Iodixanol
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
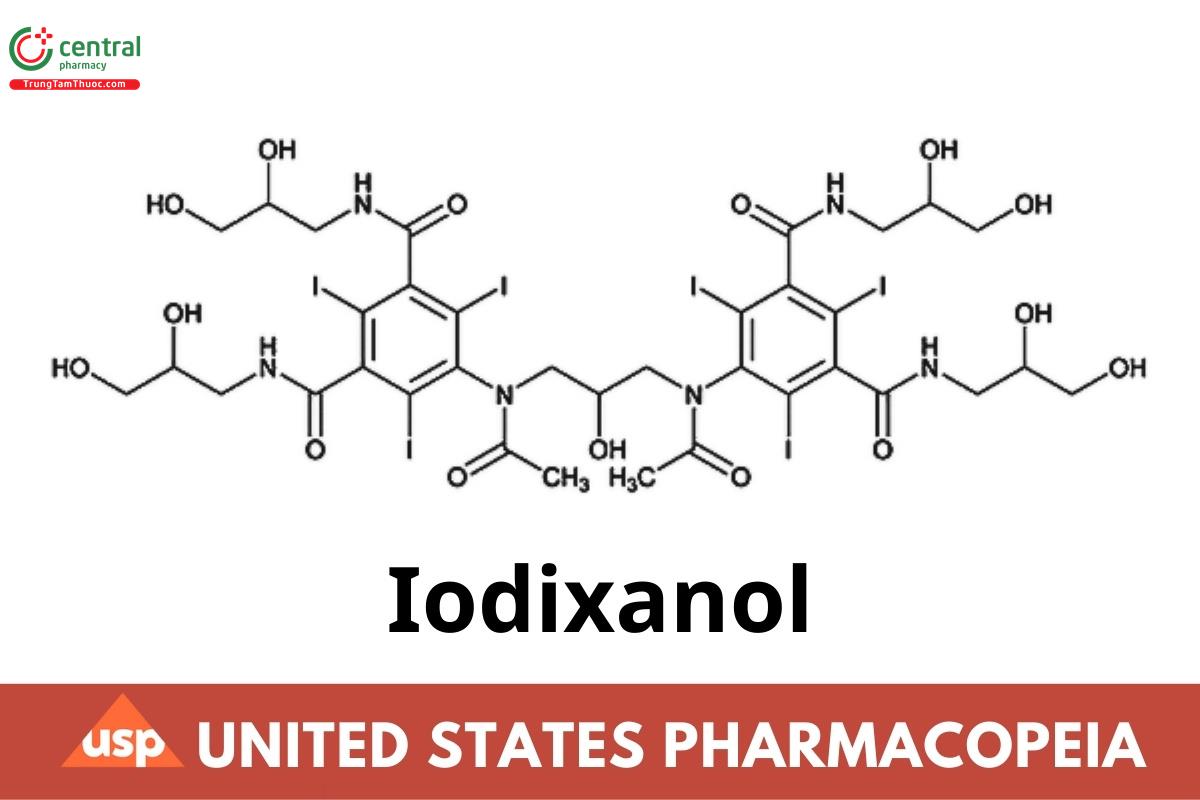
C35H44I6N6O15 1550.18
1,3-Benzenedicarboxamide, 5,5′-[(2-hydroxy-1,3-propanediyl)bis(acetylimino)]bis[N,N′-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-2,4,6-triiodo-;
5,5′-[(2-Hydroxytrimethylene)bis(acetylimino)]bis[N,N′-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-2,4,6-triiodoisophthalamide] CAS RN®: 92339-11-2; UNII: HW8W27HTXX
1 DEFINITION
Iodixanol contains NLT 98.6% and NMT 101.0% of iodixanol (C35H44I6N6O15), calculated on the anhydrous basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
A. SPECTROSCOPIC IDENTIFICATION TESTS 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197K
B. The retention times of the three principal peaks of the Sample solution correspond to those of the Identification solution, as obtained in the test for Limit of Iodixanol Related Compound E and Iodixanol Impurity H. [Note-A third isomer may appear as a minor peak.]
3 ASSAY
3.1 PROCEDURE
Sample solution:
Transfer 500 mg of Iodixanol to a glass-stoppered, 125-mL conical flask. Add 25 mL of 1.25 N sodium hydroxide and 500 mg of powdered zinc. Connect the flask to a reflux condenser, and reflux for 1 h. Cool the flask to room temperature, rinse the condenser with 20 mL of water, disconnect the flask from the condenser, and pass the mixture through a filter. Rinse the flask and the filter thoroughly with small portions of water, adding the rinsings to the filtrate. Add 5 mL of glacial acetic acid.
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry 〈541〉.)
Mode: Direct titration
Titrant: 0.1 N silver nitrate VS
Endpoint detection: Potentiometric
Analysis
Sample: Sample solution
Titrate the Sample solution with the Titrant.
Calculate the percentage of iodixanol (C35H44I6N6O15) in the portion of Iodixanol taken:
Result = [(V × N × F) / W] × 100
V = sample titrant volume (mL)
N = Titrant normality (meq/mL)
F = equivalent weight of iodixanol, 258.4 mg/meq
W = weight of iodixanol (mg)
Acceptance criteria: 98.6%–101.0% on the anhydrous basis
4 IMPURITIES
4.1 LIMIT OF FREE IODIDE
Sample solution: 5 g of Iodixanol in 30 mL of water
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry 〈541〉.)
Mode: Direct titration
Titrant: 0.001 N silver nitrate VS
Endpoint detection: Potentiometric
Analysis
Calculate the percentage of free iodide in the portion of Iodixanol taken:
Result = [(V × N × F) / W] × 100
V = sample titrant volume (mL)
N = Titrant normality (meq/mL)
F = equivalent weight of iodide, 0.1269 mg/meq
W = weight of iodixanol (mg)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.001%
4.2 LIMIT OF FREE AROMATIC AMINE
[Note-Rinse all glassware with water.]
Standard solution: 4 µg/mL of sodium chloride in water
Sample solution: 2 g of Iodixanol in 100 mL of water
Acceptance criteria: The specific conductance in the Sample solution is NMT that of the Standard solution (equivalent to NMT 0.02% of ionic compounds, as sodium chloride).
4.3 LIMIT OF FREE AROMATIC AMINE
Solution A: 3 mg/mL of N-(1-naphthyl)ethylenediamine dihydrochloride in a mixture of propylene glycol and water (70:30)
Blank solution: Add 15 mL of water to a 25-mL volumetric flask.
Standard stock solution: 10 µg/mL of USP Iohexol Related Compound B RS in water
Standard solution: Transfer 10.0 mL of the Standard stock solution and 5 mL of water to a 25-mL volumetric flask.
Sample solution: Transfer 200 mg of Iodixanol to a 25-mL volumetric flask, and add 15 mL of water.
Instrumental conditions
Mode: UV-Vis
Analytical wavelength: 495 nm
Cell: 5 cm
Analysis
Samples: Blank solution, Standard solution, and Sample solution
Treat the Samples as follows. Place the flask in an ice bath for 5 min. Add 1.5 mL of 6 N hydrochloric acid, and mix by swirling. Add 1.0 mL of sodium nitrite solution (20 mg/mL), and allow to stand in the ice bath for 4 min. Remove the flask from the ice bath, add 1.0 mL of sulfamic acid solution (40 mg/mL), and swirl gently until gas evolution ceases.
[Caution-Considerable pressure is produced.]
Add 1.0 mL of Solution A, dilute with water to volume, and allow to stand for 5 min.
Measure the absorbance of the Standard solution and the Sample solution against the Blank solution.
Acceptance criteria: The absorbance of the Sample solution is NMT that of the Standard solution (NMT 0.05% of free aromatic amine).
4.4 LIMIT OF 2-METHOXYETHANOL
Internal standard solution: 0.01 mg/mL of secondary butyl alcohol in water
Standard stock solution: 0.005 mg/mL of methanol and 0.01 mg/mL (ERR 1-Mar-2022) each of isopropyl alcohol, secondary butyl alcohol, and 2-methoxyethanol in Internal standard solution
Standard solution: Transfer about 0.25 g of USP Iodixanol RS and 1.0 mL of Standard stock solution to a headspace vial and seal the vial with a septum and crimp cap.
Sample solution: Transfer about 0.25 g of Iodixanol and 1.0 mL of Internal standard solution to a headspace vial and seal the vial with a septum and crimp cap.
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: GC with suitable headspace autosampler
Detector: Flame ionization
Column: 0.53-mm × 30-m fused-silica; coated with a 1-µm phase G16
Temperatures
Autosampler: 105°
Needle: 130°–140°
Injection port: 150°
Detector: 200°
Column: See Table 1
Table 1
| Initial Temperature (°) | Temperature Ramp (°/min) | Final Temperature (°) | Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
| 40 | - | 40 | 3 |
| 40 | 8 | 100 | 1 |
Carrier gas: Helium
Flow rate: 11 mL/min
Injection volume: 1 mL of the headspace
System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
[Note-The typical relative retention times for methanol, isopropyl alcohol, secondary butyl alcohol, and 2-methoxyethanol are 0.5, 0.6, 1.0, and 1.9 respectively.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 1.0 between methanol and isopropyl alcohol
Relative standard deviation: NMT 10.0% for the ratio of 2-methoxyethanol to internal standard
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the amount of 2-methoxyethanol in the portion of Iodixanol taken:
Result = (RU/RS) × (CS/CU)
RU = peak response ratio of 2-methoxyethanol to the internal standard from the Sample solution
RS = peak response ratio of 2-methoxyethanol to the internal standard from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of 2-methoxyethanol in the Standard solution (µg/mL)
CU = concentration of Iodixanol in Sample solution (g/mL)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 10 µg/g of 2-methoxyethanol
4.5 ORGANIC IMPURITIES
Solution A: Water
Solution B: Acetonitrile and water (50:50)
System suitability solution:
0.25 mg/mL of USP Iodixanol RS,
0.0025 mg/mL of USP Iodixanol Related Compound C RS, and
0.005 mg/mL of USP Iodixanol Related Compound D RS in water
Sample solution: 2.5 mg/mL of Iodixanol in water
Mobile phase: See Table 2
Table 2
| Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) |
| 0 | 94 | 6 |
| 2 | 94 | 6 |
| 32 | 80 | 20 |
| 72 | 0 | 100 |
| 82 | 0 | 100 |
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 254 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Injection volume: 10 µL
System suitability
Sample: System suitability solution
Use the chromatogram from the System suitability solution to identify the peaks based on the relative retention times given in Table 3.
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 1.5 between the two peaks due to iodixanol related compound D
Peak-to-valley ratio: NLT 1.3 between the first iodixanol peak and iodixanol related compound C (first peak)
Analysis
Sample: Sample solution
[Note-If iodixanol related compound C is present, only the first and larger peak with a retention time of 1.04 relative to the main iodixanol peak is seen between the two principal iodixanol peaks; the second iodixanol related compound C peak co-elutes with iodixanol. The area of the first and larger peak corresponds to approximately 80% of the total area of iodixanol related compound C. Determine the peak area of the first peak by drawing a vertical line through the minimum before the peak and a horizontal baseline at the minimum after the peak.]
Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the Sample solution:
Result = (rU/rT) × (1/F) × 100
rU = peak response of each impurity in the Sample solution
rT = sum of all peak responses greater than 0.05% of the principal peaks in the Sample solution
F = relative response factor (see Table 3)
Acceptance criteria: See Table 3. Disregard any impurity less than or equal to 0.05%.
Table 3
| Name | Relative Retention Time | Relative Response Factor | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
| Iodixanol related compound D (first peak) | 0.8 | 1.0 | Sum of both peaks 0.1% if present |
| Iodixanol related compound D (second peak) | 0.9 | 1.0 | - |
| Iodixanol (first peak) | 1.0 | - | - |
| Iodixanol related compound C (first peak) | 1.04 | 0.76 | 0.4 |
| Overalkylated impurities | 1.3-1.7 | 1.0 | (Sum of all) 1.0 |
| Any individual unspecified impurity | - | 1.0 | 0.10 |
| Total impurities | - | - | 1.5 |
4.6 LIMIT OF IODIXANOL RELATED COMPOUND E AND IODIXANOL IMPURITY H
Solution A: Acetonitrile and water (50:50)
Solution B: Acetonitrile
Mobile phase: See Table 4
Table 4
| Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) |
| 0 | 30 | 70 |
| 2 | 30 | 70 |
| 27 | 68 | 32 |
System suitability solution: 0.25 mg/mL of USP Iodixanol RS and 0.025 mg/mL of USP Iodixanol Related Compound E RS in water
Identification solution: 2.5 mg/mL of USP Iodixanol RS in water
Sample solution: 2.5 mg/mL of Iodixanol in water
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 254 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L8
Flow rate: 1.7 mL/min
Injection volume: 10 µL
System suitability
Sample: System suitability solution
[Note-See Table 5 for relative retention times.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 5.0 between iodixanol related compound E (first peak) and iodixanol (first peak)
Analysis
Samples: Identification solution and Sample solution
[Note-Iodixanol related compound E exhibits two peaks, the second of which may partly overlap with one of iodixanol peaks; use only the area of the first and larger peak of iodixanol related compound E, which corresponds to approximately 60% of the total area of iodixanol related compound E.]
Use the chromatograms obtained from the Identification solution and Sample solution for Identification test B.
Calculate the percentage of iodixanol related compound E and iodixanol impurity H in the Sample solution:
Result = (rU/rT) × (1/F) × 100
rU = peak response of each impurity in the Sample solution
rT = sum of all peak responses greater than 0.05% of the principal peaks in the Sample solution
F = relative response factor (see Table 5)
Acceptance criteria: See Table 5.
Table 5
| Name | Relative Retention Time | Relative Response Factor | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
| Iodixanol related compound E (first peak) | 0.7 | 0.58 | Sum of both peaks 0.3 |
| Iodixanol related compound E (second peak) | 0.8 | 1.0 | — |
| Iodixanol (first peak) | 1.0 | — | — |
| Iodixanol impurity Hᵃ | 1.4 | 1.0 | 0.6 |
ᵃ 5-[[3-[[3-[[[3-[[3-[3,5-bis-[[[2,3-Dihydroxypropyl]amino]carbonyl]-2,4,6-triiodophenyl]-2-hydroxypropyl](acetylimino)]-5-[[[2,3-dihydroxypropyl]amino]carbonyl]-2,4,6-triiodophenyl]carbonyl]amino]-2-hydroxypropyl]oxy]-2-hydroxypropyl](acetylimino)]-N,N′-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-2,4,6-triiodo-1,3-benzenedicarboxamide.
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
WATER DETERMINATION, Method I (921): NMT 4.0%
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
PACKAGING AND STORAGE: Preserve in well-closed, light-resistant containers. Store at room temperature.
USP REFERENCE STANDARDS (11)
USP lodixanol RS
USP lodixanol Related Compound C RS
5-[Acetyl[3-[[3,5-bis[[(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)amino]carbonyl]-2,4,6-triiodophenyl]amino]-2-hydroxypropyl]amino]N,N′-bis-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-2,4,6-triiodo-1,3-benzenedicarboxamide.
C33H42I6N6O14 1508.15
USP Iodixanol Related Compound D RS
5-[Acetyl(2-hydroxy-3-methoxypropyl)amino]-N,N′-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-2,4,6-triiodo-1,3-benzenedicarboxamide.
C20H28I3N3O9 835.16
USP Iodixanol Related Compound E RS
(5-{N-[3-(N-{3-Carbamoyl-5-[(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)carbamoyl]-2,4,6-triiodophenyl}acetamido)-2-hydroxypropyl]acetamido}-N1,N3-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-2,4,6-triiodoisophthalamide.
USP Iohexol Related Compound B RS
5-Amino-N,N′-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-2,4,6-triiodo-1,3-benzenedicarboxamide.
C14H18I3N3O6 705.02


