Parachlorophenol
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
The omission of this monograph has been postponed. As of November 1, 2020 this monograph remains official USP text. (RB 1-Nov-2020)
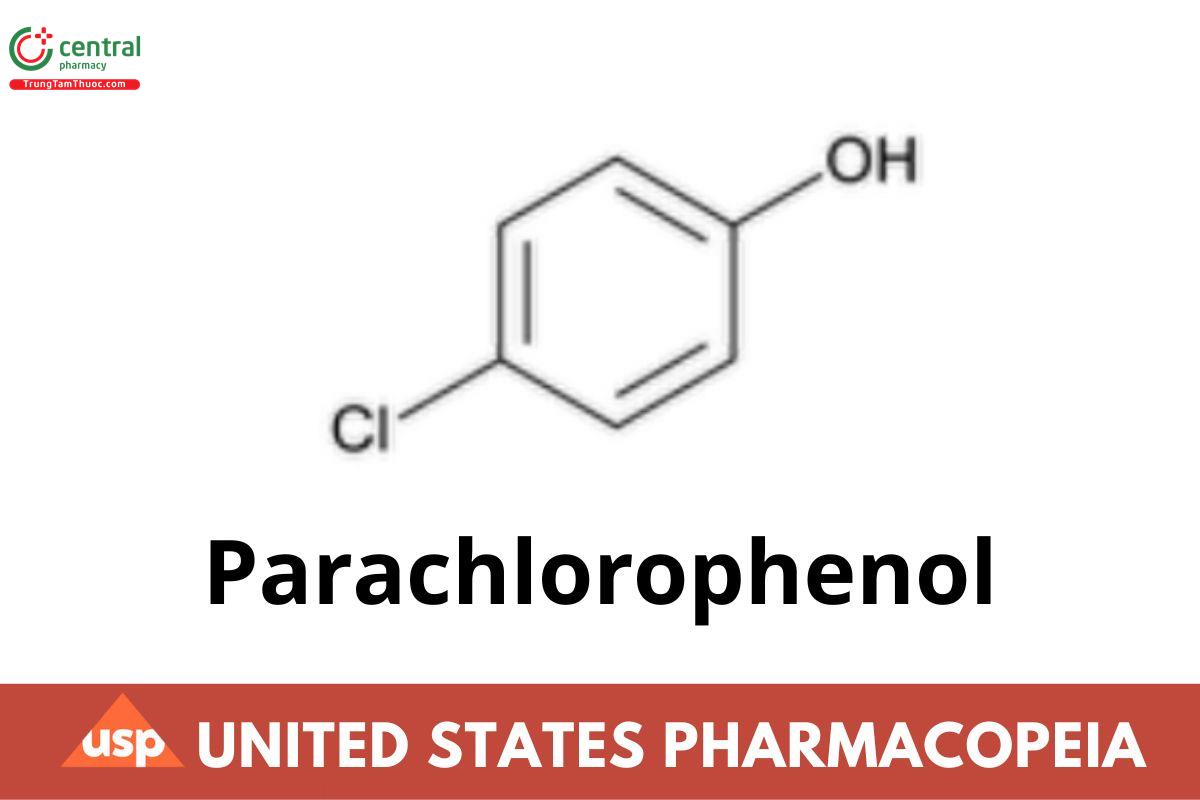
C6H5ClO 128.56
Phenol, 4-chloro-;
p-Chlorophenol CAS RN®: 106-48-9; UNII: 3DLC36A01X.
1 DEFINITION
Parachlorophenol contains NLT 99.0% and NMT 100.5% of parachlorophenol (C6H5ClO).
2 IDENTIFICATION
A.
Sample solution: 10 mg/mL of Parachlorophenol
Analysis: Add bromine TS dropwise to the Sample solution.
Acceptance criteria: A white precipitate is formed; at first it redissolves, but then it becomes permanent as an excess of the reagent is added.
B.
Sample solution: 10 mg/mL of Parachlorophenol
Analysis: Add 1 drop of ferric chloride TS to 10 mL of Sample solution.
Acceptance criteria: The solution acquires a violet-blue color.
C.
Analysis: Heat a few crystals, held on a copper wire, in the edge of a nonluminous ame.
Acceptance criteria: A green color is imparted to the flame.
D.
Sample: 1 g of Parachlorophenol
Analysis: Mix the Sample and 5 mL of sodium hydroxide solution (1 in 3), then add 1.5 g of monochloroacetic acid. Shake, and heat on a steam bath for 1 h. Cool, dilute with 15 mL of water, and acidify with hydrochloric acid. Extract with 50 mL of ether, wash the ether solution with 10 mL of cold water, then extract the ether solution with 25 mL of sodium carbonate solution (1 in 20). Acidify the solution with hydrochloric acid, collect the resulting precipitate on a filter, and recrystallize it from hot water.
Acceptance criteria: The resulting parachlorophenoxyacetic acid melts between 154° and 158°.
3 ASSAY
Procedure
Sample: 1 g of Parachlorophenol
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry 〈541〉.)
Mode: Residual titration
Titrant: 0.1 N bromine VS
Back-titrant: 0.1 N sodium thiosulfate VS
Endpoint detection: Visual
Analysis: Transfer the Sample to a 500-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve and dilute with water to volume. Transfer a 25.0-mL portion of the solution to an iodine flask, cool in an ice bath to 4°, and add 20.0 mL of Titrant. Add 5 mL of hydrochloric acid, and immediately insert the stopper. Maintain the flask at a temperature of 4° for 30 min, shaking at frequent intervals. Allow it to stand for 15 min, remove the stopper just sufficiently to introduce quickly 5 mL of potassium iodide solution (1 in 5), taking care that no bromine vapor escapes, and at once insert the stopper in the flask. Shake thoroughly, remove the stopper, and rinse it and the neck of the flask with a small portion of water, allowing the washings to flow into the flask. Shake the mixture, and titrate the liberated iodine with Back-titrant, using 3 mL of starch TS as the indicator. Perform a blank determination. Each mL of 0.1 N bromine is equivalent to 3.214 mg of parachlorophenol (C6H5ClO).
Acceptance criteria: 99.0%–100.5%
4 IMPURITIES
4.1 Limit of Nonvolatile Residue
Sample: 1 g of Parachlorophenol
Analysis: Heat the Sample in a tared container on a steam bath until it is volatilized, and dry at 105° for 1 h.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.1% of residue remains.
4.2 Limit of Chloride
Sample solution: 10 mg/mL of Parachlorophenol
Analysis: Acidify 10 mL of Sample solution with 2 N nitric acid, and add a few drops of silver nitrate TS.
Acceptance criteria: No turbidity or opalescence is produced.
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
Clarity and Reaction of Solution
Sample solution: 10 mg/mL of Parachlorophenol
Acceptance criteria: Solution is clear and is acid to litmus.
Congealing Temperature 〈651〉: Between 42° and 44°
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in tight, light-resistant


