Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
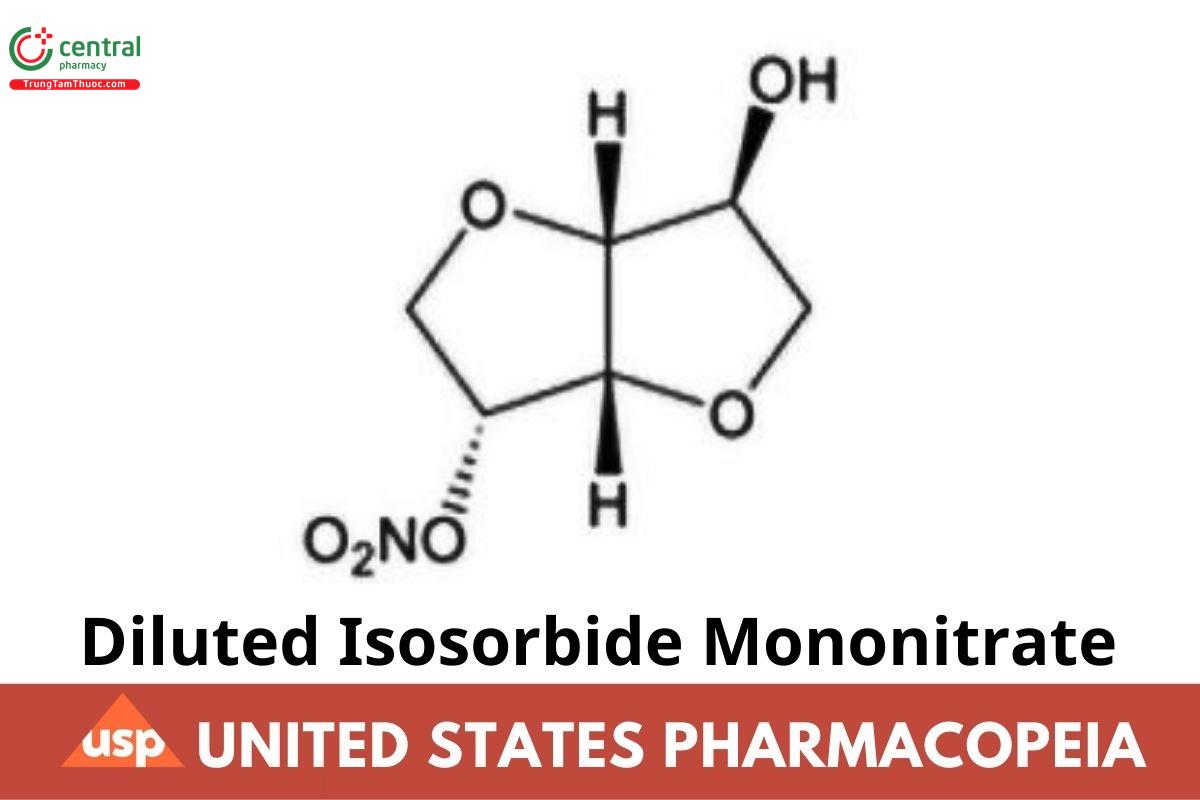
C₆H₉NO₆ 191.14
D-Glucitol, 1,4:3,6-dianhydro-, 5-nitrate;
1,4:3,6-Dianhydro-D-glucitol 5-nitrate CAS RN®: 16051-77-7; UNII: LX1OH63030.
1 DEFINITION
Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate is a dry mixture of isosorbide mononitrate (C₆H₉NO₆) with lactose or other suitable excipients to permit safe handling. It contains NLT 95.0% and NMT 105.0% of the labeled amount of isosorbide mononitrate (C₆H₉NO₆).
[Caution-Exercise proper precautions in handling undiluted isosorbide mononitrate, which is a powerful explosive and can be exploded by percussion or excessive heat. Only exceedingly small amounts should be isolated.]
2 IDENTIFICATION
Change to read:
2.1 A. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197A or 197K
Sample: Shake a suitable amount of Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate, equivalent to about 25 mg of isosorbide mononitrate, with 10 mL of acetone for 5 min. Filter, evaporate to dryness at a temperature below 40°, dry the residue in a vacuum over phosphorus pentoxide for 16 h, and use the residue.
Standard: Prepare as directed for the Sample using a suitable amount of USP Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate RS.
Acceptance criteria: Meets the requirements
2.2 B. The retention time of the major peak of the Sample solution corresponds to that of Standard solution A, as obtained in the Assay.
3 ASSAY
Change to read:
3.1 Procedure
Mobile phase: Methanol and water (5:95)
Standard solution A: 2.0 mg/mL of isosorbide mononitrate prepared as follows. Transfer a suitable amount of USP Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate RS to a suitable volumetric flask, dissolve in a suitable volume of water, add a volume of methanol equivalent to 4% of the flask volume, and dilute with water to volume.
Standard solution B: 0.05 mg/mL of isosorbide mononitrate related compound A prepared as follows. Transfer a suitable amount of USP Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate Related Compound A RS to a suitable volumetric flask, dissolve in a suitable volume of water, add a volume of methanol equivalent to 4% of the flask volume, and dilute with water to volume.
System suitability solution: 0.02 mg/mL of isosorbide mononitrate and 0.005 mg/mL of isosorbide mononitrate related compound A prepared as follows. Transfer 1.0 mL of Standard solution A, 10.0 mL of Standard solution B, and 4.0 mL of methanol to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. Filter a portion of the solution, discarding the first few milliliters of the filtrate.
Sample solution: Nominally 2.0 mg/mL of isosorbide mononitrate from Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate prepared as follows. Transfer a suitable amount of Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate to a suitable volumetric flask, dissolve in 50% of the flask volume of water, add a volume of methanol equivalent to 4% of the flask volume, and dilute with water to volume. Filter a portion of the solution, discarding the first few milliliters of the filtrate.
Chromatographic system
- (See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
- Mode: LC
- Detector: UV 220 nm
- Column: 4-mm × 12.5-cm; 5-µm packing L1
- Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min, increase to 3.0 mL/min at about 8.5 min. [Note-Make sure that the isosorbide mononitrate peak has completely eluted before increasing the flow rate.]
- Injection volume: 50 µL
- Run time: NLT 5 times the retention time of isosorbide mononitrate
System suitability
- Samples: Standard solution A and System suitability solution
- [Note-The relative retention times for isosorbide mononitrate related compound A and isosorbide mononitrate are 0.8 and 1.0, respectively.]
- Suitability requirements
- Resolution: NLT 2.0 between isosorbide mononitrate related compound A and isosorbide mononitrate, System suitability solution
- Relative standard deviation: NMT 0.73%, Standard solution A
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution A and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of the labeled amount of isosorbide mononitrate (C₆H₉NO₆) in the portion of Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate taken:
Result = (rᵤ/rₛ) × (Cₛ/Cᵤ) × 100
rᵤ = peak response of isosorbide mononitrate from the Sample solution
rₛ = peak response of isosorbide mononitrate from Standard solution A
Cₛ = concentration of isosorbide mononitrate in Standard solution A (mg/mL)
Cᵤ = nominal concentration of isosorbide mononitrate in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: 95.0%–105.0%
4 IMPURITIES
Add the following:
4.1 Limit of Nitrate
[Note-Use water with a resistivity of NLT 18 megohm-cm to prepare the solutions.]
Mobile phase: 20 mM potassium hydroxide in water. [Note-Mobile phase can be generated electrolytically using an automatic eluant generator.]
Sensitivity solution: 0.5 µg/mL of USP Potassium Nitrate RS in water
Standard solution: 5.0 µg/mL of USP Potassium Nitrate RS in water
Sample solution: Nominally 1000 µg/mL of isosorbide mononitrate from Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate in water
Chromatographic system
- (See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
- Mode: LC
- Detector: Conductivity with suppression
- Columns
- Guard: 4.0-mm × 5-cm; 13-µm packing L120. [Note-Alternatively, a 4.0-mm × 0.5-cm column that contains 5.0-µm packing L91 may be used.]
- Analytical: 4.0-mm × 25-cm; 7.5-µm packing L113. [Note-Alternatively, a 4.0-mm × 15-cm column that contains 5.0-µm packing L91 may be used.]
- Column temperature: 30°
- Flow rate: 1 mL/min
- Injection volume: 100 µL
- Run time: NLT 2 times the retention time of nitrate
System suitability
- Sample: Sensitivity solution
- Suitability requirements
- Relative standard deviation: NMT 5.0%
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of nitrate as potassium nitrate relative to the labeled amount of isosorbide mononitrate in the portion of Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate taken:
Result = (rᵤ/rₛ) × (Cₛ/Cᵤ) × 100
rᵤ = peak response of the nitrate ion from the Sample solution
rₛ = peak response of the nitrate ion from the Standard solution
Cₛ = concentration of USP Potassium Nitrate RS in the Standard solution (µg/mL)
Cᵤ = nominal concentration of isosorbide mononitrate in the Sample solution (µg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.5%, calculated as potassium nitrate
Change to read:
4.2 Organic Impurities
[Note-It is recommended to use GC-grade methanol to prepare the solutions.]
Sensitivity solution: 1.5 µg/mL of isosorbide mononitrate in methanol prepared as follows. Transfer a suitable amount of USP Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate RS to a suitable volumetric flask. Add methanol to about 80% of the final volume and sonicate for 30 min with intermittent shaking. Dilute with methanol to volume. Centrifuge a portion of the solution and use the clear supernatant.
Standard solution: 3 µg/mL of isosorbide mononitrate, 15 µg/mL of isosorbide, and 7.5 µg/mL each of isosorbide mononitrate related compound A and isosorbide dinitrate in methanol prepared as follows. Transfer a suitable amount of USP Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate RS, USP Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate Related Compound A RS, and USP Diluted Isosorbide Dinitrate RS to a suitable volumetric flask. Add methanol to about 80% of the final volume and sonicate for 30 min with intermittent shaking. Add an appropriate amount of USP Isosorbide RS to the volumetric flask, and dilute with methanol to volume. Centrifuge a portion of the solution and use the clear supernatant.
Sample solution: Nominally 3 mg/mL of isosorbide mononitrate in methanol prepared as follows. Transfer a suitable amount of Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate to a suitable volumetric flask. Add methanol to about 80% of the final volume, sonicate for 30 min with intermittent shaking, and dilute with methanol to volume. Centrifuge a portion of the solution and use the clear supernatant.
Chromatographic system
- (See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
- Mode: GC
- Detector: Flame ionization
- Column: 0.53-mm × 30-m fused-silica capillary; coated with a 1.5-µm film of phase G2
- Temperatures
- Injection port: 150°
- Column: 125°
- Detector: 275°
- Carrier gas: Hydrogen
- Flow rate: 180 cm/s (linear velocity)
- Injection volume: 1 µL
- Injection type: Split, split ratio 1:6
- Run time: NLT 3 times the retention time of isosorbide mononitrate
System suitability
- Samples: Sensitivity solution and Standard solution
- [Note-See Table 1 for the relative retention times.]
- Suitability requirements
- Relative standard deviation: NMT 5.0% each for isosorbide mononitrate, isosorbide, isosorbide mononitrate related compound A, and isosorbide dinitrate, Standard solution
- Signal-to-noise ratio: NLT 10, Sensitivity solution
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of isosorbide, isosorbide mononitrate related compound A, and isosorbide dinitrate relative to the labeled amount of isosorbide mononitrate in the portion of Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate taken:
Result = (rᵤ/rₛ) × (Cₛ/Cᵤ) × 100
rᵤ = peak response of isosorbide, isosorbide mononitrate related compound A, or isosorbide dinitrate from the Sample solution
rₛ = peak response of isosorbide, isosorbide mononitrate related compound A, or isosorbide dinitrate from the Standard solution
Cₛ = concentration of isosorbide, isosorbide mononitrate related compound A, or isosorbide dinitrate in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
Cᵤ = nominal concentration of isosorbide mononitrate in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Calculate the percentage of any unspecified impurity relative to the labeled amount of isosorbide mononitrate in the portion of Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate taken:
Result = (rᵤ/rₛ) × (Cₛ/Cᵤ) × 100
rᵤ = peak response of each unspecified impurity from the Sample solution
rₛ = peak response of isosorbide mononitrate from the Standard solution
Cₛ = concentration of isosorbide mononitrate in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
Cᵤ = nominal concentration of isosorbide mononitrate in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: See Table 1. The reporting threshold is 0.05%.
Table 1
| Name | Relative Retention Time | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
| Isosorbide | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| Isosorbide mononitrate related compound A | 0.6 | 0.25 |
| Isosorbide mononitrate | 1.0 | - |
| Isosorbide dinitrate | 1.6 | 0.25 |
| Any unspecified impurity | - | 0.10 |
| Total impurities | - | 0.5 |
5 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
5.1 Packaging and Storage
Preserve in tight containers. Store at a temperature of 20°–30°.
Change to read:
5.2 USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Isosorbide RS
[Note-USP Diluted Isosorbide Dinitrate RS, USP Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate RS, and USP Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate Related Compound A RS are dry mixtures of an active component with suitable excipients to permit safe handling. For quantitative applications, calculate the concentration of the active component on the basis of the content stated on the label.]
USP Diluted Isosorbide Dinitrate RS
USP Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate RS
USP Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate Related Compound A RS
1,4:3,6-Dianhydro-d-glucitol 2-nitrate in lactose.
C₆H₉NO₆ 191.14
USP Potassium Nitrate RS


