Loratadine
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
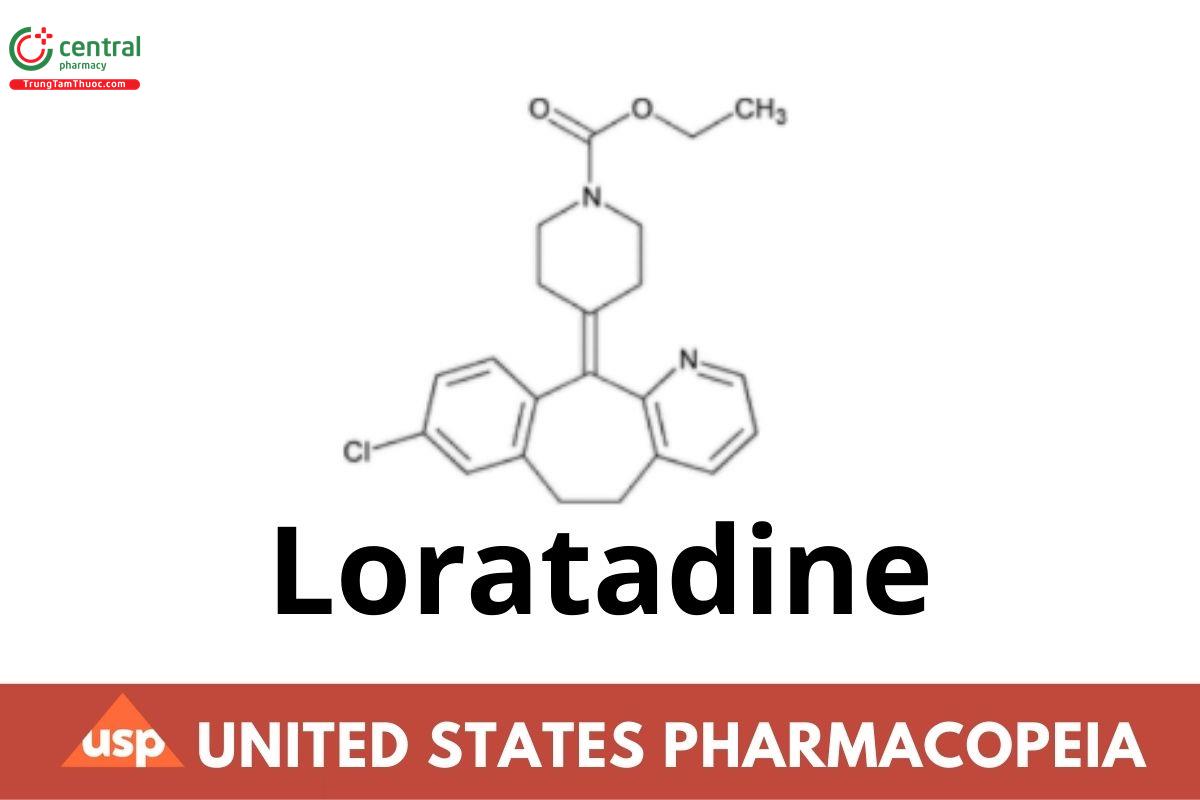
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
DOWNLOAD PDF HERE
1 DEFINITION
Loratadine contains NLT 98.5% and NMT 101.0% of loratadine (C22H23ClN2O2), calculated on the dried basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
Change to read:
A. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197M (CN 1-May-2020)
B. The retention time of the major peak of the Sample solution corresponds to that of the Standard solution, as obtained in the Assay.
3 ASSAY
Procedure
Buffer A (0.01 M dibasic potassium phosphate): 1.74 g/L of anhydrous dibasic potassium phosphate in water
Buffer B (0.6 M dibasic potassium phosphate): 105 g/L of anhydrous dibasic potassium phosphate in water 0.05 N hydrochloric acid: Transfer 500 mL of water to a 1000-mL volumetric flask, add 83 mL of hydrochloric acid, and dilute with water to volume. Transfer 50 mL of this solution into a 1000-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Mobile phase: Acetonitrile, methanol, and Buffer A (60:60:70). Adjust with 10% phosphoric acid to an apparent pH of 7.2.
Diluent: Transfer 400 mL of 0.05 N hydrochloric acid and 80 mL of Buffer B to a 1-L volumetric flask. Dilute with a mixture of acetonitrile and methanol (1:1) to volume.
Standard solution: 0.4 mg/mL of USP Loratadine RS in Diluent
Sample solution: 0.4 mg/mL of Loratadine in Diluent
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 254 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 15-cm; 5-μm packing L7
Column temperature: 25°–35°
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Injection volume: 15 μL
System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation: NMT 2.0%
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of loratadine (C22H23ClN2O2) in the portion of Loratadine taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
rU = peak response from the Sample solution
rS = peak response from the Standard solution
CS= concentration of USP Loratadine RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: 98.5%–101.0% on the dried basis
4 IMPURITIES
Residue on Ignition 〈281〉: NMT 0.1%
Organic Impurities, Procedure 1
[Note—On the basis of the synthetic route, perform either Procedure 1 or Procedure 2. Procedure 2 is recommended if 4,8-dichloro-5,6-dihydro-11H-benzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridin-11-one is a potential related compound.]
Mobile phase and Diluent: Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Standard solution: 0.8 μg/mL of USP Loratadine RS in Diluent
Sample solution: 0.4 mg/mL of Loratadine in Diluent
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 254 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 15-cm; 5-μm packing L7
Column temperature: 25°–35°
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Injection volume: 50 μL
System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation: NMT 4.0%
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Loratadine taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × (1/F) × 100
rU = peak area of each impurity from the Sample solution
rS = peak area of loratadine from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Loratadine RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Loratadine in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
F = relative response factor as listed in Table 1
Acceptance criteria: See Table 1.
Table 1
| Name | Relative Retention Time | Relative Response Factor | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
| Fluoroloratadinea | 0.79 | 0.25 | 0.2 |
| Loratadine | 1.0 | - | - |
| Any other individual impurity | - | 1.0 | 0.1 |
| Total impurities | - | - | 0.3 |
a Ethyl 4-(8-chloro-11-fluoro-5,6-dihydro-11H-benzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridin-11-yl) piperidin-1-carboxylate.
Organic Impurities, Procedure 2
Solution A: Dissolve 0.96 g of 1-pentanesulfonic acid sodium salt in 900 mL of water. Adjust with phosphoric acid solution (1 in 10) to a pH of 3.00 ± 0.05, and dilute with water to 1 L.
Solution B: Acetonitrile
Mobile phase: See Table 2.
Table 2
Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) |
| 0 | 75 | 25 |
| 20 | 50 | 50 |
| 30 | 40 | 60 |
| 35 | 30 | 70 |
| 45 | 30 | 70 |
| 50 | 75 | 25 |
Standard stock solution: 0.1 mg/mL each of USP Loratadine RS, USP Loratadine Related Compound A RS, and USP Loratadine Related Compound B RS in methanol
Standard solution: 0.01 mg/mL each of USP Loratadine RS, USP Loratadine Related Compound A RS, and USP Loratadine Related Compound B RS prepared as follows. Transfer 1.0 mL of the Standard stock solution to a 10-mL volumetric flask, add 2 mL of Solution A, and dilute with methanol to volume.
Sample solution: 10 mg/mL of Loratadine prepared as follows. Transfer 100 mg of Loratadine to a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in 2mL of methanol. Add 2 mL of Solution A, and then dilute with methanol to volume.
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 254 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-μm packing L1
Flow rate: 1.2 mL/min
Injection volume: 20 μL
System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 1.5 between loratadine related compound A and loratadine related compound B
Relative standard deviation: NMT 10% for the loratadine peak
Analysis
Sample: Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Loratadine taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × (1/F) × 100
rU = peak area of each individual impurity from the Sample solution
rS = peak area of loratadine from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Loratadine RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Loratadine in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
F = relative response factor as listed in Table 3
Acceptance criteria: See Table 3.
Table 3
| Name | Relative Retention Time | Relative Response Factor | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
| Loratadine related compound A | 0.50 | 1.00 | 0.1 |
| Loratadine related compound B | 0.53 | 0.89 | 0.1 |
Loratadine related compound Ca | 0.70 | 0.60 | 0.1 |
Hydroxy deacyl analogb | 0.75 | 0.46 | 0.1 |
| Loratadine | 1.00 | - | - |
Dichlorobenzocycloheptapyridi nonec | 1.23 | 0.92 | 0.1 |
| Hydroxyloratadined | 1.60 | 0.42 | 0.1 |
| 4-Chloroloratadinee | 1.83 | 1.08 | 0.1 |
Any individual unknown impurity | - | 1.0 | 0.10 |
| Total impurities | - | - | 0.3 |
a 8-Chloro-5,6-dihydro-11H-benzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridin-11-one.
b 8-Chloro-5,6-dihydro-11-hydroxy-11-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)-11H-benzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridine.
c 4,8-Dichloro-5,6-dihydro-11H-benzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridin-11-one.
d Ethyl 4-(8-chloro-11-hydroxy-5,6-dihydro-11H-benzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridin-11-yl) piperidin-1-carboxylate.
e Ethyl 4-(4,8-dichloro-5,6-dihydro-11H-benzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridin-11-ylidene)piperidin-1-carboxylate.
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
Loss on Drying 〈731〉
Analysis: Dry a sample at 100° to constant weight.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.5%
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in well-closed containers, and store between 2° and 30°.
Labeling: If a test for Organic Impurities other than Procedure 1 is used, then the labeling states with which Organic Impurities test the article complies.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Loratadine RS
USP Loratadine Related Compound A RS
8-Chloro-5,6-dihydro-11-(piperidin-4-ylidene)-11H-benzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridine.
C19H19ClN2 310.82
USP Loratadine Related Compound B RS
8-Chloro-5,6-dihydro-11-(N-methylpiperidin-4-ylidene)-11H-benzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridine.
C20H21ClN2 324.85


