Enoxaparin Sodium
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
1 DEFINITION
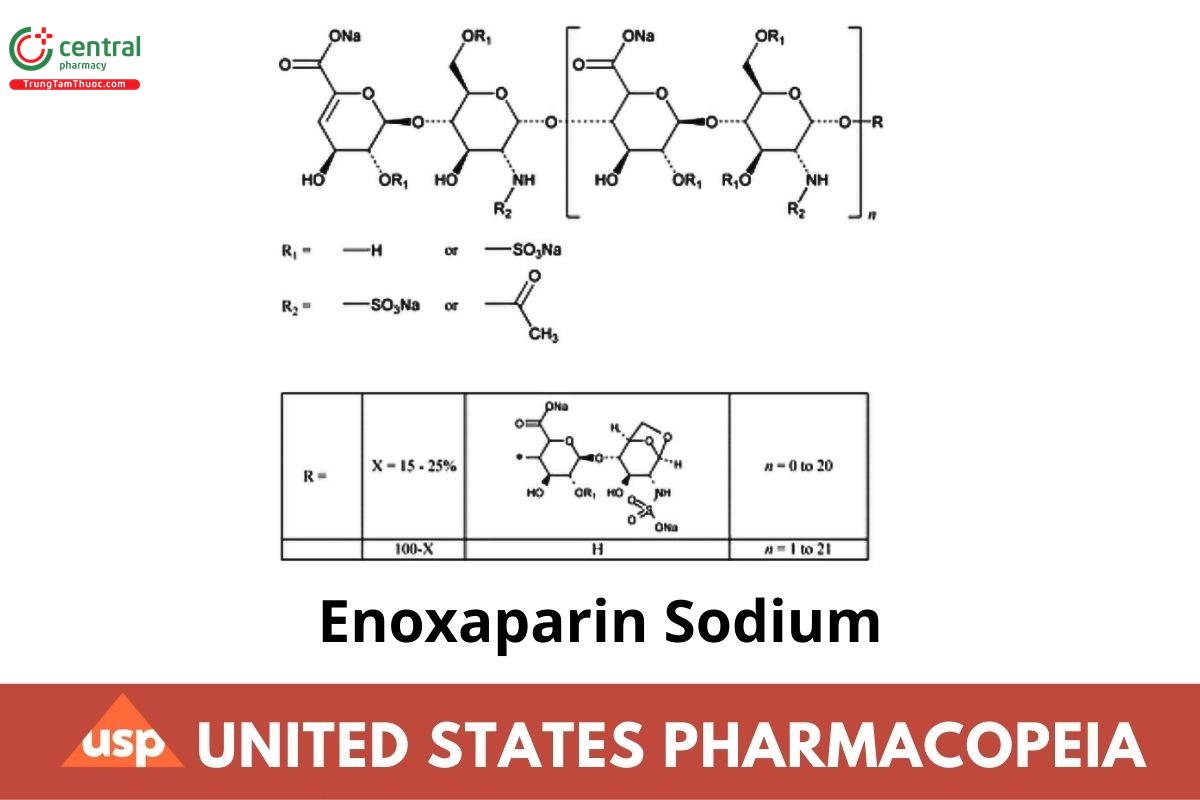
Enoxaparin Sodium is the sodium salt of a depolymerized heparin. It is obtained by alkaline depolymerization of heparin benzyl ester. The starting material, heparin, is obtained exclusively from porcine intestinal mucosa. Heparin source material used in the manufacture of Enoxaparin Sodium complies with the compendial requirements stated in the Heparin Sodium monograph. Enoxaparin Sodium consists of a complex set of oligosaccharides that have not yet been completely characterized. The majority of the components have a 4-enopyranose uronate structure at the nonreducing end of their chain. About 20% of the materials contain a 1,6-anhydro derivative on the reducing end of the chain, the range being between 15% and 25%. The weight-average molecular weight of Enoxaparin Sodium is 4500 Da, the range being between 3800 and 5000 Da; about 16% have a molecular weight of less than 2000 Da, the range being between 12.0% and 20.0%; about 74% have a molecular weight between 2000 and 8000 Da, the range being between 68.0% and 82.0% NMT 18.0% have a molecular weight higher than 8000 Da. When prepared as a solution, the solution is analyzed for clarity and degree of color using a validated method. The degree of sulfation is NLT 1.8 per disaccharide unit. It has a potency of NLT 90 and NMT 125 Anti-Factor Xa International Units (IU)/mg, and NLT 20.0 and NMT 35.0 Anti-Factor Ila IU/mg, calculated on the dried basis. The ratio of Anti-Factor Xa activity to Anti-Factor Ila activity is between 3.3 and 5.3.
2 IDENTIFICATION
A. SPECTROSCOPIC IDENTIFICATION TESTS (197), Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy: 197U
Medium: 0.01 N hydrochloric acid
Sample solution: 500 µg/mL
Acceptance criteria: The spectra exhibit maxima at 231 ± 2 nm
B. 13C NMR SPECTRUM
(See Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (761).)
Standard solution: Dissolve 200 mg of USP Enoxaparin Sodium RS in a mixture of 0.2 ml of deuterium oxide and 0.8 ml of water Add 0.05 ml of deuterated methanol to serve as an intermal reference.
Sample solution: Dissolve 200 mg of Enoxaparin Sodium in a mixture of 0.2 mL of deuterium oxide and 0.8 mL of water. Add 0.05 ml of deuterated methanol.
Analysis: Transfer the Standard solution and the Sample solution to NMR tubes of 5-mm diameter. Using a pulsed (Fourier transform) NMR spectrometer operating at NLT 75 MHz for 13C, record the 12C NMR spectra of the Standard solution and the Sample solution at 40
Acceptance criteria: The spectra are similar.
C. The ratio of the numencal value of the Arti-Factor Xas activity in Art-Factor Xa IU/mg, to the numerical value of the And-Factor la activity in Art-Factor la U/mg as determined by the Assay (Anti-Factor Xa Activity) and the test for And-Factor fla Activity, respectively, is NLT 3.3 and NMT 5.3.
Change to read:
D. Molecular Weight Distribution and Weight-Average Molecular WeightSee Low Molecular Weight Prepare Molecular Wear Determinations (2091)
System suitability solution: 5 mg/ml of USP Enoxanario Sodium in Mobile phase. Filter using a nylon membrane of 0.45-μm pore size.
System suitability
Sample: System suitability solution
Suitability requirements
Weight-average molecular weight (M): Take the mean of the calculated M from the duplicate injections of the System aufability σολιτίση, από round to the nearest 50 Da. The Chromatographic system is suitable if the M is within 150 De of the labeled M value as stated in the USP certificate for USP Enoxapaon Sodium RS
Analyslis: Take the mean of the calculated M fren the dupizate injections of the Sample andution, and round to the nearest 50 Da. Average The calculated percentage of enoxaparin sodium chains with molecular weight lower than 2000, (M. percentage of enoxaparin sodium chains with molecular weight in the range of 2000-8000, (M) and percentage of encscaparin sediurn chaine with molecular weight greater than 8000, (M) from the duplicate injections of the Sample solution, express to the neurest 0.5%.
Acceptance criteris
For M : 3800–5000 Da
For M : 12.0%–20.0%
For M : 68.0%–82.0%
For NMT 18.0%
E. Identification Tests—General (191), Chemical Identification Tests, Sodium: Meets the inquirement
3 ASSAY
Acetic acid solution: Glacial acetic acid and water (42:50)
pH 7.4 polyethylene glycol 6000 buffer: Dissolve 6.00 g of trialbyshemeshaminomethane and 8.77 g of sodium chloride in 500 ml of water. Add 1.0 g of polyethylene glycol 6000, adjust with bydrushionc aud to as of 7.4, and dilute with water to 1000 mL
pH7.4 buffer: Dissolve 6.08 g of trechonmabyCuminomethane and 8.77 g of sodium chloride is 500 ml of Adjust with hydrochloric acid to a pH of 7.4 and dilute with matter to 1000 ml.
pH 8.4 buffer: Drive 300 g of trahydrumeyamingmethane, 12 g of audum shiocate and 1.40 g of edetate sodium in 250 mi, af water Adjust with hydrochloric acid to a pt of 4 and dilute with water to 500 ml
Human antithrombin III anlutions Reconstitute a vial of antithronbini (see agents, indicaturn, and Solutions hagent Specifications) water to obtain a solution containing 5 Antithrombin III Derts/mi. Dilute this schution with pif 7.4 polyethylene glycol 6000 bufty to obtain a solution having a concentration of 1.0 Antithrombin III Unit/mi
Factor Xa solution: Reconstitute a weighed quantity of trovine factor Xa (Rampanta indicanes and Sabatoto-Reagent Spécification in
pH7.4 polyethylene glycol 6000 buffer to obtain a solution that gives an increase in absorbance value at 405 nm of NMT 0.20 absorbance units/min when assayed as described below but asing as an appropriate volume, V, the volume in pl. of pH 7.4 buffer instead of V μL of the erioxapann solution.
Chromogenic substrate solution: Prepare a solution of a maltable chromogenic substrate for amidolytic test (see spents Indicators and Solutions Imagent Sexcification for factor Xa in water to obtain a concentration of about 3 mM. Dilute with pH 8.4 Buffer to obtain a solution having a concentration of 0.5
Standard solutions: Reconstitute the entire contents of an ampul of USP Enoxaparin Sedium for Bintars RBS with water and dilute with pri 7 buffer to obtein four dilutions in the concentration range between 0.025 and 0.2 Anti-factor Xa IU/mL.
Sample solutions: Proceed as directed for the Standare anlutions to cibtain concentrations of Enoxssarin Sodium similar to those obtained for the Standard solutions.
Analysis
Samples: Acetic acid solution, pH 74 buffer, Human antivomb solution, Factor Xa solution, Chromogenic substrate solution, Standant molutions, and Sande alations
Label 18 suitable tubes B and B2 for blanks: T1, 12, 13 and 14 each in duplicate for the dilutions of the Sample solutions and 51, 52, 53, and S4 each in duplicate for the dilutions of the Standard solutions. Non-Treat the tubes in the order 81, 51, 52, 83, 84, 11, 12, 13, 14, 11, 12, 13, 14, 51, 52, 53, 54, 82) To each tube add the same volume, V (20-50 µL) of suman antithrombin solution and an equal volume, V, of either the blank (pH74 buffer) or an appropriate dilution of the Sample sclidons or the Standard solutions Mir, but do not allow bubbles to form. Incubate at 37" for 1.0 min. Add to each tube 27 (40-100 μL) of Factor Xe sciution, and incubate for 10 min. Add a 50 (100-250 µl volume of Chromogenic substrate solution. Stop the reaction after 4.0 min with a 5V (100-250 µL) volume of Acette acid solutions. Meanure the absorbance of each solution at 405 rem, susing a suitable spectrophotometer ser violet-Woble Soestay (837)) agamst brank 31. The reading of blank $12 relative to blank BT is NMT 10.05 absorbance unit
Calculatione: For each series, calculate the regression of the absorbance against log concentrations of the Sample solutions and of the Standard solutions, and calculate the potency of the Enoxaparım Sodium in IU of Anti-Factor Ka activityvin, using statistical methods for parallel Bine assays. The four Independent log relative potency estimates are then combined to obtain the final geometric mean its
confidence limits are calculated. Express the Anti Factor Xa activity of Enoxaparin Sodiuming Acceptance criteria: The potency in NLT 90 and NMT 125 Artifactor Xa Uing on the dried basic
4 OTHER COMPONENTS
Benzyl Alcohol Content
Mobile phase: Acetonitrile methan and water (3.1:16)
Standard solution: 0.1 mg/mL of USP Benzyl Alcohol RS in water
Sample solution: Weigh 1.5 g of Enoxaparin Sodium into a 10-m volumetric flask, and dissolve in 50 m of sodium Allow tu stand at room temperature for about 1 h. Add 1.5 mL of glacial acetic acid, dilute with a to volume, and mix
Chromatographic system
See Chromateraphy 1821) Setem Sultabit)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 256 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 15-cm stainless steel; packing L7
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min, maintained constant to ±10%
Injection volume: 20 μL
Analysis
Samples: Standards and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of benzyl alcohol in the portion of Enoxaparin Sodium taken:
Result = (rU/(rS) × (CS /CU) x 100
rU = peak area of benzyl alcohol from the sample solution
rS = peak area of benzyl alcohol from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of benzyl alcohol in the Standard solution (mg/ml)
CU = concentration of Enoxaparin Sodium in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0,1%
Nitrogen Determination (461), Method II: 1.8-2.5% on the dried bams
(See Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy)
Cesium chloride solution 1.27 mg/mL of costum oblonde hidrochloric acid
Standard solution A: 0.0025% of sodium chloride Cesum chloride auton
Standard solution : 60050% of sodium chiende in Cesium chloride solution
Standard solution C: 0.0075% of sodium chloride in Cesium chloride solution
Sample solution: Transter 50.3 mg of Enoxaparin Sodium to a 100-ml volumetric fask, and dissolve in and elilute with Cesium chloride solution to volume.
Analysis
Samples: Cesium chiotole solution, Standard solution A. Standard solution B Standard solution C, and Sample solution
Concomitantly determine the sosorbances of the Cestum chloride solution (blank), Sample solution, and Standard solutions at 330.3 mm, using a sodium hollow-cathode lamp and an air-acetylene flame. Using the absorbances of Standard solutions A-C, determine the sodium content in the Sangle solution after an appropriate blank correction.
Acceptance criteria: 11.3%-13.h on the dried basis
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
pH: 6.2-7.7 for a 100% solution in water.
Sample: 10.0%
Analysis: Dry the Sample in a vacuum at 70 for 6 h
Acceptance criteria: NMT 100%
Sample solution: 0.5 mg/ml, of Enoxapann Sodium in 11323 Mharoshioris ac
(See Attrautolet Vible Spectroscopy(BSD)
Analysis: Obtain the UV spects of the Standard solution and the Sample salution between 200 and 300 m against a 0.01 Nhudrochloric acid blank.
Calculate the spoofic absorbance at the wavelength of maximum absorbance at 231 +2 nm, with reference to the cried outstamos
Result = A x 100 x 1000/[M x I x (100-E)]
A = absorbance at the wavelength of maxmum absorbance
M = weight of Enoxaparin Sudium in the Sample acution (mg)
I = path length (typically 1 cm)
E = loss on drying (%)
Acceptance criteria: 14.0-200.0 on the dried basis
Bacterial Endotoxins Test 〈85〉: It contains NMT 0.01 USP Endotoxin Unit/IU of Anti-Factor Xa activity.
Anti-Factor IIa Activity
Acetic acid solution, pH 7.4 polyethylene glycol 6000 buffer, pH 7.4 buffer, pH 8.4 buffer, and Human antithrombin III solution: Proceed as directed in the Assay for Anti-Factor Xa Activity, except that the concentration of the Human antithrombin at solution is 1.5 Antithrombin UnitimL
Thrombin human solution: lleconstitute thrombin human (see leggents imcators and Golutions Resent Specification) in water and dilute in pH 7.4 polyethylene glycol 6000 buffer to obtain a solution having a concentration of 5 Thrombin Unts/m
Chromogenic substrate solution: Prepare a solution of a saltable chmmmogenic substrate for an amidolytic test (ane Brants indicators.ond Boutons-Remount Sexcitations for thrombin in to obtain a concentration of about 3 m immediately before uso, dilute with gif buffer to 15 m
Standard solutions: Reconstitute the entire contents of an ampul of USP Enoxaparin Sodium for Diosssays is with wates and dilute with phr 74 buffer to obtain four dilutions having concentrations in the range between 0.015 and 0.075 IU-of Anti-Factor Ila activity/ml
Sample solutions: Proceed as directed under Standard solutions to obtain concentrations of Enoxapann Sodium similar to those obtained for The Standard solutions
Analysis: Pmceed as directed in the Assay for Anti-Factor Xs Activity, except use Thrambir hanan ankition instead of Factor Xa anktion and
use Human antithrombination as described above
Calculations: For each series, calculate the regression of the absorbance against log concentrations of the Sample solutions and of the Standard solutions, and calculate the potency of the Enoxapam Sodium in U of Anti-factor fla activity/mg using statistical methods for parallel ling line assays. The four independent dilution estimates are then combined to abtain the final weighted mean. Then calculate the confidence limits Express the Anti Factor ila activity of Enoxaparin Sodium/img
Acceptance criteria: It has a potency of NL.7 20.0 and MMT 350 Anti Factor la IU/mg on the dried basis
MOLAR RATIO OF SULATE TO CARRYLATE
Mobile phase: Carbon dioxide-free water
Sample solution: 5 mg/mL of Enoxaparin Sodium in Mobile phase
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: Ion
Columns: One 1.5-cm × 2.5-cm column, packed with an anion-exchange resin packing L64; and one 1.5-cm × 7.5-cm column, packed with a
cation-exchange resin packing L65. The outlet of the anion-exchange column is connected to the inlet of the cation-exchange column.
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Analysis
Sample: Sample solution
[Note—Regenerate the anion-exchange column and the cation-exchange column with 1 N sodium hydroxide and 1 N hydrochloric acid, respectively, between two injections.]
Inject the Sample solution into the anion-exchange column, and collect the eluate from the cation-exchange column in a beaker at the outlet until the ion detector reading retums to the baseline volue. Quantitatively transfer the elkarte to a titration vessel containing a magnetic stiming bar and dilute with Mobile phase is about 60 mL. Position the titration vessel on a magnetic stirrer and immerse the electrodes. Note the initial conductivity reading, and timate with approximately 1.aodium hydroxide added in 100-µl portions. Non Prepare the sodium hydnszide solution in Mobile phase Record the buret reading and the conductivity meter reading after each addition of the sodium hydroxide solution.
Calculations: Pict the conductivity measurements on the y-axis against the volumes of sodium hydroxide added on the xaxis The graph will have three trear sections-an initial downward slope, a middle slight rive, and a finalitat. For each of these sections draw the best-ht atraight lines, using Sinear regression analysis. At the points where the first and second straight Siness intersect and where the second and Third lines intersect, craw perpendiculars to the axis to determine the volumes of sodium hydroxide taken up by the sample at those points. The point where the fest and second Ines intersect comesponds to the volume of sodium hydroxide taken up by the sulfate groups (VS). The point where the second and third lines intersect corresponds to the volume of sodium hydroxide consumed by the sulfate and the carboxylate groups together (VT).
Calculate the molar ratio of sulfate to carboxylate:
Result = VS(VT-VS)
Acceptance criteria: The molar ratio of sulfate to carbonylate is NCT 1.8
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Раскали мав това: Preserve in tight containers, and stare below 400, preferably at room temperature.


