.1%
4.1 Limit of Paroxetine Related Compound C
Mobile phase: n-Hexane, absolute alcohol, trifluoroacetic acid, and water (900:100:2:2)
Diluent: n-Hexane and absolute alcohol (50:50)
System suitability solution: 0.1 mg/mL each of USP Paroxetine Hydrochloride RS and USP Paroxetine Related Compound C RS in Diluent Standard solution: 0.1 mg/mL of USP Paroxetine Related Compound C RS in Diluent
Sample solution: 5 mg/mL of Paroxetine Hydrochloride in Diluent
4.1.1 Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 295 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 10-µm packing L51
Column temperature: 30°
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Injection volume: 5 µL
Run time: NLT 2.3 times the retention time of paroxetine
4.1.2 System suitability
Samples: System suitability solution and Standard solution
[Note—The relative retention times for paroxetine related compound C and paroxetine are about 0.6 and 1.0, respectively.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 2.0 between paroxetine and paroxetine related compound C, System suitability solution
Tailing factor: NMT 2.5 for the paroxetine related compound C peak, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation: NMT 10.0% for paroxetine related compound C, Standard solution
4.1.3 Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of paroxetine related compound C in the portion of Paroxetine Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rU /rS ) × (CS /CU ) × 100
rU = peak response of paroxetine related compound C from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of paroxetine related compound C from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Paroxetine Related Compound C RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Paroxetine Hydrochloride, on the anhydrous basis, in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.1%
4.2 Limit of Paroxetine Related Compound E
[Note—Perform this test only if paroxetine related compound E is a known process impurity.]
Solution A: Dissolve 30 g of sodium perchlorate in 900 mL of water. Add 3.5 mL of phosphoric acid and 2.4 mL of triethylamine. Dilute with water to 1000 mL. Adjust with phosphoric acid or triethylamine to a pH of 2.0.
Solution B: Acetonitrile
Mobile phase: See Table 1.
Table 1
Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) |
0 | 85 | 15 |
2 | 85 | 15 |
20 | 80 | 20 |
20.1 | 55 | 45 |
25 | 55 | 45 |
26 | 85 | 15 |
35 | 85 | 15 |
Diluent: Acetonitrile and water (20:80)
Sensitivity solution: 0.006 μg/mL of USP Paroxetine Related Compound E RS (equivalent to 0.005 μg/mL of paroxetine related compound E free base) in Diluent
Standard solution: 0.012 μg/mL of USP Paroxetine Related Compound E RS (equivalent to 0.010 μg/mL of paroxetine related compound E free base) in Diluent
Sample solution: 10,000 μg/mL of Paroxetine Hydrochloride in Diluent. Sonicate as needed to aid dissolution.
4.2.1 Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 242 nm
Column: 3.0-mm × 15-cm; 3-µm packing L1
Column temperature: 35°
Flow rate: 0.6 mL/min
Injection volume: 100 µL
4.2.2 System suitability
Sample: Sensitivity solution and Standard solution
[Note—The relative retention times for paroxetine related compound E and paroxetine are about 0.6 and 1.0, respectively.] Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation: NMT 10.0%, Standard solution
Signal-to-noise ratio: NLT 10, Sensitivity solution
4.2.3 Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of paroxetine related compound E in the portion of Paroxetine Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rU /rS ) × (CS /CU) × (Mr1 /Mr2) × 100
rU = peak response of paroxetine related compound E from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of paroxetine related compound E from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Paroxetine Related Compound E RS in the Standard solution (μg/mL)
CU = concentration of Paroxetine Hydrochloride, on the anhydrous basis, in the Sample solution (μg/mL)
Mr1 = molecular weight of paroxetine related compound E (free base), 191.25
Mr2 = molecular weight of paroxetine related compound E (hydrochloride salt), 227.71
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.0001%
4.3 Organic Impurities, Procedure 1
Perform either Organic Impurities, Procedure 1 or Organic Impurities, Procedure 2, depending on the synthetic route. Organic Impurities, Procedure 2 is recommended if paroxetine related compound F or paroxetine related compound G are potential impurities. Solution A: Tetrahydrofuran, water, and trifluoroacetic acid (20:180:1)
Solution B: Acetonitrile, tetrahydrofuran, and trifluoroacetic acid (180:20:1)
Mobile phase: See Table 2.
Table 2
Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) |
0 | 80 | 20 |
30 | 80 | 20 |
50 | 20 | 80 |
60 | 20 | 80 |
70 | 80 | 20 |
Diluent: Tetrahydrofuran and water (1:9)
System suitability solution: 1 mg/mL of USP Paroxetine System Suitability Mixture A RS in Diluent. Sonication may be necessary to achieve complete dissolution.
Standard solution: 0.001 mg/mL of USP Paroxetine Hydrochloride RS in Diluent
Sample solution: 1 mg/mL of Paroxetine Hydrochloride in Diluent. Sonicate to dissolve.
4.3.1 Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 285 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L7
Column temperature: 40°
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Injection volume: 20 µL
4.3.2 System suitability
Sample: System suitability solution
[Note—See Table 3 for relative retention times.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 2.0 between paroxetine related compound A and paroxetine related compound B
Tailing factor: 0.8–2.0 for paroxetine related compound A
Relative standard deviation: NMT 2.0% for paroxetine related compound A
4.3.3 Analysis
Samples: Diluent, Standard solution, and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Paroxetine Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rU /rS ) × (CS /CU) × 100
rU = peak area of each impurity from the Sample solution, excluding peaks from the chromatogram of the Diluent
rS = peak area of paroxetine from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Paroxetine Hydrochloride RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Paroxetine Hydrochloride, on the anhydrous basis, in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: See Table 3.
Table 3
Name | Relative Retention Time | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
Paroxetine related compound A | 0.66 | 0.1 |
Paroxetine related compound B | 0.73 | 0.3 |
Paroxetine | 1.0 | — |
Any unspecified impurity | — | 0.1 |
Total impurities | — L | 1.0 |
5 Organic Impurities, Procedure 2
Buffer: Dissolve 3.4 g of monobasic potassium phosphate and 3.4 g of tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfate in 1.0 L of water. Solution A: Acetonitrile and Buffer (2:98)
Solution B: Acetonitrile and Buffer (40:60)
Mobile phase: See Table 4.
Table 4
Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) |
0 | 100 | 0 |
5 | 100 | 0 |
70 | 40 | 60 |
90 | 0 | 100 |
95 | 0 | 100 |
95.1 | 100 | 0 |
110 | 100 | 0 |
Diluent: Acetonitrile and Buffer (10:90)
Identification solution: 2 mg/mL of USP Paroxetine Hydrochloride RS, 0.01 mg/mL of USP Paroxetine Related Compound B RS, 0.01 mg/mL of USP Paroxetine Related Compound F RS, and 0.004 mg/mL of USP Paroxetine Related Compound G RS in Diluent Standard solution: 0.004 mg/mL of USP Paroxetine Hydrochloride RS, 0.01 mg/mL of USP Paroxetine Related Compound B RS, 0.01 mg/mL of USP Paroxetine Related Compound F RS, and 0.004 mg/mL of USP Paroxetine Related Compound G RS in Diluent Sample solution: 0.5 mg/mL of Paroxetine Hydrochloride in Diluent
4.3.4 Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 210 nm
Column: 3.9-mm × 15-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min
Injection volume: 25 µL
4.3.5 System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
[Note—See Table 5 for relative retention times.]
Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation: NMT 10.0% for each of paroxetine related compound B, paroxetine related compound F, paroxetine hydrochloride, and paroxetine related compound G
4.3.6 Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of paroxetine related compound B, paroxetine related compound F, and paroxetine related compound G in the portion of Paroxetine Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rU /rS ) × (CS /CU) × 100
rU = peak response of the corresponding impurity from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of the corresponding impurity from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of the corresponding Reference Standard in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Paroxetine Hydrochloride, on the anhydrous basis, in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Calculate the percentage of any individual unspecified impurity in the portion of Paroxetine Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rU /rS ) × (CS /CU ) × 100
rU = peak response of any individual unspecified impurity from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of paroxetine from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Paroxetine Hydrochloride RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Paroxetine Hydrochloride, on the anhydrous basis, in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: See Table 5.
Table 5
Name | Relative Retention Time | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
Paroxetine related compound B | 0.91 | 0.5 |
Paroxetine related compound F | 0.96 | 0.2 |
Paroxetine | 1.0 | — |
Paroxetine related compound G | 1.34 | 0.2 |
Any unspecified impurity | — | 0.1 |
Total impurities | — | 1.0 |
6 SPECIFIC TESTS
Water Determination 〈921〉, Method I
Anhydrous form: NMT 1.5%
Hemihydrate form: 2.2%–2.8%
7 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve the anhydrous form in tight containers. Preserve the hemihydrate form in well-closed containers. Store at room temperature.
Labeling: Label the article to indicate whether it is the anhydrous form or the hemihydrate form, and label it to indicate with which Organic Impurities test the article complies.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Paroxetine Hydrochloride RS
USP Paroxetine Related Compound B RS
(3S,4R)-3-[(Benzodioxol-5-yloxy)methyl]-4-phenylpiperidine hydrochloride.
C19H21NO3 · HCl 347.84
USP Paroxetine Related Compound C RS
(3R,4S)-3-[(Benzodioxol-5-yloxy)methyl]-4-(4-uorophenyl)piperidine hydrochloride;
Also known as (+)-trans-Paroxetine hydrochloride.
C19H20FNO3 · HCl 365.83
USP Paroxetine Related Compound E RS
4-(4-Fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine hydrochloride.
C12H14FN · HCl 227.71
[Note—Paroxetine related compound E was previous identied as 1-methyl-4-(p-uorophenyl)-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine hydrochloride.] USP Paroxetine Related Compound F RS
(3S,4R)-3-[(Benzodioxol-5-yloxy)methyl]-4-(4-uorophenyl)-1-methylpiperidine.
C20H22FNO3 343.39
USP Paroxetine Related Compound G RS
(3SR,4RS)-3-[(Benzodioxol-5-yloxy)methyl]-4-(4′-uorobiphenyl-4-yl)piperidine hydrochloride;
Also known as(±)trans-3-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yloxy)methyl]-4-(4′′-uorophenyl-4′-phenyl)piperidine hydrochloride.
C25H24FNO3 · HCl 441.93
USP Paroxetine System Suitability Mixture A RS
Contains a mixture of the following three compounds:
Paroxetine hydrochloride.
Paroxetine related compound A: (3S,4R)-3-[(Benzodioxol-5-yloxy)methyl]-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)piperidine hydrochloride; Also known as piperidine, 3-[(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yloxy)methyl]-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-, hydrochloride (3S-trans)-.
C20H23NO4 ∙HCl 377.86
Paroxetine related compound B: (3S,4R)-3-[(Benzodioxol-5-yloxy)methyl]-4-phenylpiperidine hydrochloride;
Also known as piperidine, 3-[(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yloxy)methyl]-4-phenyl-,hydrochloride (3S-trans)-.
C19H21NO3∙HCl 347.84


