Ferrous Fumarate
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
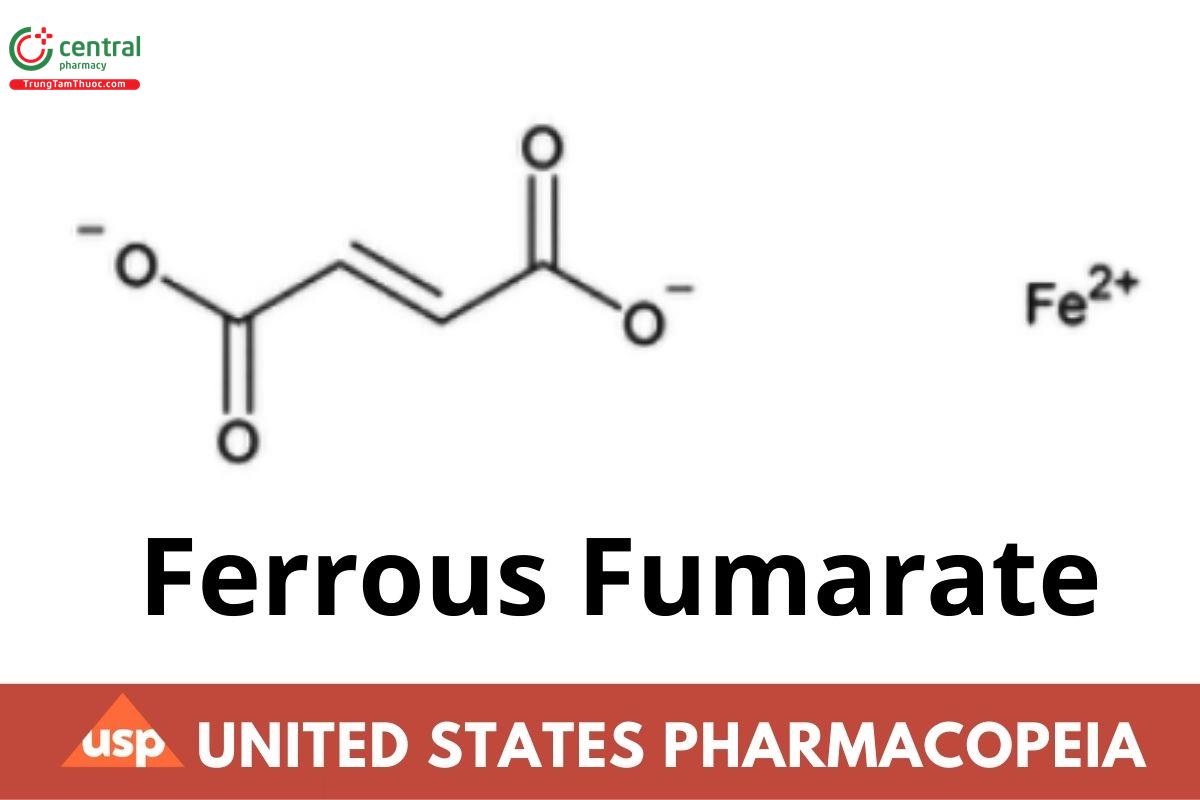
C4H2FeO4 169.90
2-Butenedioic acid, (E)-, iron(2+) salt;
Iron(2+) fumarate CAS RN®: 141-01-5; UNII: R5L488RY0Q.
1 DEFINITION
Ferrous Fumarate contains NLT 97.0% and NMT 101.0% of ferrous fumarate (C4H2FeO4), calculated on the dried basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared Absorption
Sample: To 1.5 g of Ferrous Fumarate, add 25 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid (1 in 2). Dilute with water to 50 mL, heat to dissolve, then cool, and filter on a ne-pore size, sintered-glass crucible. Wash the precipitate with dilute hydrochloric acid (3 in 100), saving the filtrate for Identification test B, and dry the precipitate at 105°.
Acceptance criteria: The IR absorption of a potassium bromide dispersion of the dried precipitate exhibits maxima only at the same wavelengths as that of a similar preparation of USP Fumaric Acid RS.
B. Identification Tests—General, Iron 〈191〉: A portion of the filtrate obtained in Identification test A meets the requirements.
3 ASSAY
Procedure
Sample: 500 mg of Ferrous Fumarate
Blank: Proceed as directed in the Analysis without the Sample.
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry 〈541〉.)
Mode: Direct titration
Titrant: 0.1 N ceric sulfate VS
Endpoint detection: Visual
Analysis: Transfer the Sample to a 500-mL conical ask, and add 25 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid (2 in 5). Heat to boiling, and add, dropwise, a solution of 112 mg/mL of stannous chloride in dilute hydrochloric acid (3 in 10) until the yellow color disappears, then add 2 drops in excess. Cool the solution in an ice bath to room temperature, add 10 mL of 50 mg/mL of mercuric chloride solution, and allow to stand for 5 min. Add 200 mL of water, 25 mL of dilute sulfuric acid (1 in 2), and 4 mL of phosphoric acid. Then add 2 drops of orthophenanthroline TS, and titrate with Titrant. Perform a blank determination.
Calculate the percentage of ferrous fumarate (C4H2FeO4) in the Sample taken:
Result = {[(VS − VB ) × N × F]/W} × 100
VS = Titrant volume consumed by the Sample (mL)
VB = Titrant volume consumed by the Blank (mL)
N = actual Titrant normality (mEq/mL)
F = equivalency factor, 169.9 mg/mEq
W = Sample weight (mg)
Acceptance criteria: 97.0%–101.0% on the dried basis
4 IMPURITIES
4.1 Sulfate
Sample solution: Transfer 1.0 g of Ferrous Fumarate to a 250-mL beaker, add 100 mL of water, and heat on a steam bath, adding hydrochloric acid dropwise until completely dissolved. [Note—About 2 mL of the acid will be required.] Filter the solution if necessary, and dilute the filtrate with water to 100 mL. Heat the filtrate to boiling, add 10 mL of barium chloride TS, warm on a steam bath for 2 h, cover, and allow to stand for 16 h. [Note—If crystals of ferrous fumarate form, warm the solution on the steam bath to dissolve them.]
Analysis: Pass the Sample solution through ashless filter paper, wash the residue with hot water until, with the addition of ammonium sulfide TS, a black precipitate is no longer formed in the filtrate. Transfer the paper containing the residue to a tared crucible. Char the paper, without burning, and ignite the crucible and its contents at 600° to constant weight.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.2%: Each mg of residue is equivalent to 0.412 mg of sulfate (SO4).
Change to read:
4.2 Arsenic 〈211〉
Procedures, Procedure 1 (CN 1-Jun-2023)
Test preparation: To 2.0 g in 10 mL of water add 10 mL of sulfuric acid. Warm to precipitate the fumaric acid completely, cool, add 30 mL of water, and filter into a 100-mL volumetric ask. Wash the precipitate with water, adding the washings to the ask, then add water to volume, and mix. Transfer 50.0 mL of this solution into the arsine generator ask, and dilute with water to 55 mL.
Analysis: Proceed as directed in the chapter, except omit the addition of 20 mL of 7 N sulfuric acid specified for the Procedure. Acceptance criteria: NMT 3 ppm
4.3 Limit of Ferric Iron
Sample: 2 g of Ferrous Fumarate
Blank: Proceed as directed in the Analysis without the Sample.
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry 〈541〉.)
Mode: Direct titration
Titrant: 0.1 N sodium thiosulfate VS
Endpoint detection: Visual
Analysis: Transfer the Sample to a glass-stoppered, 250-mL conical ask, add 25 mL of water and 4 mL of hydrochloric acid, and heat on a hot plate until solution is complete. Insert the stopper in the ask, and cool to room temperature. Add 3 g of potassium iodide, insert the stopper in the ask, swirl to mix, and allow to stand in the dark for 5 min. Remove the stopper, add 75 mL of water, and titrate with the Titrant, adding 3 mL of starch TS as the endpoint is approached. Perform a blank determination.
Calculate the percentage of ferric iron in the portion of Ferrous Fumarate taken:
Result = {[(VS − VB) × N × F]/W} × 100
VS = Titrant volume consumed by the Sample (mL)
VB = Titrant volume consumed by the Blank (mL)
N = Titrant normality (mEq/mL)
F = equivalency factor, 55.85 mg/mEq
W = Sample weight (mg)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 2.0%
4.4 Limit of Lead
[Note—For the preparation of all aqueous solutions and for the rinsing of glassware before use, use water that has been passed through a strong-acid, strong-base, mixed-bed ion-exchange resin. Select all reagents to have as low a content of lead as practicable, and store all reagent solutions in containers of borosilicate glass. Cleanse glassware before use by soaking in warm nitric acid (1 in 2) for 30 min and by rinsing with deionized water.]
Ascorbic acid–sodium iodide solution: 100 mg/mL of ascorbic acid and 192.5 mg/mL of sodium iodide
Trioctylphosphine oxide solution: 50 mg/mL of trioctylphosphine oxide in 4-methyl-2-pentanone. [Caution—This solution causes irritation. Avoid contact with eyes, skin, and clothing. Take special precautions in disposing of unused portions of solutions to which this reagent is added.]
Standard solution: Transfer 5.0 mL of lead nitrate stock solution TS to a 100-mL volumetric ask. Dilute with water to volume, and mix. Transfer 2.0 mL of the resulting solution to a 50-mL beaker. To this beaker add 6 mL of nitric acid and 10 mL of perchloric acid, and evaporate in a hood to dryness. [Caution—Use perchloric acid in a well-ventilated fume hood with proper precautions.] Cool, dissolve the residues in 10 mL of 9 N hydrochloric acid, and transfer with the aid of about 10 mL of water to a 50-mL volumetric ask. Add 20 mL of Ascorbic acid–sodium iodide solution and 5.0 mL of Trioctylphosphine oxide solution, shake for 30 s, and allow to separate. Add water to bring the organic solvent layer into the neck of the ask, shake again, and allow to separate. The organic solvent layer is the Standard solution, and it contains 2.0 µg/mL of lead.
Sample solution: Transfer 1.0 g of Ferrous Fumarate to a 50-mL beaker, and add 6 mL of nitric acid and 10 mL of perchloric acid. [Caution— Use perchloric acid in a well-ventilated fume hood with proper precautions.]
Cover with a ribbed watch glass, and heat in a hood until completely dry. Cool, dissolve the residue in 10 mL of 9 N hydrochloric acid, and transfer with the aid of about 10 mL of water to a 50-mL volumetric ask. Add 20 mL of Ascorbic acid–sodium iodide solution and 5.0 mL of Trioctylphosphine oxide solution, shake for 30 s, and allow to separate. Add water to bring the organic solvent layer into the neck of the ask, shake again, and allow to separate. The organic layer is the Sample solution.
Blank: To a 50-mL beaker add 6 mL of nitric acid and 10 mL of perchloric acid, and evaporate in a hood to dryness. [Caution—Use perchloric acid in a well-ventilated fume hood with proper precautions.]
Cool, dissolve the residue in 10 mL of 9 N hydrochloric acid, and transfer with the aid of about 10 mL of water to a 50-mL volumetric ask. Add 20 mL of Ascorbic acid–sodium iodide solution and 5.0 mL of Trioctylphosphine oxide solution, shake for 30 s, and allow to separate. Add water to bring the organic solvent layer into the neck of the ask, shake again, and allow to separate. The organic layer is the Blank, and it contains 0 µg/mL of lead.
Instrumental conditions
(See Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy 〈852〉.)
Mode: Atomic absorption spectrophotometry
Analytical wavelength: 283.3 nm
Lamp: Lead hollow-cathode
Flame: Air–acetylene
System suitability
Samples: Standard solution and Blank
Suitability requirements: The absorbance of the Standard solution and the absorbance of the Blank are significantly different. Analysis
Samples: Standard solution, Sample solution, and Blank
Concomitantly determine the absorbances of the Blank, Standard solution, and the Sample solution. Use the Blank to set the instrument to zero.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 10 ppm: The absorbance of the Sample solution does not exceed that of the Standard solution. Change to read:
4.5 Mercury
[Note—Carry out this test in subdued light, because mercuric dithizonate is light sensitive.]
Hydroxylamine hydrochloride solution, Standard mercury solution, Dithizone extraction solution, and Diluted dithizone extraction solution: Prepare as directed in Mercury 〈261〉, Procedures, Procedure 1 (CN 1-Jun-2023).
Control solution: Mix 3.0 mL of Standard mercury solution, 30 mL of dilute nitric acid (1 in 10), 5 mL of 250 mg/mL of sodium citrate solution, and 1 mL of Hydroxylamine hydrochloride solution.
Test preparation: Dissolve 1 g of Ferrous Fumarate in 30 mL of dilute nitric acid (1 in 10) with the aid of heat, on a steam bath. Cool quickly by immersing in an ice bath, and pass through a ne-porosity filter that previously has been washed with dilute nitric acid (1 in 10) and water. To the filtrate add 20 mL of 250 mg/mL of sodium citrate solution and 1 mL of Hydroxylamine hydrochloride solution.
Analysis: Adjust the Control solution to a pH of 1.8 with ammonium hydroxide, and the Sample solution to a pH of 1.8 with sulfuric acid. Separately transfer the solutions to separators. Treat the Sample solution and the Control solution in parallel as follows. Extract with two 5-mL portions of Dithizone extraction solution and 5 mL of chloroform, pooling the chloroform extracts in a second
separator. Add 10 mL of hydrochloric acid (1 in 2), shake, allow the layers to separate, and discard the chloroform layer. Wash the acid extract with 3 mL of chloroform, and discard the washing. Add 0.1 mL of 20 mg/mL edetate disodium solution and 2 mL of 6 N acetic acid, mix, and add slowly 5 mL of ammonium hydroxide. Close the separator, cool it under cold running water, and dry its outer surface. Remove the stopper, and pour the contents into a beaker. Adjust the Sample solution and the Control solution to a pH of 1.8 in the same
manner as before, and return the solutions to their respective separators. Add 5.0 mL of Diluted dithizone extraction solution, shake vigorously, and allow the layers to separate. Using Diluted dithizone extraction solution as a color blank, compare the colors developed in the chloroform layers of the Sample solution and the Control solution.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 3 µg/g: The color developed by the Sample solution is not more intense than that developed by the Control solution.
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
Loss on Drying 〈731〉
Analysis: Dry at 105° for 16 h.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 1.5%
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in well-closed containers.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Fumaric Acid RS.


