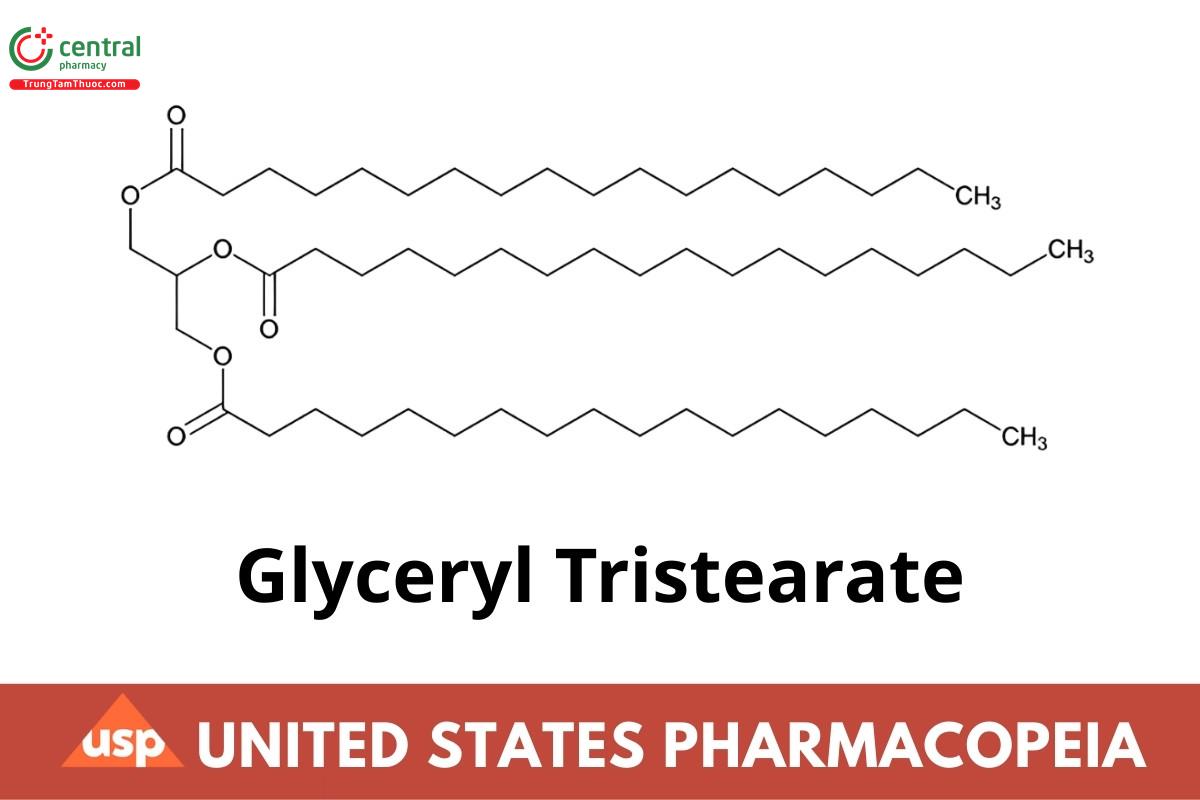
Glyceryl Tristearate
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
C57H110O6 891.48
Octadecanoic acid, 1,1',1"-(1,2,3-propanetriyl) ester;
Octadecanoic acid, 1,2,3-propanetriyl ester;
Glycerol trioctadecanoate;
Tristearoylglycerol CAS RN®: 555-43-1.
1 DEFINITION
Glyceryl Tristearate contains NLT 90.0% of triglycerides of saturated fatty acids, chiefly glyceryl tristearate (C57H110O6).
2 IDENTIFICATION
FATTY ACID COMPOSITION
Boron trifluoride methanol solution: 140 mg/mL of boron trifluoride in methanol
Saturated sodium chloride solution: Mix 1 part of sodium chloride with 2 parts of water, shake from time to time, and allow to stand. Before use, decant the solution from any undissolved substance and filter, if necessary.
Standard solution 1: 0.5 mg/mL of USP Methyl Myristate RS, 2.0 mg/mL of USP Methyl Stearate RS, and 2.0 mg/mL of USP Methyl Oleate RS in n-heptane
Standard solution 2: 0.05 mg/mL of USP Methyl Myristate RS, 0.2 mg/mL of USP Methyl Stearate RS, and 0.2 mg/mL of USP Methyl Oleate RS in n-heptane, diluted from Standard solution 1
Standard solution 3: Dissolve a quantity of an ester mixture1 containing methyl hexanoate, methyl caprylate, methyl caprate, methyl laurate, methyl myristate, methyl palmitate, methyl palmitoleate, methyl stearate, methyl oleate, methyl linoleate, and methyl arachidate in n-heptane to make a solution of about 9.0 mg/mL for methyl stearate and 0.1-0.2 mg/mL for each other methyl ester.
Sample solution: Transfer 100 mg of Glyceryl Tristearate to a 25-mL conical flask fitted with a suitable water-cooled reflux condenser and a magnetic stir bar. Add 2 mL of a 20-mg/mL solution of sodium hydroxide in methanol, mix, and reflux for about 30 min. Add 2 mL of Boron trifluoride methanol solution through the condenser, and reflux for about 30 min. Add 4 mL of n-heptane through the condenser, and reflux for 5 min. Cool, remove the condenser, add about 10 mL of Saturated sodium chloride solution, and shake. Add a quantity of Saturated sodium chloride solution to bring the upper layer up to the neck of the flask, and allow the layers to separate. Collect 2 mL of the n-heptane layer (the upper layer); wash with three quantities of water (2 mL each), and dry the n-heptane phase over anhydrous sodium sulfate.
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography (621), System Suitability.)
Mode: GC
Detector: Flame ionization
Column: 0.53-mm x 30-m capillary, bonded with a 1.0-µm layer of phase G16
Temperatures
Injection port: 250°
Detector: 250°
Column: See Table 1.
Table 1
| Initial Temperature (°) | Temperature Ramp (°/min) | Final Temperature (°) | Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
| 50 | 20 | 180 | — |
| 180 | 9 | 240 | 12 |
Carrier gas: Helium
Flow rate: 10 mL/min
Injection volume: 2 µL
Injection type: Split ratio, 4:1
System suitability
Samples: Standard solution 1 and Standard solution 2
[NOTE-The relative retention times for methyl myristate, methyl stearate, and methyl oleate are about 0.70, 1.00, and 1.01, respectively.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 1.5 between methyl stearate and methyl oleate, Standard solution 1
Signal-to-noise ratio: NLT 5 for methyl myristate, Standard solution 2
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution 3 and Sample solution
Measure the areas for the peaks of the methyl esters of the fatty acids. Disregard any peak with an area less than 0.05% of the total area and any peak due to the solvent. [NOTE-Relative retention times for several methyl esters are summarized in Table 2.]
Table 2
| Carbon-Chain Length | Number of Double Bonds | Relative Retention Times |
| 12 | 0 | 0.58 |
| 14 | 0 | 0.70 |
| 16 | 0 | 0.83 |
| 18 | 0 | 1.00 |
| 18 | 1 | 1.01 |
| 20 | 0 | 1.14 |
Take the main component of Standard solution 3 as a reference component, and calculate the calibration factor, FFA, for each fatty acid methyl ester:
Result = (FMC x PFA1 x AMC)/(PMC x AFA1)
FMC = factor for the main component, 1
PFA1 = percentage by weight of the fatty acid methyl ester in Standard solution 3
AMC = peak area of the main component in Standard solution 3
PMC = percentage by weight of the main component of Standard solution 3
AFA1 = peak area of the fatty acid methyl ester in Standard solution 3
Calculate the percentage of the fatty acid methyl ester by weight in the portion of Glyceryl Tristearate taken:
Result = [(AFA2 x FFA)/AT] x 100
AFA2 = peak area of the fatty acid methyl ester in the Sample solution
FFA = calibration factor
AT = sum of the peak areas of the fatty acid methyl esters in the Sample solution
Acceptance criteria: Glyceryl Tristearate exhibits the composition profile of fatty acids shown in Table 3.
Table 3
| Carbon-Chain Length | Number of Double Bonds | Percentage (w/w) |
| 6, 8, 10 | 0 | 0.0–0.3 |
| 12 | 0 | 0.0–0.5 |
| 14 | 0 | 0.0–0.5 |
| 16 | 0 | 0.0–2.0 |
| 16 | 1 | 0.0–0.1 |
| 18 | 0 | ≥97 |
| 18 | 1 | 0.0–0.5 |
| 18 | 2 | 0.0–0.5 |
| 20 | 0 | 0.0–1.0 |
3 ASSAY
CONTENT OF TRIGLYCERIDES
Mobile phase: Tetrahydrofuran
System suitability solution: 40 mg/mL of USP Glyceryl Distearate RS in Mobile phase
Sample solution: 8 mg/mL of Glyceryl Tristearate in Mobile phase
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography (621), System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: Refractive index
Column: 7.5-mm × 60-cm; 3-µm or 5-µm 100-Å packing L21
Temperatures
Column: 40°
Detector: 40°
[NOTE-Two or three 7.5-mm x 30-cm L21 columns may be used in place of the one 60-cm column, provided that system suitability requirements are met. The column temperature may be lowered to ambient temperature, although working at 40° provides stable separation conditions and ensures better sample solubility.]
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Injection volume: 40 µL
System suitability
Sample: System suitability solution
[NOTE-The relative retention times for triglycerides, diglycerides, monoglycerides, and Glycerin are 0.78, 0.81, 0.86, and 1.00, respectively.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 1.0 between the diglycerides and the monoglycerides
Relative standard deviation: NMT 2.0%, determined for the monoglycerides peak
Analysis
Samples: System suitability solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of triglycerides in the portion of Glyceryl Tristearate taken:
Result = (rU/rT) × 100
rU = peak response of the triglycerides from the Sample solution
rT = sum of all the glyceride peak responses from the Sample solution
Acceptance criteria: NLT 90.0% of triglycerides
4 IMPURITIES
4.1 RESIDUE ON IGNITION (281)
NMT 0.1%
4.2 ALKALINE IMPURITIES
Analysis: Prepare a mixture of 2.0 g of Glyceryl Tristearate, 15 mL of alcohol, and 30 mL of ether. Dissolve by gentle heating. Add 0.05 mL of bromophenol blue TS, and titrate with 0.01 N hydrochloric acid VS until the mixture turns yellow.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.4 mL of 0.01 N hydrochloric acid is required.
4.3 LIMIT OF NICKEL
[CAUTION-When using closed high-pressure digestion vessels and laboratory microwave equipment, be familiar with the safety and operating instructions given by the manufacturer.]
Magnesium nitrate solution: 10 mg/mL of magnesium nitrate in water
Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate solution: 100 mg/mL of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate in water
Standard stock solution: Transfer 5.0 mL of nickel standard solution TS to a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to make a solution containing 5 µg/mL of nickel.
Standard solutions: To four identical 25-mL volumetric flasks, each containing 6 mL of nitric acid, transfer 25, 50, 75, and 100 µL, respectively, of the Standard stock solution. To each flask add 0.5 mL of Magnesium nitrate solution and 0.5 mL of Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate solution, and dilute with water to volume. These solutions contain 0.005, 0.01, 0.015, and 0.02 µg/mL, respectively, of nickel.
Sample solution: Transfer 0.25 g of Glyceryl Tristearate to a suitable high-pressure-resistant digestion vessel (fluoropolymer or quartz), and add 6.0 mL of nitric acid and 2.0 mL of 30% hydrogen peroxide. Place the closed vessel in a laboratory microwave oven, and digest using an appropriate program (e.g., 1000 W for 40 min). Allow the digestion vessel to cool before opening. Add 2.0 mL of 30% hydrogen peroxide, and repeat the digestion step. Allow the digestion vessel to cool before opening. Quantitatively transfer the contents to a 25-mL volumetric flask, add 0.5 mL of Magnesium nitrate solution and 0.5 mL of Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate solution, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Blank solution: Add 6.0 mL of nitric acid and 2.0 mL of 30% Hydrogen peroxide to a high-pressure-resistant digestion vessel, and proceed as directed for the Sample solution.
Zero solution: Into a 50.0-mL volumetric flask, introduce 1.0 mL of Magnesium nitrate solution, 1.0 mL of Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate solution, and 12.0 mL of nitric acid. Dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Instrumental conditions
(See Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (852).)
Mode: Atomic absorption spectrophotometry
Analytical wavelength: Maximum absorbance at 232.0 nm
Detection: Graphite furnace
Lamp: Nickel hollow-cathode
Tube: Pyrolytically coated
Other: Background compensation system
Furnace program: See Table 4.
[NOTE-The temperature program may be modified to obtain optimum furnace temperatures.]
Table 4
| Step | Dry | Ash | Cool | Atomize |
| Temperature (°) | 120 | 1100 | 800 | 2600 |
| Ramp time (s) | 5 | 30 | 5 | — |
| Hold time (s) | 35 | 10 | 5 (decrease) | 7 |
Analysis
Samples: Standard solutions, Sample solution, and Blank solution
Use the Zero solution to set the instrument to zero. Concomitantly determine the absorbances of the Samples at least three times each.
Record the average of the steady readings for each of the solutions. If necessary, dilute the Sample solution with the Zero solution to obtain a reading within the calibrated absorbance range.
Plot the absorbances versus the concentrations of nickel, in µg/mL, in the Standard solutions. On the basis of the calibration curve, determine the concentrations of nickel, in µg/mL, in the Sample solution and the Blank solution from the corresponding absorptions. Obtain the correct concentration of nickel, CC, in µg/mL, in the Sample solution.
Calculate the content of nickel, in µg/g (ppm), in the portion of Glyceryl Tristearate taken:
[NOTE-If the Sample solution is diluted with the Zero solution, apply an appropriate correction factor for dilution.]
Result = (CC x V)/W
CC = concentration of nickel in the Sample solution (µg/mL)
V = volume of the Sample solution, 25 mL
W = weight of Glyceryl Tristearate taken to prepare the Sample solution (g)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 1 µg/g (ppm)
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
MELTING RANGE OR TEMPERATURE (741), Procedures, Procedure for Class II: 69°-73°
FATS AND FIXED OILS (401), Acid Value: NMT 1.0
FATS AND FIXED OILS (401), Hydroxyl Value: NMT 5.0
FATS AND FIXED OILS (401), Saponification Value: 186-192
FATS AND FIXED OILS (401), Peroxide Value: NMT 3
FATS AND FIXED OILS (401), Unsaponifiable Matter: NMT 0.5%
WATER DETERMINATION (921), Method I, Method la: NMT 0.1%
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
6.1 PACKAGING AND STORAGE
Preserve in tight containers, and store at room temperature. Protect from moisture.
6.2 USP REFERENCE STANDARDS (11)
USP Glyceryl Distearate RS
USP Methyl Myristate RS
USP Methyl Oleate RS
USP Methyl Stearate RS
1 Ester mixture can be obtained commercially from Nu-Chek-Prep, Inc., P.O. Box 295, Elysian, MN 56028, or from Sigma-Aldrich; or it can be prepared by mixing a commercially-available ester mixture with methyl stearate.


