Fludarabine Phosphate
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
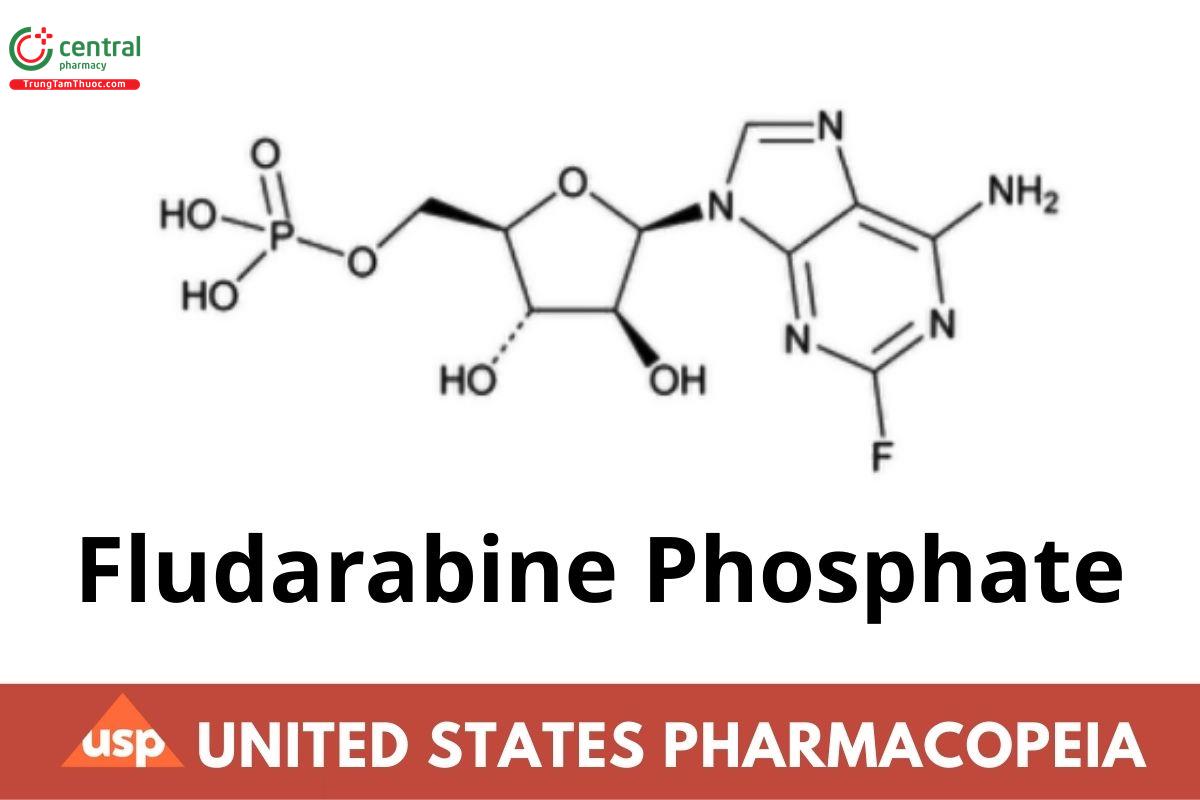
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
C10H13FN5O7P 365.21
9H-Purin-6-amine, 2-uoro-9-(5-O-phosphono-β-d-arabinofuranosyl)-;
9-β-d-Arabinofuranosyl-2-uoroadenine 5′-(dihydrogen phosphate) CAS RN®: 75607-67-9; UNII: 1X9VK9O1SC.
1 DEFINITION
Fludarabine Phosphate contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of fludarabine phosphate (C10H13FN5O7P), calculated on the anhydrous, solvent free basis.
[Caution—Fludarabine phosphate is potentially cytotoxic. Great care should be taken to prevent inhaling particles and exposing the skin to it.]
2 IDENTIFICATION
Change to read:
A. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197A or 197K (CN 1-May-2020)
B. The retention time of the major peak of the Sample solution corresponds to that of the Standard solution, as obtained in the Assay.
3 ASSAY
Procedure
Solution A: 10 mM monobasic potassium phosphate
Mobile phase: Methanol and Solution A (6:94)
Standard solution: 0.02 mg/mL of USP Fludarabine Phosphate RS in Mobile phase
Sample solution: 0.02 mg/mL of Fludarabine Phosphate in Mobile phase
3.1 Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 260 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 15-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min
Injection volume: 10 µL
3.2 System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation: NMT 1.0%
3.3 Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of udarabine phosphate (C10H13FN5O7P) in the portion of Fludarabine Phosphate taken:
Result = (rU /rS ) × (CS /CU) × 100
rU = peak response from the Sample solution
rS = peak response from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Fludarabine Phosphate RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Fludarabine Phosphate in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: 98.0%–102.0% on the anhydrous, solvent-free basis
4 IMPURITIES
4.1 Chloride
Standard stock solution: 82.4 µg/mL of sodium chloride in water
Standard solution: Transfer 2.0 mL of Standard stock solution to a test tube, add 13.0 mL of water, and mix.
Sample solution: Transfer 50.0 mg of Fludarabine Phosphate to a test tube, add 15 mL of water to dissolve, and heat gently if necessary. Analysis: Add 1.0 mL of nitric acid to the Standard solution and Sample solution, and place each in separate, colorless test tubes containing 1.0 mL of silver nitrate TS.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.2%; the Sample solution shows less turbidity than the Standard solution.
4.2 Limit of Free Phosphate
Reagent solution: Mix 4 g of finely powdered ammonium molybdate and 0.1 g of finely powdered ammonium vanadate in a 150-mL beaker. Add 70 mL of water, and grind the particles using a glass rod. A clear solution is obtained within a few minutes. Add 20 mL of nitric acid, adjust to room temperature, and dilute with water to 100 mL.
Standard solution: 7.16 µg/mL of potassium dihydrogen phosphate in water. Transfer 2.0 mL of this solution to a test tube.
Sample solution: Transfer 10 mg of Fludarabine Phosphate in 2.0 mL of water to a test tube and heat gently.
Blank: 2.0 mL of water in a test tube
Analysis: To each of the test tubes containing the Standard solution, Sample solution, and Blank, add 2.0 mL of Reagent solution. Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.1%; the color of the Standard solution must be more intense than that of the Blank. Viewed downward in diffuse daylight against a white background, the yellow coloration of the Sample solution must not be more intense than that of the Standard solution.
4.3 Limit of Sodium
Standard stock solution: 2.54 mg/mL of sodium chloride in water. Sodium chloride is previously dried at 105° for 2 h.
Standard solution: 1 µg/mL of sodium in water, from Standard stock solution
Sample solution: 0.5 mg/mL of Fludarabine Phosphate in water
Instrumental conditions Mode: Flame photometry
Analytical wavelength: Sodium emission line at 589.0 nm
Blank: Water
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.2%; the emission response of the Sample solution is NMT that of the Standard solution.
4.4 Organic Impurities, Procedure 1: Early-Eluting Impurities
Mobile phase, Standard solution, and Chromatographic system: Proceed as directed in the Assay.
System suitability solution: 10 mg of Fludarabine Phosphate in 10 mL of 0.1 N hydrochloric acid. Heat the solution at 80° in a water bath for 15 min.
Sensitivity solution: 0.5 µg/mL of USP Fludarabine Phosphate RS in Mobile phase, from the Standard solution Sample solution: 1 mg/mL of Fludarabine Phosphate in Mobile phase
4.4.1 System suitability
Samples: Standard solution, System suitability solution, and Sensitivity solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 2.0 between the iso-ara-guanine monophosphate and isoguanine peaks, System suitability solution Relative standard deviation: NMT 2.0%, Standard solution
Signal-to-noise ratio: NLT 10, Sensitivity solution
4.4.2 Analysis
Sample: Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each early-eluting impurity in the portion of Fludarabine Phosphate taken:
Result = (rU /rS ) × (1/F1) × 100
rU = peak response of each individual impurity from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of udarabine phosphate from the Sample solution
F1 = relative response factor for each individual impurity (see Table 1)
Acceptance criteria: See Table 1.
Table 1
Name | Relative Retention Time | Relative Response Factor | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
Iso-ara-guanine monophosphatea | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.8 |
Isoguanineb | 0.34 | 0.40 | 0.2 |
3′,5′-Diphosphate analogc | 0.42 | 0.53 | 0.4 |
Any individual, unspecied impurity | <1.0 | 1.0 | 0.1 |
Fludarabine phosphate | 1.0 | — | — |
a 6-Amino-9-β-D-arabinofuranosyl-2-oxo-1H-purine 5’-(dihydrogen phosphate).
b 6-Amino-1H-purin-2(9H)-one.
c 9-β-D-Arabinofuranosyl-2-uoroadenine 3’,5’-bis(dihydrogen phosphate).
4.5 Organic Impurities, Procedure 2: Late-Eluting Impurities
Solvent A: 10 mM monobasic potassium phosphate
Mobile phase: Methanol and Solvent A (1:4)
Standard solution and Chromatographic system: Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Sensitivity solution and Sample solution: Prepare as directed in Organic Impurities, Procedure 1: Early-Eluting Impurities.
4.5.1 System suitability
Samples: Standard solution and Sensitivity solution
Suitability requirements
Tailing factor: NMT 2.0, Standard solution
Relative standard deviation: NMT 2.0%, Standard solution
Signal-to-noise ratio: NLT 10, Sensitivity solution
4.5.2 Analysis
Sample: Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each late-eluting impurity in the portion of Fludarabine Phosphate taken:
Result = (rU /rS) × (1/F2) × 100
rU = peak response of each individual impurity from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of udarabine phosphate from the Sample solution
F2 = relative response factor for each individual impurity (see Table 2)
Acceptance criteria: See Table 2.
Table 2
Name | Relative Retention Time | Relative Response Factor | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
Fludarabine phosphate | 1.0 | — | — |
2-Fluoroadeninea | 1.5 | 2.0 | 0.1 |
2-Fluoro-ara-adenineb | 1.9 | 1.7 | 0.2 |
2-Ethoxyphosphate analogc | 2.5 | 0.56 | 0.2 |
Any individual, unspecied impurity | >1.0 | 1.0 | 0.1 |
Total unspecied impuritiesd | — | — | 0.5 |
Total impuritiese | — | — | 1.5 |
a 2-Fluoro-9H-purin-6-amine.
b 9-β-D-Arabinofuranosyl-2-fluoroadenine.
c 2-Ethoxy-9-β-D-arabinofuranosyladenine 5’-(dihydrogen phosphate).
d The sum of all unspecified impurities found in Organic Impurities, Procedure 1: Early-Eluting Impurities and Organic Impurities, Procedure 2: Late-Eluting Impurities.
e The sum of all impurities found in Organic Impurities, Procedure 1: Early-Eluting Impurities and Organic Impurities, Procedure 2: Late-Eluting Impurities.
4.6 Limit of Alcohol
Standard solution: 0.50 mg/mL of alcohol in dimethylformamide
Sample solution: 50 mg/mL of Fludarabine Phosphate in dimethylformamide
Blank: Dimethylformamide
4.6.1 Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.) Mode: GC equipped with a headspace injector Detector: Flame ionization
Column: 0.25-mm × 30-m; 1.4-µm coating of phase G43
Temperatures
Injection port: 160°
Detector: 250°
Column: See Table 3.
Table 3
Initial Temperature (°) | Temperature Ramp (°/min) | Final Temperature (°) | Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
40 | 0 | 40 | 10 |
40 | 5 | 70 | — |
70 | 30 | 220 | — |
Carrier gas: Helium
Flow rate: 27 cm/s
Sample
Volume: 2 mL/vial. [Note—Seal the vials using a flanged cap so that the cap can no longer be turned.]
Conditioning temperature: 80°
Conditioning time: 60 min
Injection volume: 1.0 mL
4.6.2 System suitability
Samples: Standard solution and Blank
[Note—The retention time for alcohol is about 3 min.]
Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation: NMT 4.0% for three injections, Standard solution
Peak interference: No peak at the retention time for alcohol, Blank
4.6.3 Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of alcohol in the portion of Fludarabine Phosphate taken:
Result = (rU /rS ) × (CS /CU) × 100
rU = peak area of alcohol from the Sample solution
rS = peak area of alcohol from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of alcohol in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Fludarabine Phosphate in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
[Note—Use the percentage obtained to calculate the Assay result on the solvent-free basis.]
Acceptance criteria: NMT 1.0%
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
Microbial Enumeration Tests 〈61〉 and Tests for Specified Microorganisms 〈62〉: The total aerobic microbial count is NMT 103 cfu/g.
Optical Rotation 〈781S〉, Procedures, Specific Rotation
Sample solution: 5 mg/mL in water
Acceptance criteria: +10° to +14°
Water Determination 〈921〉, Method I: NMT 3.0%
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in well-closed, light-resistant containers, and store in a refrigerator.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Fludarabine Phosphate RS.


