Moexipril Hydrochloride
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
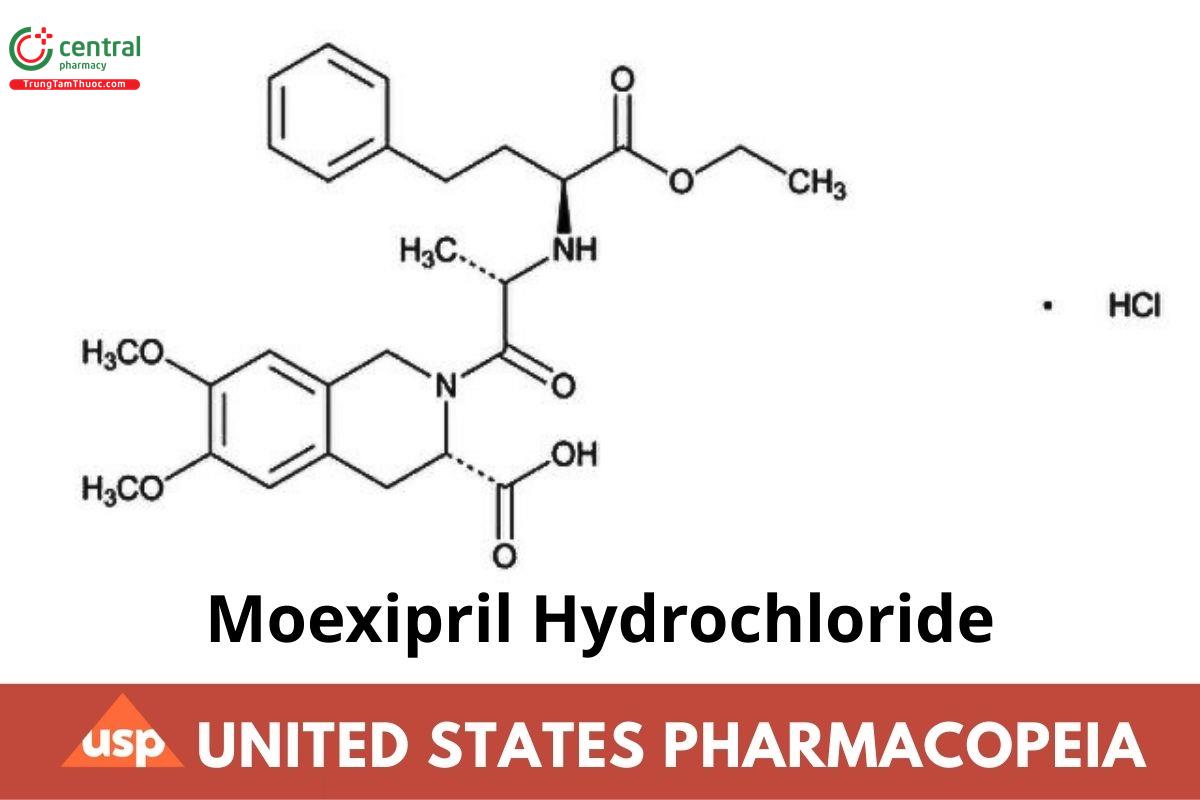
C₂₇H₃₄N₂O₇ · HCl 535.03
3-Isoquinolinecarboxylic acid, 2-[2-[[1-(ethoxycarbonyl)-3-phenylpropyl]amino]-1-oxopropyl]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6,7-dimethoxy-, monohydrochloride, [3S-[2[R*(R*)],3R*]]-;
(3S)-2-[(2S)-N-[(1S)-1-Carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]alanyl]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6,7-dimethoxy-3-isoquinolinecarboxylic acid, 2-ethyl ester, monohydrochloride CAS RN®: 82586-52-5 UNII: Q1UMG3UH45
1 DEFINITION
Moexipril Hydrochloride contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of moexipril hydrochloride (C₂₇H₃₄N₂O₇ · HCl), calculated on the anhydrous basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
Change to read:
A. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197K
B. The relative retention time of the major peak of the Sample solution corresponds to that of the Standard solution, as obtained in the Assay.
C. Identification Tests-General 〈191〉, Chloride: Meets the requirements
3 ASSAY
3.1 Procedure
Buffer: 1.32 g/L of dibasic ammonium phosphate. Adjust with diluted phosphoric acid to a pH of 7.5.
Solution A: Acetonitrile and tetrahydrofuran (95:5)
Mobile phase: Solution A and Buffer (30:70)
Standard solution: 0.1 mg/mL of USP Moexipril Hydrochloride RS in Mobile phase. [Note-Sonication may be necessary for complete dissolution.]
Sample solution: 0.1 mg/mL of Moexipril Hydrochloride in Mobile phase. [Note-Sonication may be necessary for complete dissolution.]
Chromatographic system
- (See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
- Mode: LC
- Detector: UV 215 nm
- Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L1
- Column temperature: 35°
- Flow rate: 1 mL/min
- Injection volume: 10 µL
- Run time: NLT 3.2 times the retention time of moexipril
System suitability
- Sample: Standard solution
- Suitability requirements
- Relative standard deviation: NMT 2.0%
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of moexipril hydrochloride (C₂₇H₃₄N₂O₇ · HCl) in the portion of Moexipril Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rᵤ/rₛ) × (Cₛ/Cᵤ) × 100
rᵤ = peak response from the Sample solution
rₛ = peak response from the Standard solution
Cₛ = concentration of USP Moexipril Hydrochloride RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
Cᵤ = concentration of Moexipril Hydrochloride in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: 98.0%–102.0% on the anhydrous basis
4 IMPURITIES
4.1 Residue on Ignition 〈281〉: NMT 0.20%
4.2 Organic Impurities
[Note-Use freshly prepared samples for analysis.]
Solution A and Chromatographic system: Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Solution B: Proceed as directed for the Buffer in the Assay.
Diluent: Solution A and Solution B (20:80)
Mobile phase: See Table 1.
Table 1
| Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) |
| 0 | 20 | 80 |
| 5 | 20 | 80 |
| 35 | 55 | 45 |
| 65 | 55 | 45 |
| 70 | 20 | 80 |
| 80 | 20 | 80 |
Standard solution 1: 4 µg/mL of USP Moexipril Hydrochloride RS in Diluent. [Note-Sonication may be necessary for complete dissolution.]
Standard solution 2: 2 mg/mL of USP Moexipril Hydrochloride RS and 3 µg/mL each of USP Moexipril Related Compound A RS, USP Moexipril Related Compound B RS, USP Moexipril Related Compound C RS, USP Moexipril Related Compound D RS, USP Moexipril Related Compound E RS, USP Moexipril Related Compound F RS, and USP Moexipril Related Compound G RS in Diluent. [Note-Sonication may be necessary for complete dissolution.]
Sample solution: 2 mg/mL of Moexipril Hydrochloride in Diluent. [Note-Sonication may be necessary for complete dissolution.]
System suitability
Samples: Standard solution 1 and Standard solution 2
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 3.5 between moexipril related compound A and moexipril related compound E; NLT 2.5 between moexipril and moexipril related compound G, Standard solution 2
Relative standard deviation: NMT 5.0% for moexipril, Standard solution 1
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution 1, Standard solution 2, and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each specified impurity in the portion of Moexipril Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rᵤ/rₛ) × (Cₛ/Cᵤ) × 100
rᵤ = peak response of each specified impurity from the Sample solution
rₛ = peak response of the corresponding Reference Standard from Standard solution 2
Cₛ = concentration of each specified impurity in Standard solution 2 (mg/mL)
Cᵤ = concentration of Moexipril Hydrochloride in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Calculate the percentage of any other individual unspecified impurity in the portion of Moexipril Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rᵤ/rₛ) × (Cₛ/Cᵤ) × 100
rᵤ = peak response of each individual unspecified impurity from the Sample solution
rₛ = peak response of moexipril from Standard solution 1
Cₛ = concentration of USP Moexipril Hydrochloride RS in Standard solution 1 (mg/mL)
Cᵤ = concentration of Moexipril Hydrochloride in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: See Table 2. Disregard peaks less than 0.05%.
Table 2
| Name | Relative Retention Time | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
| Moexipril related compound Eᵃ | 0.14 | 0.15 |
| Moexipril related compound Aᵇ | 0.28 | 0.20 |
| Moexipril related compound Fᶜ | 0.62 | 0.15 |
| Moexipril related compound Gᵈ | 0.90 | 0.15 |
| Moexipril | 1.00 | - |
| Moexipril related compound Dᵉ | 1.28 | 0.15 |
| Moexipril related compound Bᶠ | 1.62 | 0.20 |
| Moexipril related compound Cᵍ | 2.26 | 0.15 |
| Any other individual unspecified impurity | - | 0.10 |
| Total impuritiesʰ | - | 1.0 |
ᵃ (S)-6,7-Dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid.
ᵇ (3S)-2-{(2S)-N-[(1S)-1-Carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]alanyl}-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6,7-dimethoxy-3-isoquinolinecarboxylic acid.
ᶜ (S)-2-[(S)-1-Ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-ylamino]propanoic acid.
ᵈ (S)-6,7-Dimethoxy-2-{(S)-2-[(S)-1-methoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-ylamino]propanoyl}-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid.
ᵉ (S)-2-{(S)-2-[(S)-4-Cyclohexyl-1-ethoxy-1-oxobutan-2-ylamino]propanoyl}-6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid.
ᶠ (S)-Ethyl 2-{(3S,11aS)-8,9-dimethoxy-3-methyl-1,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-1H-pyrazino[1,2-b]isoquinolin-2(6H,11H,11aH)-yl}-4-phenylbutanoate.
ᵍ (S)-tert-Butyl 2-{(S)-2-[(S)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-ylamino]propanoyl}-6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylate.
ʰ Sum of all specified and unspecified impurities.
4.3 Content of Imidazole
Mobile phase: Hexane, isopropyl alcohol, and diethyl amine (52:48:0.025)
Standard solution: 0.01 mg/mL of USP Imidazole RS in Mobile phase. [Note-Sonication may be necessary for complete dissolution.]
Sample solution: 2 mg/mL of Moexipril Hydrochloride in Mobile phase. [Note-Sonication may be necessary for complete dissolution. Use freshly prepared Sample solution for analysis.]
Chromatographic system
- (See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
- Mode: LC
- Detector: UV 215 nm
- Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L3
- Flow rate: 1 mL/min
- Injection volume: 20 µL
- Run time: NLT 3.3 times the retention time of imidazole
System suitability
- Sample: Standard solution
- Suitability requirements
- Relative standard deviation: NMT 5.0%
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of imidazole in the portion of Moexipril Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rᵤ/rₛ) × (Cₛ/Cᵤ) × 100
rᵤ = peak response of imidazole from the Sample solution
rₛ = peak response of imidazole from the Standard solution
Cₛ = concentration of USP Imidazole RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
Cᵤ = concentration of Moexipril Hydrochloride in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.03%
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
Water Determination 〈921〉, Method I, Method Ia: NMT 1.5%
Optical Rotation 〈781S〉, Procedures, Specific Rotation
Sample solution: 0.011 g/mL of Moexipril Hydrochloride in alcohol.
Sonicate to dissolve the sample.
Acceptance criteria: +30.0° to +38.0°
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in tight containers, protected from moisture. Store at room temperature.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Imidazole RS
USP Moexipril Hydrochloride RS
USP Moexipril Related Compound A RS
(3S)-2-{(2S)-N-[(1S)-1-Carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]alanyl}-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6,7-dimethoxy-3-isoquinolinecarboxylic acid.
C25H30N2O7 470.51
USP Moexipril Related Compound B RS
(S)-Ethyl 2-{(3S,11aS)-8,9-dimethoxy-3-methyl-1,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-1H-pyrazino[1,2-b]isoquinolin-2(6H,11H,11aH)-yl}-4-phenylbutanoate.
C₂₇H₃₂N₂O₆ 480.55
USP Moexipril Related Compound C RS
(S)-tert-Butyl 2-{(S)-2-[(S)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-ylamino]propanoyl}-6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylate.
C31H42N2O7 554.67
USP Moexipril Related Compound D RS
(S)-2-{(S)-2-[(S)-4-Cyclohexyl-1-ethoxy-1-oxobutan-2-ylamino]propanoyl}-6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid.
C27H40N2O7 504.62
USP Moexipril Related Compound E RS
(S)-6,7-Dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid.
C₁₂H₁₅NO₄ 237.25
USP Moexipril Related Compound F RS
(S)-2-[(S)-1-Ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-ylamino]propanoic acid.
C₁₅H₂₁NO₄ 279.33
USP Moexipril Related Compound G RS
(S)-6,7-Dimethoxy-2-{(S)-2-[(S)-1-methoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-ylamino]propanoyl}-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid.
C₂₆H₃₂N₂O₇ 484.54


