Glyceryl Monocaprylocaprate
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
C₁₁H₂₂O₄ C₁₃H₂₆O₄
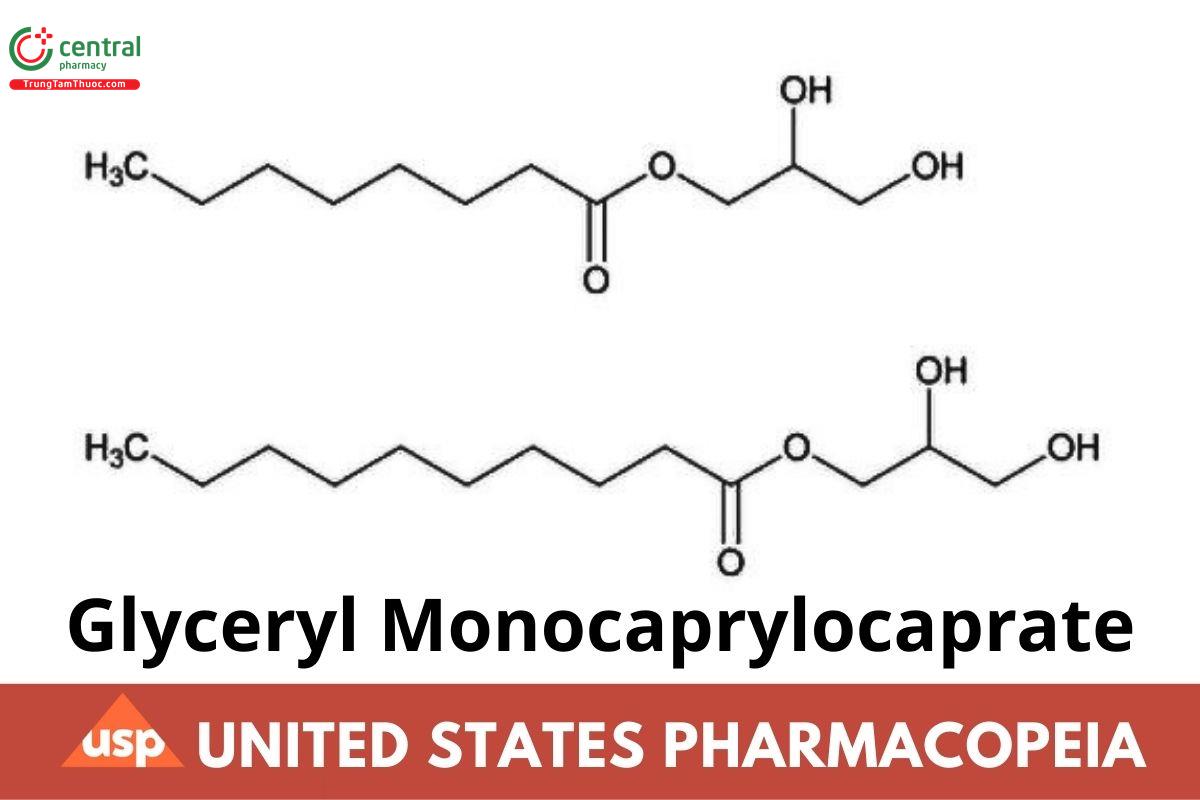
Octanoic acid, monoester with 1,2,3-propanetriol and decanoic acid, monoester with 1,2,3-propanetriol;
Caprylic acid monoglyceride and capric acid monoglyceride;
Glyceryl monooctanoate and glyceryl monodecanoate;
Monoglycerides, C8-10
C8-10 monoglycerides
CAS RN®: 91052-46-9.
1 DEFINITION
Change to read:
Glyceryl Monocaprylocaprate is a mixture of glyceryl monoesters, mainly mono-O-octanoylglycerol and mono-O-decanoylglycerol, containing variable quantities of diesters and triesters of fatty acids composed predominately of caprylic acid and capric acid. The requirements for monoester, diester, and triester content are: Monoesters: NLT 75.1%; Diesters: NMT 24.9%; and Triesters: NMT 5.0%.
2 IDENTIFICATION
2.1 A. Fatty Acid Composition
Boron trifluoride methanol solution: 140 mg/mL of boron trifluoride in methanol
Saturated sodium chloride solution: Mix 1 part sodium chloride with 2 parts water, shake from time to time, and allow to stand. Before use, decant the solution from any undissolved substance and filter, if necessary.
Standard solution 1: 1.0 mg/mL of USP Methyl Caproate RS, 1.0 mg/mL of USP Methyl Caprylate RS, and 2.0 mg/mL of USP Methyl Caprate RS in n-heptane
Standard solution 2: 0.1 mg/mL of USP Methyl Caproate RS, 0.1 mg/mL of USP Methyl Caprylate RS, and 0.2 mg/mL of USP Methyl Caprate RS in n-heptane, diluted from Standard solution 1
Standard solution 3: Prepare an ester mixture either by mixing a commercially available ester mixture with methyl caprylate and methyl caprate, or by using USP Methyl Caproate RS, USP Methyl Caprylate RS, USP Methyl Caprate RS, USP Methyl Laurate RS, and USP Methyl Myristate RS. Dissolve a quantity of the prepared ester mixture containing methyl caproate, methyl caprylate, methyl caprate, methyl laurate, and methyl myristate in n-heptane to make a solution of about 5.0–9.0 mg/mL for methyl caprylate, 1.0–5.0 mg/mL for methyl caprate, and 0.1–0.3 mg/mL for each of the other methyl esters.
Sample solution: Transfer 100 mg of Glyceryl Monocaprylocaprate to a 25-mL conical flask fitted with a suitable water-cooled reflux condenser and a magnetic stir bar. Add 2 mL of a 20-mg/mL solution of sodium hydroxide in methanol, mix, and reflux for about 30 min.
Add 2 mL of Boron trifluoride methanol solution through the condenser and reflux for about 30 min. Add 4 mL of n-heptane through the condenser and reflux for 5 min. Cool, remove the condenser, add about 10 mL of Saturated sodium chloride solution, shake, add a quantity of Saturated sodium chloride solution to bring the upper layer up to the neck of the flask, and allow the layers to separate. Collect 2 mL of the n-heptane layer (upper layer), wash with three quantities each of 2 mL of water, and dry the n-heptane phase over anhydrous sodium sulfate.
Chromatographic system
- (See Chromatography (621), System Suitability.)
- Mode: GC
- Detector: Flame ionization
- Column: 0.53-mm x 30-m capillary; bonded with a 1.0-µm layer of phase G16
- Temperatures
- Injection port: 250°
- Detector: 250"
- Column: See Table 1.
Table 1
| Initial Temperature (°) | Temperature Ramp (°/min) | Final Temperature (°) | Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
| 50 | 20 | 180 | - |
| 180 | 9 | 240 | 12 |
- Carrier gas: Helium
- Flow rate: 10 mL/min
- Injection volume: 2 µL
- Injection type: Split injection; split ratio, 4:1
System suitability
- Samples: Standard solution 1 and Standard solution 2
- [Note-The relative retention times for methyl caproate, methyl caprylate, and methyl caprate are about 0.7, 1.0, and 1.3, respectively.]
- Suitability requirements
- Resolution: NLT 4.0 between the methyl caprylate and methyl caprate peaks, Standard solution 1
- Signal-to-noise ratio: NLT 10 for the methyl caproate peak, Standard solution 2
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution 3 and Sample solution
Measure the peak areas for the methyl esters of the fatty acids. Disregard any peaks with an area less than 0.05% of the total area and any peak due to the solvent. [Note-The relative retention times for several methyl esters are summarized in Table 2.]
Table 2
| Carbon-Chain Length | Number of Double Bonds | Relative Retention Times |
| 6 | 0 | 0.7 |
| 8 | 0 | 1.0 |
| 10 | 0 | 1.3 |
| 12 | 0 | 1.6 |
| 14 | 0 | 1.9 |
Take the main component in Standard solution 3 as a reference component and calculate the calibration factor, FFA, for each fatty acid methyl ester:
FFA = (FMC × PFA1 × AMC)/(PMC × AFA1)
FMC = factor for the main component, 1
PFA1 = percentage by weight of the fatty acid methyl ester in Standard solution 3
AMC = peak area of the main component from Standard solution 3
PMC = percentage by weight of the main component in Standard solution 3
AFA1 = peak area of the fatty acid methyl ester from Standard solution 3
Calculate the percentage of the fatty acid methyl ester by weight in the portion of Glyceryl Monocaprylocaprate taken:
Result = [(AFA2 × FFA)/AT] × 100
AFA2 = peak area of the fatty acid methyl ester from the Sample solution
AT = sum of the peak areas of the fatty acid methyl esters from the Sample solution
Acceptance criteria: Glyceryl Monocaprylocaprate exhibits the composition profile of fatty acids shown in Table 3.
Table 3
| Carbon-Chain Length | Number of Double Bonds | Percentage (%, w/w) |
| 6 | 0 | ≤3.0 |
| 8 | 0 | 50.0–90.0 |
| 10 | 0 | 10.0–50.0 |
| 12 | 0 | ≤3.0 |
| 14 | 0 | ≤1.0 |
2.2 B. Glyceride Content
It meets the requirements of the test for Content of Monoglycerides, Diglycerides, and Triglycerides in the Assay.
Change to read:
2.3 C. Fats and Fixed Oils 〈401〉, Procedures, Saponification Value
225–255
3 ASSAY
Change to read:
3.1 Content of Monoglycerides, Diglycerides, and Triglycerides
System suitability solution: 20 mg/mL each of 1-monooctanoyl-rac-glycerol and 1-monodecanoyl-rac-glycerol in tetrahydrofuran
Standard solution: 50 mg/mL of USP Glyceryl Mono and Dicaprylocaprate RS in tetrahydrofuran
Sample solution: 50 mg/mL of Glyceryl Monocaprylocaprate in tetrahydrofuran
Chromatographic system
- (See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
- Mode: GC
- Detector: Flame ionization
- Column: 0.32-mm × 10-m; bonded with a 0.1-µm layer of phase G27
- Temperatures
- Injection port: 350°
- Detector: 370°
- Column: See Table 4.
Table 4
| Initial Temperature (°) | Temperature Ramp (°/min) | Final Temperature (°) | Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
| 60 | - | 60 | 3 |
| 60 | 8 | 340 | 12 |
- Carrier gas: Helium
- Flow rate: 2.3 mL/min
- Injection volume: 1 µL
- Injection type: Split injection; split ratio, 50:1
System suitability
- Samples: System suitability solution and Standard solution
- [Note-The typical relative retention times for monoglycerides, diglycerides, and triglycerides are 1.0–1.2, 1.5–1.9, and 2.0–2.3, respectively, Standard solution.]
- Suitability requirements
- Resolution: NLT 5.0 between the 1-monooctanoyl-rac-glycerol and 1-monodecanoyl-rac-glycerol peaks, System suitability solution
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Based on the chromatogram from the Standard solution, identify the peaks due to monoglycerides, diglycerides, and triglycerides in the Sample solution.
For the calculation of the contents of monoglycerides, diglycerides, and triglycerides, disregard the peaks with retention times less than those of the monoglycerides, which are due to impurities of the solvent and to the free fatty acids.
Calculate the percentage content of free fatty acids (CA):
CA = [(IA × F × Mr1)/Mr2] × 100
IA = acid value for Glyceryl Monocaprylocaprate, determined from the test for Acid Value
F = conversion factor, 10⁻³ g/mg
Mr1 = molecular weight of caprylic acid, 144.21 g/mol
Mr2 = molecular weight of potassium hydroxide, 56.11 g/mol
Calculate the percentage of monoglycerides, diglycerides, or triglycerides in the portion of Glyceryl Monocaprylocaprate taken:
Result = (ru/rT) × [(100 − CA − CW − CG)/100] × 100
ru = peak responses of the monoglycerides, diglycerides, or triglycerides from the Sample solution
rT = sum of all the glyceride peak responses from the Sample solution
CA = percentage of free fatty acids, determined above
CW = percentage of water, determined from the test for Water Determination
CG = percentage of free Glycerin, determined from the test for Limit of Free Glycerol
Acceptance criteria
- Monoesters: NLT 75.1%
- Diesters: NMT 24.9%
- Triesters: NMT 5.0%
4 IMPURITIES
4.1 Total Ash
Sample: 1.0 g
Analysis: Heat a silica or platinum crucible to redness for 30 min, allow to cool in a desiccator, and weigh. Evenly distribute the Sample in the crucible. Dry at 100°–105° for 1 h and ignite to constant weight in a muffle furnace at 600 ± 25°, allowing the crucible to cool in a desiccator after each ignition. Flames should not be produced at any time during the procedure. If after prolonged ignition the ash still contains black particles, take up with hot water, pass through an ashless filter paper, and ignite the residue and the filter paper. Combine the filtrate with the ash, carefully evaporate to dryness, and ignite to constant mass.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.5%
4.2 Limit of Free Glycerol
Sample: 1.2 g
Periodic acetic acid solution: Dissolve 0.446 g of sodium periodate in 2.5 mL of a 25% (v/v) solution of sulfuric acid, and dilute with glacial acetic acid to 100.0 mL.
Potassium iodide solution: 75 mg/mL of potassium iodide
Blank: 25 mL of methylene chloride
Titrimetric system
- (See Titrimetry 〈541〉)
- Mode: Residual titration
- Titrant: 0.1 M sodium thiosulfate VS
- Endpoint detection: Visual
Analysis: Dissolve the Sample in 25 mL of methylene chloride. Heat to about 50° and allow to cool. Add 100 mL of water. Shake and add 25 mL of Periodic acetic acid solution. Shake again and allow to stand for 30 min. Add 40 mL of Potassium iodide solution and allow to stand for 1 min. Add 1 mL of starch TS and titrate the liberated iodine with Titrant until the aqueous phase becomes colorless. Perform a blank determination.
Calculate the percentage of free Glycerol in the portion of Glyceryl Monocaprylocaprate taken:
Result = {[(VB − VS) × N × E × F]/W} × 100
VB = Titrant volume consumed in the Blank titration (mL)
VS = Titrant volume consumed in the Sample titration (mL)
N = actual normality of the Titrant (mEq/mL)
E = equivalent factor for glycerol, 23 mg/mEq
F = conversion factor, 10⁻³ g/mg
W = weight of Glyceryl Monocaprylocaprate taken for the titration (g)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 3.0%
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
Fats and Fixed Oils 〈401〉, Procedures, Acid Value: NMT 3.0
Fats and Fixed Oils 〈401〉, Procedures, Peroxide Value: NMT 1
Water Determination 〈921〉, Method I, Method Ia: NMT 1.0%
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
6.1 Packaging and Storage
Preserve in tight containers, and store at room temperature. Protect from moisture.
Delete the following:
6.2 Labeling
Label it to indicate the type (Type I or Type II).
Change to read:
6.3 USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Glyceryl Mono and Dicaprylocaprate RS [Note-May also be labeled as USP Glyceryl Monocaprylocaprate RS (Type I) until May 1, 2025.]
USP Methyl Caprate RS
USP Methyl Caproate RS
USP Methyl Caprylate RS
USP Methyl Laurate RS
USP Methyl Myristate RS


