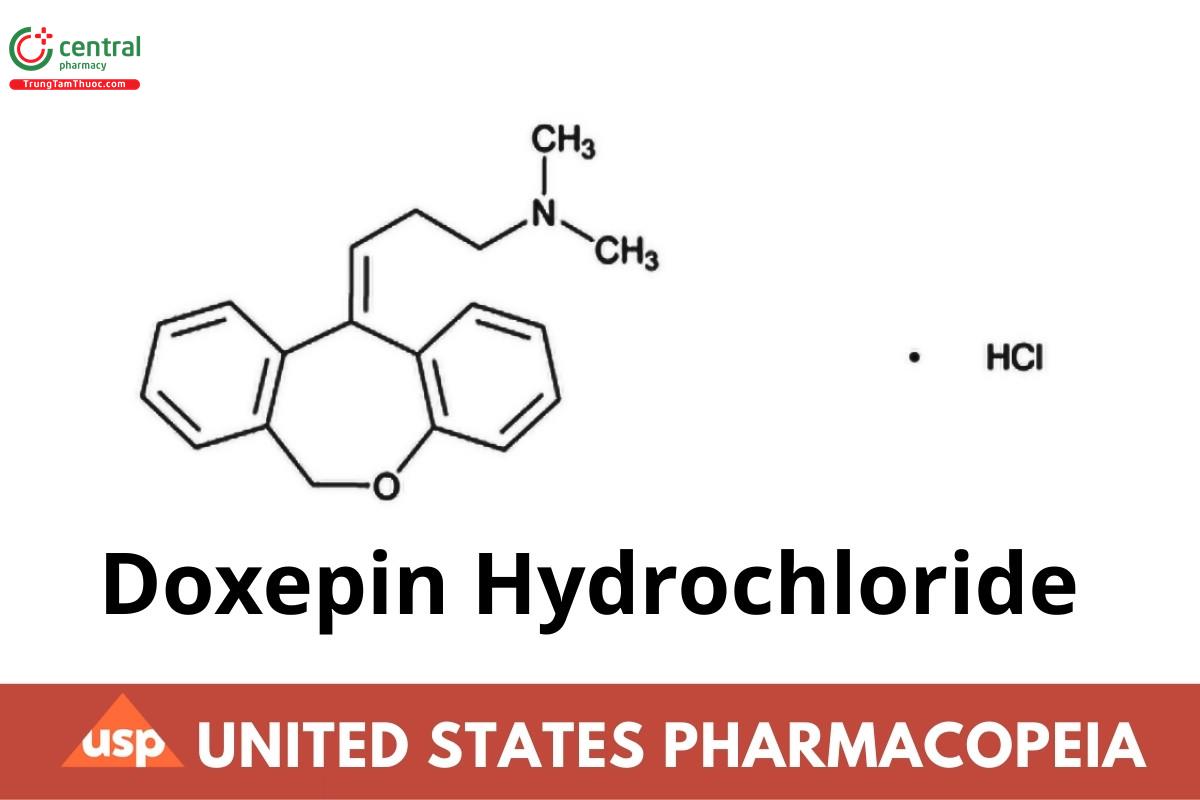
Doxepin Hydrochloride
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
1-Propanamine, 3-dibenz[b,e]oxepin-11(6H)ylidene-N,N- dimethyl-, hydrochloride;
N,N-Dimethyldibenz[b,e]oxepin-Δ11-
11-(6H)-γ-propylamine hydrochloride CAS RN®: 1229-29-4; UNII: 3U9A0FE9N5.
(E)-isomer CAS RN®: 4698-39-9; UNII: CU61C5RH24.
(Z)-isomer CAS RN®: 25127-31-5; UNII: XI27WMG8QK.
1 DEFINITION
Doxepin Hydrochloride, an (E) and (Z) geometric isomer mixture, contains the equivalent of NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of doxepin hydrochloride (C19H21NO · HCl), calculated on the dried basis. It contains NLT 13.6% and NMT 18.1% of the (Z)-isomer, and NLT 81.4% and NMT 88.2% of the (E)-isomer.
2 IDENTIFICATION
Change to read:
A. SPECTROSCOPIC IDENTIFICATION TESTS (197), Infrared Spectroscopy: 197K or 197A (USP 1-May-2021)
Change to read:
B. The retention times of the major peaks for the (E)- and (Z)-isomers of the Sample solution correspond to those (USP 1-May-2021) of the Standard solution, as obtained in the Assay.
Change to read:
C. IDENTIFICATION TESTS GENERAL (191), Chemical Identification Tests. Chloride
Diluent: Alcohol and water (50:50)
Sample solution: 10 mg/mL of Doxepin Hydrochloride in Diluent
Acceptance criteria: Meets the requirements of the test for amine hydrochlorides (USP 1-May-2021)
3 ASSAY
Change to read:
PROCEDURE
Solution A: 27.6 g/L of monobasic sodium phosphate in water (USP 1-May-2021)
Mobile phase: Methanol and Solution A (30:70) (USP 1-May-2021) Adjust with diluted phosphoric acid (USP 1-May-2021) to a pH of 2.5.
Standard solution: 0.1 mg/mL of USP Doxepin Hydrochloride RS in Mobile phase
Sample solution: 0.1 mg/mL of Doxepin Hydrochloride in Mobile phase. Sonication may be used to aid in dissolution.
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography (621) System Suitability)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 254 nm
Column: 4-mm x 12.5-cm 5-µm (USP 1-May-2021) Packing L7
Column temperature: 50°
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Injection volume: 20 µl
Run time: NLT 2 times the retention time of the (E)-isomer (USP 1-May-2021)
System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
[Note: The relative retention times for the (E) and (2) isomera are 1.0 and 1.1, respectively) (USP 1-Mar-2021)
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 1.5 between the (E)- and (Z)-isomers
Tailing factor: NMT 2.0 each for (USP 1-May-2021) the (E)- and (Z)-isomers
Relative standard deviation: NMT 2.0% each for the (E)- and (Z)-isomers (USP 1-May-2021)
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of doxepin hydrochloride (C19H21NO · HCl) in the portion of Doxepin Hydrochloride taken:
Result = [(rU(Z) + rU(E) )/(rS(Z) + rS(E) ] × (CS /CU ) × 100
rU(Z) = peak response of the (Z)-isomer from the Sample solution
rU(E) = peak response of the (E)-isomer from the Sample solution
rS(Z) = peak response of the (Z)-isomer from the Standard solution
rS(E) = peak response of the (E)-isomer from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Doxepin Hydrochloride RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Doxepin Hydrochloride in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Calculate the percentage of the (Z)-isoner of doxepin hydrochloride (C19H21NO · HCl) in the portion of Doxepin Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rU(Z)/(rS(Z)) × (CS /CU ) × 100
rU(Z) = peak response of the (Z)-isomer from the Sample solution
rU(E) = peak response of the (Z)-isomer from the Standard solution
rS(Z) = concentration of the (Z)-isomer in the Standard solution (mg/mL) based on the labeled percentage of the (Z)-isomer in USP Doxepin Hydrochloride RS
rS(E) = concentration of Doxepin Hydrochloride in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Calculate the percentage of the (E)-isomer of doxepin hydrochloride (C,H, NO-HCI) in the portion of Doxepin Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rU(E)/(rS(E)) × (CS /CU ) × 100
rU(E) = peak response of the (E)-isomer from the Sample solution
rS(E) = peak response of the (E)-isomer from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of the (E)-isomer in the Standard solution (mg/ml) based on the labeled percentage of the (E)-isomer in USP Doxepin Hydrochloride RS
CU = concentration of Doxepin Hydrochloride in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria
Doxepin hydrochloride: 98.0%-102.0% on the dried basis
(Z)-Isomer of doxepin hydrochloride: 13.6%-18.1%
(E)-Isomer of doxepin hydrochloride: 81.4%-88.2%
4 IMPURITIES
RESIDUE ON IGNITION (281): NMT 0.2%
Change to read:
ORGANIC IMPURITIES
[NOTE-This procedure is not intended to resolve the (E)- and (Z)-isomers of doxepin hydrochloride. Minor variations in Mobile phase composition could result in a shoulder in the trailing edge of doxepin. In cases where there may be separation, both the (E)- and (Z)-isomers should be used in the appropriate calculation.
Solution A: Transfer 1 mL of phosphoric acid to a 10-ml volumetric flask containing about 5 mL of water. Cool and dilute with water to volume (USP 1-May-2021)
Buffer: 1.42 g/L of dibasic sodium phosphate, adjusted with Solution A to a pH of 7.7
aps/fgtamthuoc.com/
USP-NF Doxepin Hydrochloride
Mobile phase: Methanol, acetonitrile, and Buffer (50:20:30)
Diluent: To each liter of Mobile phase add 2 mL of 2N sodium hydroxide TS (USP 1-May-2021)
Standard solution: 0.001 mg/mL each of USP Doxepin Hydrochloride RS, USP Doxepin Related Compound A RS, and USP Doxepin Related Compound B RS: and 0.002 mg/mL of USP Doxepin Related Compound C RS in Diluent. Sonication for about 1 min may be used to aid the initial dissolution of the compounds.
*Sensitivity solution: 0.0005 mg/mL each of USP Doxepin Hydrochloride RS, USP Doxepin Related Compound A RS, and USP Doxepin Related Compound B RS: and 0.001 mg/mL of USP Doxepin Related Compound C RS from Standard solution in Diluent (USP 1-May-2021)
Sample solution: 1 mg/mL of Doxepin Hydrochloride in Diluent
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography (621). System Suitability)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 215 nm
Column: 4.6-mm x 25-cm, 5-um packing L1
Column temperature: 30"
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Injection volume: 20 µL
Run time: 2.2 times the retention time of doxepin
System suitability
Samples: Standard solution and Sensitivity solution (USP 1-May-2021)
[Nom-See Table 1 for relative retention times. The doxepin related compound C peak will be the largest peak in the Standard solution chromatogram.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 1.5 between doxepin related compound A and doxepin related compound C; NLT 1.5 between doxepin related compound
C and doxepin related compound B, Standard solution
Relative standard deviation: NMT 5.0% for doxepin, Standard solution (USP 1-May-2021)
Signal-to-noise ratio: NLT 10 for doxepin, doxepin related compound A, doxepin related compound B, and doxepin related compound C, Sensitivity solution (USP 1-May-2021)
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each doxepin related compound in the portion of Doxepin Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rU/(rS) × (CS /CU ) × 100
rU = peak response of doxepin related compound A, B, or C from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of doxepin related compound A, B, or C from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Doxepin Related Compound A RS, USP Doxepin Related Compound B RS, or USP Doxepin Related Compound C RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Doxepin Hydrochloride in the Sample solution (mg/ml.)
Acceptance criteria: See Table 1. Disregard any peak with a relative retention time less than 0.25. The reporting threshold is 0.05% (USP 1-May-2021)
| Name | Relative Retention Time | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
| Doxepin related compound A | 0.48 | 0.10 |
| Doxepin related compound C | 0.55 | 0.20 |
| Doxepin related compound B | 0.63 | 0.10 |
| Doxepin | 1.0 | - |
| Any individual, unspecified impurity | - | 0.10 |
| Total impurities | - | 0.50 (USP3-May-2021) |
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
LOSS ON DRYING (731)
Analysis: Dry under vacuum at 60 for 3 h.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.5%
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
PACKAGING AND STORAGE: Preserve in well-closed containers.


