Levocarnitine
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
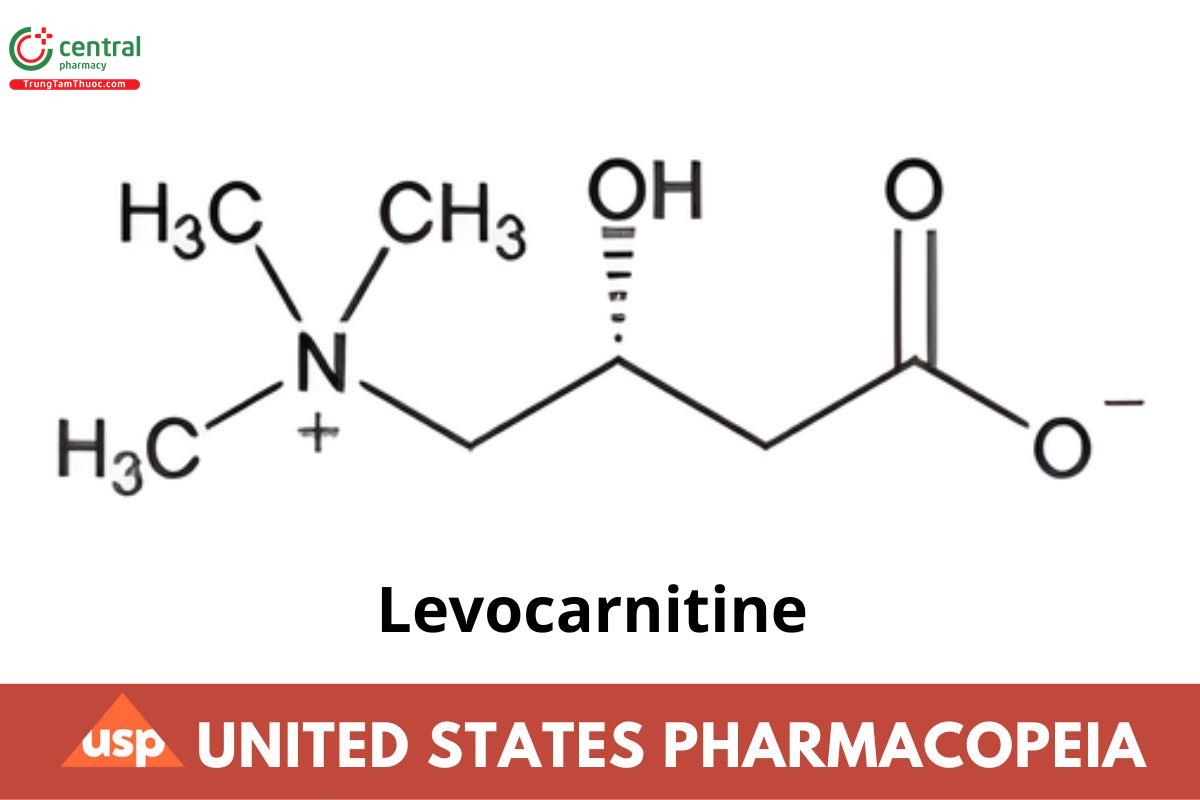
C7H15NO3 161.20
(R)-3-Carboxy-2-hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethyl-1-propanaminium, inner salt;
(R)-(3-Carboxy-2-hydroxypropyl)trimethylammonium, inner salt CAS RN®: 541-15-1; UNII: 0G389FZZ9M.
1 DEFINITION
Levocarnitine contains NLT 97.0% and NMT 103.0% of levocarnitine (C7H15NO3 ), calculated on the anhydrous basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
A. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197K
Analysis: Dry the sample and USP Levocarnitine RS under vacuum at 50° for 5 h.
Acceptance criteria: Meets the requirements
B. The retention time of the major peak of the derivatized Sample solution corresponds to that of the levocarnitine peak of the derivatized System suitability solution, as obtained in the test for Enantiomeric Purity.
3 ASSAY
Procedure
Sample: 100 mg of Levocarnitine
Blank: Mix 3 mL of formic acid with 50 mL of glacial acetic acid.
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry 〈541〉.)
Mode: Direct titration
Titrant: 0.1 N perchloric acid VS
Endpoint detection: Visual
Analysis: Dissolve the Sample in a mixture of 3 mL of formic acid and 50 mL of glacial acetic acid. Add 2 drops of crystal violet TS, and titrate with the Titrant to an emerald green endpoint. Perform the blank determination.
Calculate the percentage of levocarnitine (C7H15NO3 ) in the portion of Levocarnitine taken:
Result = {[(VS − VB ) × NA × F]/W} × 100
VS = Titrant volume consumed by the Sample (mL)
VB = Titrant volume consumed by the Blank (mL)
NA = actual normality of the Titrant (mEq/mL)
F = equivalency factor, 161.2 mg/mEq
W = Sample weight (mg)
Acceptance criteria: 97.0%–103.0% on the anhydrous basis
4 IMPURITIES
Residue on Ignition 〈281〉: NMT 0.5%
Chloride and Sulfate 〈221〉, Chloride
Standard solution: 0.50 mL of 0.020 N hydrochloric acid
Sample: 0.090 g of Levocarnitine
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.4%
Enantiomeric Purity
Buffer solution: Mix thoroughly 2000 mL of water with 5 mL of phosphoric acid, and add accurately 13.6 mL of triethylamine dropwise while stirring.
Solution A: Mix 1500 mL of Buffer solution and 500 mL of acetonitrile. Adjust the solution with phosphoric acid to a pH of 2.6.
Solution B: Acetonitrile
Carbonate buffer solution: Transfer 338 mg of sodium carbonate and 152 mg of sodium bicarbonate to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in and dilute with water to volume.
Sodium hydroxide solution: 30% solution of sodium hydroxide in water
Acetate buffer solution: Transfer 0.3 mL of glacial acetic acid to a 100-mL volumetric flask, add 90 mL of water to dissolve, adjust with Sodium hydroxide solution to a pH of 4.2, and dilute with water to volume.
Derivatization reagent: (+)-1-(9-Fluorenyl)ethyl chloroformate solution ((+)-FLEC)
System suitability solution: 1.25 mg/mL of USP Levocarnitine RS in water
Sample solution: 1.25 mg/mL of Levocarnitine in water
Blank: Water
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: Fluorescence
Excitation wavelength: 260 nm
Emission wavelength: 315 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 7.5-cm; 2.7-μm packing L1
Column temperature: 30°
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min
Injection volume: 20.0 μL
Mobile phase: See Table 1.
Table 1
| Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 100 | 0 |
| 7.4 | 100 | 0 |
| 7.5 | 2 | 98 |
| 9.1 | 2 | 98 |
| 9.3 | 100 | 0 |
| 11.0 | 100 | 0 |
After each sequence of samples, rinse the column with water for 10 min and then with acetonitrile and water (98:2) for another 10 min.
System suitability
Sample: Derivatized System suitability solution. Prepare as directed in Analysis.
[Note—The relative retention times for the (+)-FLEC derivatives of d-carnitine and L-Carnitine are about 0.87 and 1.0, respectively.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 2.0 between (+)-FLEC derivatives of d-carnitine and l-carnitine
Analysis
Samples: System suitability solution, Sample solution, and Blank
Transfer 30.0 μL of the Blank, System suitability solution, and Sample solution to separate 10-mL test tubes. Add 30 μL of Carbonate buffer solution and 80 μL of Derivatization reagent to each test tube and mix by vortex mixer. Allow the solutions to react for 1 h at 45° over a water bath. Cool the test tubes to room temperature, add 5.0 mL of Acetate buffer solution to each test tube, mix by vortex mixer, and transfer to vials for chromatographic analyses.
Separately inject and analyze equal volumes of derivatized Blank, derivatized System suitability solution, and derivatized Sample solution.
Identify the two diastereomer peaks due to (+)-FLEC derivatives of d-carnitine and l-carnitine from the derivatized System suitability solution and derivatized Sample solution. Depending on the enantiomeric purity of the Derivatization reagent, these two peaks may contain co-eluting enantiomers of (−)-FLEC derivatives with d- and l-carnitines, which are accounted in the percentage calculations below. There should be no peaks observed at the retention times of d- and l-carnitine derivatives from the derivatized Blank.
Calculate the percentage of l-carnitine derivative (R ) from the derivatized Sample solution:
Result = rL /(rL + r D) × 100
rL = peak response of the l-carnitine derivative from the derivatized Sample solution
rD = peak response of the d-carnitine derivative from the derivatized Sample solution
Calculate the corrected percentage of l-carnitine (C7H15NO3 ) (C ) in the portion of Levocarnitine taken:
Result = (RL − PB )/(PA − PB ) × 100
RL = percentage of l-carnitine derivative, calculated previously
PA = percentage of (−)-FLEC as determined for (+)-1-(9-Fluorenyl)ethyl chloroformate solution
PB = percentage of (+)-FLEC as determined for (+)-1-(9-Fluorenyl)ethyl chloroformate solution
Calculate the corrected percentage of d-carnitine in the portion of Levocarnitine taken:
Result = 100 − CL
CL = corrected percentage of l-carnitine, calculated previously
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.2% of d-carnitine
Limit of Potassium
[Note—The Standard solution and the Sample solutions may be modified, if necessary, to obtain solutions of suitable concentrations adaptable to the linear or working range of the instrument.]
Standard solution: 31.25 μg/mL of potassium in water, prepared from potassium chloride previously dried at 105° for 2 h
Sample stock solution: 0.625 mg/mL of Levocarnitine in water
Sample solution A: Transfer 20.0 mL of the Sample stock solution to a 25-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. This solution contains 500 μg/mL of Levocarnitine and 0 μg/mL of added potassium from the Standard solution.
Sample solution B: Transfer 20.0 mL of the Sample stock solution to a 25-mL volumetric flask, add 2.0 mL of the Standard solution, and dilute with water to volume. This solution contains 500 μg/mL of Levocarnitine and 2.5 μg/mL of added potassium from the Standard solution.
Sample solution C: Transfer 20.0 mL of the Sample stock solution to a 25-mL volumetric flask, add 4.0 mL of the Standard solution, and dilute with water to volume. This solution contains 500 μg/mL of Levocarnitine and 5.0 μg/mL of added potassium from the Standard solution.
Blank: Water
Instrumental conditions
(See Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy 〈852〉.)
Mode: Atomic absorption spectrophotometry
Analytical wavelength: 766.7 nm
Lamp: Potassium hollow-cathode
Flame: Air–acetylene
Analysis
Samples: Sample solution A, Sample solution B, Sample solution C, and Blank
Determine the absorbances of the solutions against the Blank. Plot the absorbances of the three Sample solutions versus their added potassium concentrations, in μg/mL. Draw the straight line best fitting the three points, and extrapolate the line until it intercepts the concentration axis. From the intercept determine the concentration, in μg/mL, of potassium in Sample solution A.
Calculate the percentage of potassium in the portion of Levocarnitine taken:
Result = (CK /CU) × 100
CK = concentration of potassium in Sample solution A (μg/mL), determined from the intercept of the linear regression line
CU = concentration of Levocarnitine in Sample solution A (μg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.2%
Limit of Sodium
[Note—The Standard solution and the Sample solutions may be modified, if necessary, to obtain solutions of suitable concentrations adaptable to the linear or working range of the instrument.]
Standard solution: 250 μg/mL of sodium in water, prepared from sodium chloride previously dried at 105° for 2 h
Sample stock solution: 40.0 mg/mL of Levocarnitine in water
Sample solution A: Transfer 20.0 mL of the Sample stock solution to a 25-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. This solution contains 32 mg/mL of Levocarnitine and 0 μg/mL of added sodium from the Standard solution.
Sample solution B: Transfer 20.0 mL of the Sample stock solution to a 25-mL volumetric flask, add 2.0 mL of the Standard solution, and dilute with water to volume. This solution contains 32 mg/mL of Levocarnitine and 20 μg/mL of added sodium from the Standard solution.
Sample solution C: Transfer 20.0 mL of the Sample stock solution to a 25-mL volumetric flask, add 4.0 mL of the Standard solution, and dilute with water to volume. This solution contains 32 mg/mL of Levocarnitine and 40 μg/mL of added sodium from the Standard solution.
Blank: Water
Instrumental conditions
(See Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy 〈852〉.)
Mode: Atomic absorption spectrophotometry
Analytical wavelength: 589.0 nm
Lamp: Sodium hollow-cathode
Flame: Air–acetylene
Analysis
Samples: Sample solution A, Sample solution B, Sample solution C, and Blank
Determine the absorbances of the solutions against the Blank. Plot the absorbances of the three Sample solutions versus their added sodium concentrations, in μg/mL. Draw the straight line best fitting the three points, and extrapolate the line until it intercepts the concentration axis. From the intercept determine the concentration, in μg/mL, of sodium in Sample solution A.
Calculate the percentage of sodium in the portion of Levocarnitine taken:
Result = (CNa /CU ) × 100
CNa = concentration of sodium in Sample solution A (μg/mL), determined from the intercept of the linear regression line
CU = concentration of Levocarnitine in Sample solution A (μg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.1%
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
pH 〈791〉
Sample solution: 50 mg/mL
Acceptance criteria: 5.5–9.5
Change to read:
Water Determination 〈921〉, Method I, Method Ia (USP 1-Dec-2021) : NMT 4.0%
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in tight containers at temperatures between −15° and 35°. Protect from light.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Levocarnitine RS


