Maltitol
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
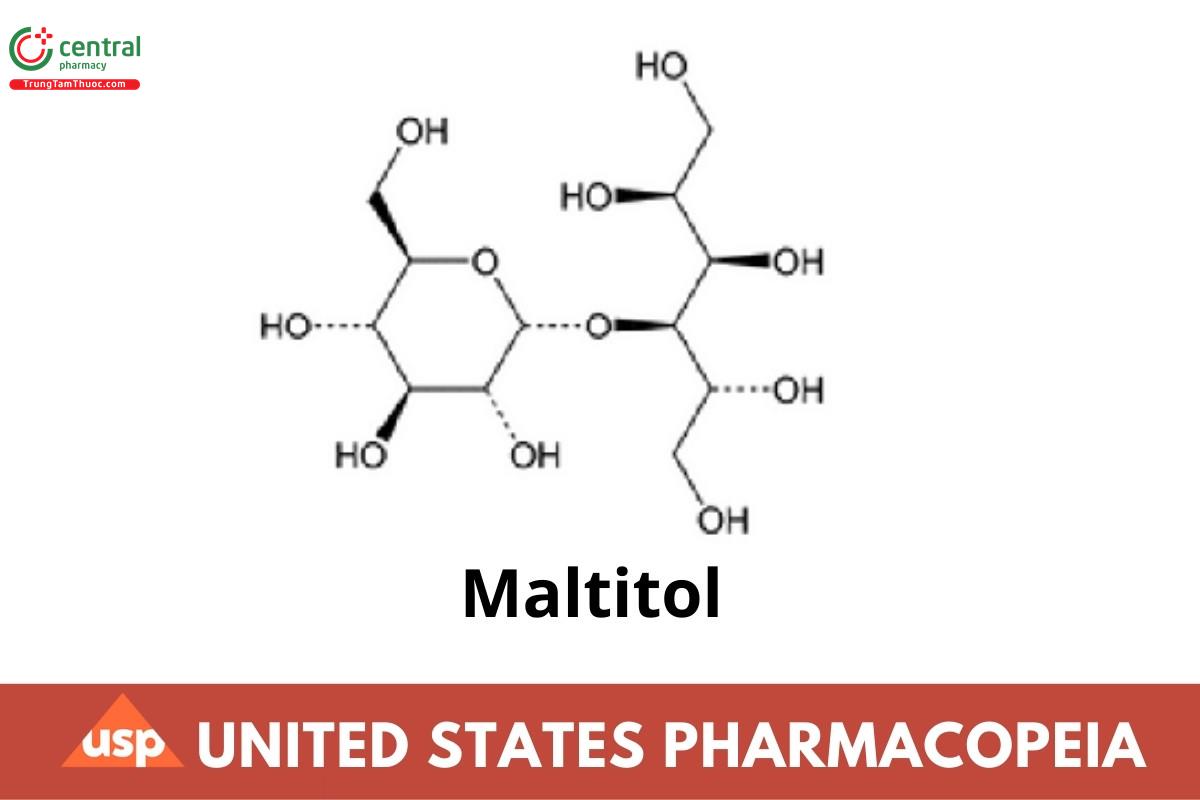
1 DEFINITION
Maltitol contains NLT 92.0% and NMT 100.5% of d-maltitol (C12H24O11), calculated on the anhydrous basis. The amounts of total sugars, other polyhydric alcohols, and any polyol anhydrides, if detected, are not included in the requirements nor in the calculated amount as stated in General Notices, 5.60.10 Other Impurities in USP and NF Articles.
2 IDENTIFICATION
A. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197K
B. The retention time of the major peak of the Sample solution corresponds to that of the Standard solution, as obtained in the Assay.
3 ASSAY
3.1 Procedure
Mobile phase: Water. [Note—Degas the Mobile phase before use.]
System suitability solution: 4.8 mg/g of USP Maltitol RS and 4.8 mg/g of sorbitol
Standard solution: 10 mg/g of USP Maltitol RS and 1.6 mg/g of sorbitol
Sample solution: Dissolve 0.20 g of Maltitol in water and dilute with water to 20 g. Record the nal solution weight, and mix thoroughly. The solution is 10 mg/g of Maltitol.
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: Refractive index
Column: 7.8-mm × 10-cm; packing L34
Temperatures
Column: 60 ± 2°
Detector: 35°
Flow rate: 0.5 mL/min
Injection volume: 10 µL
System suitability
Samples: System suitability solution and Standard solution
[Note—The relative retention times for maltitol and Sorbitol are 0.48 and 1.0, respectively.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 2.0 between maltitol and sorbitol, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation: NMT 2.0%, Standard solution
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of d-maltitol (C12H24O11) in the portion of Maltitol taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × [100/(100 − W)] × 100
rU = peak response of maltitol from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of maltitol from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Maltitol RS in the Standard solution (mg/g)
CU = concentration of Maltitol in the Sample solution (mg/g)
W = percentage obtained in the test for Water Determination (%)
Acceptance criteria: 92.0%–100.5% on the anhydrous basis
4 IMPURITIES
Change to read:
4.1 Limit of Nickel
[Note—When water is specied as the diluent, use deionized ultra-ltered water. Use of glass volumetric asks is discouraged.] Digest solution: Add 360 mL of hydrochloric acid, ultratrace, and 240 mL of nitric acid, ultratrace, to 1200 mL of water.
Blank solution: Add 40 mL of nitric acid, ultratrace, to a 2000-mL volumetric ask, dilute with water to volume, and mix well.
Internal standard solution: Transfer 2.0 mL of solution containing 1000 mg/L of yttrium1 to a 1000-mL volumetric ask, dilute with Blank solution to volume, and mix well. The Internal standard solution contains 2 µg/mL of yttrium. [Note—The concentration of the Internal standard solution can be adjusted if a high number of signal counts from the Internal standard solution causes an artifact.]
Standard stock solution: [Note—Prepare this solution fresh every 2 months.] Quantitatively dilute an accurately measured volume of the solution containing 1000 mg/L of nickel with Blank solution to obtain a solution containing 10 µg/mL of nickel.
Standard nickel solution A: [Note—Prepare this solution fresh weekly.] Pipet 1.0 mL of Standard stock solution into a 200-mL volumetric ask. Dilute the content in the ask with Blank solution to volume, and mix well. This solution contains 50 ng/mL of nickel.
Standard nickel solution B: [Note—Prepare this solution fresh weekly.] Pipet 2.0 mL of Standard stock solution into a 200-mL volumetric ask. Dilute the content in the ask with Blank solution to volume, and mix well. This solution contains 100 ng/mL of nickel.
Standard nickel solution C: [Note—Prepare this solution fresh weekly.] Pipet 4.0 mL of Standard stock solution into a 200-mL volumetric ask. Dilute the content in the ask with Blank solution to volume, and mix well. This solution contains 200 ng/mL of nickel.
Sample solution: Transfer 10.0 g of Maltitol into a 125-mL conical ask. Add 40 mL of Digest solution, and place on a hot plate. Heat the solution for about 20 min, being careful to prevent the solution from boiling over. Pull the sample off of the hot plate just before it turns a dark caramel color. [Note—Do not overburn the sample.] Transfer the ask's contents into a clean, dry, 50-mL volumetric ask with washings of Blank solution. Dilute with Blank solution to volume. Filter the sample into a 15-mL centrifuge tube, using a 10-mL disposable syringe tted with a syringe lter of 0.45-µm pore size.
Instrumental conditions
(See Plasma Spectrochemistry 〈730〉.)
Mode: ICP–OES
Emission wavelengths: 232.005 nm for nickel and 371.029 nm for yttrium. Set the sample read time and other instrument parameters as appropriate or as recommended by the instrument manufacturer.
System suitability
Samples: Blank solution, Standard nickel solution A, Standard nickel solution B, and Standard nickel solution C
Suitability requirements
[Note—Instrument performance must be veried to conform to the manufacturer’s specications for resolution and sensitivity. Before analyzing samples, the instrument must pass a suitable performance check.]
Correlation coecient: NLT 0.999, determined from the Calibration curve constructed in the Analysis
Analysis
Samples: Blank solution, Standard nickel solution A, Standard nickel solution B, Standard nickel solution C, and Sample solution [Note—The following analysis is described for one type of ICP–OES instruments. If a different ICP–OES instrument is used, follow the instrument manufacturer's recommendations for operation.]
Take 3 replicate scans with the integration set as recommended by the instrument manufacturer. Follow the instrument manufacturer's recommendations for delivering the sample. Add the Internal standard solution in-line via a mixing block between the sample probe and the spray chamber. Flush the samples through the system before analysis. Program a read delay into the sampling routine to allow for fluid ow equilibration after the high-speed ush and before the rst analytical read of the sample. Between samples, wash the pumping system by ushing the Blank solution.
Calibration curve: Generate the calibration curve using the Blank solution, Standard nickel solution A, Standard nickel solution B, and Standard nickel solution C as follows. Scan the Internal standard solution while running the Blank solution to measure the intensity of the yttrium emission. Hold this value constant throughout the remainder of the test. Separately scan the Blank solution, Standard nickel solution A, Standard nickel solution B, and Standard nickel solution C for nickel and yttrium. [Note—Add the Internal standard solution via an in-line mixing chamber.] Normalize the yttrium intensity to the value of the Internal standard solution. Apply this normalization factor to the nickel intensity, which is then referred to as the corrected nickel intensity. Construct a calibration curve by plotting the corrected nickel intensity versus the known concentrations, in ng/mL, of nickel.
Similarly, analyze the Sample solution. Plot the intensity of the emission of the Sample solution on the calibration curve. Determine the concentration of nickel (C), in ng/mL, in the Sample solution through the calibration curve.
Calculate the content, in µg/g, of nickel in the portion of Maltitol taken:
Result = (F × V × C)/W
F = conversion factor, 10−3 µg/ng (ng to µg)
V = volume of the Sample solution, 50 mL
C = concentration of nickel in the Sample solution (ng/mL)
W = weight of Maltitol (g)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 1 µg/g (NF 1-May-2021)
4.2 Reducing Sugars
[Note—The amount determined in this test is not included in the calculated amount as required in General Notices, 5.60.10 Other Impurities in USP and NF Articles.]
Sample: 3.3 g
Titrimetric system
Mode: Residual titration
Titrant: 0.05 N sodium thiosulfate VS
Endpoint detection: Visual
Analysis: Dissolve the Sample in 3 mL of water with the aid of gentle heat. Cool and add 20.0 mL of cupric citrate TS and a few glass beads. Heat so that boiling begins after 4 min, and maintain boiling for 3 min. Cool rapidly and add 40 mL of diluted acetic acid, 60 mL of water, and 20.0 mL of 0.05 N iodine VS. With continuous shaking, add 25 mL of solution of hydrochloric acid in water (6:94). When the precipitate has dissolved, titrate the excess of iodine with Titrant using 2 mL of starch TS, added toward the end of the titration, as an indicator. Acceptance criteria: NLT 12.8 mL of Titrant is required, corresponding to NMT 0.3% of reducing sugars, as Glucose.
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
5.1 Microbial Enumeration Tests 〈61〉 and Tests for Specified Microorganisms 〈62〉:
The total aerobic microbial count using the Plate Method does not exceed 103 cfu/g, and the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 102 cfu/g.
5.2 Conductivity
Sample solution: 200 mg/mL
Analysis: Using an appropriate conductivity meter, choose a conductivity cell that is appropriate for the properties and conductivity of the solution to be examined. Use a certied reference material, for example a solution of potassium chloride, that is appropriate for the measurement.
The conductivity value of the certied reference material should be near the expected conductivity value of the solution to be examined. After calibrating the apparatus with a certied reference material solution, rinse the conductivity cell several times with water and at least twice with the aqueous solution to be examined. Measure the conductivity of the Sample solution at a temperature of 20°, while gently stirring with a magnetic stirrer.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 20 µS/cm
5.3 Water Determination 〈921〉, Method I: NMT 1.0%
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
6.1 Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in well-closed containers. No storage requirements are specied.
6.2 USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Maltitol RS


