Diisopropanolamine
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
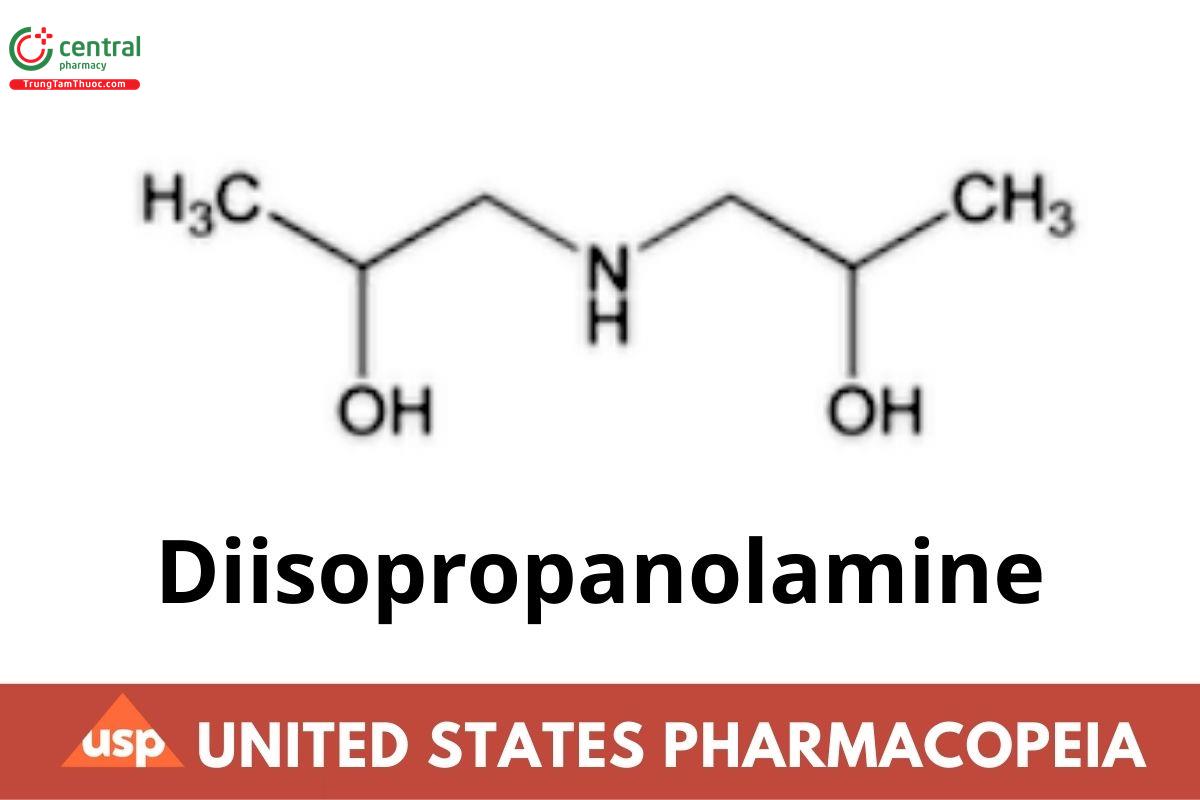
C6H15NO2 133.19
2-Propanol, 1,1′-iminobis-;
1,1′-Iminodi-2-propanol CAS RN®: 110-97-4.
1 DEFINITION
Diisopropanolamine is a mixture of isopropanolamines, consisting largely of diisopropanolamine. It contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of isopropanolamines, calculated as NH(C3H6OH)2 on the anhydrous basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
A. The IR absorption spectrum of a thin lm exhibits regions of absorption between 2.8 and 4.0 µm, between 6.7 and 7.1 µm, and between 8.5 and 9.4 µm; and several characteristic peaks, the most pronounced being at about 7.3, 7.5, 8.3, 9.6, 10.4, and 10.7 µm.
3 ASSAY
Procedure
Sample: 2 g
Blank: 50 mL of water
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry 〈541〉.)
Mode: Direct titration
Titrant: 0.5 N hydrochloric acid VS
Endpoint detection: Visual
Analysis: Transfer the Sample to a 250-mL conical ask. Add 50 mL of water and bromocresol green TS. Titrate with Titrant. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction.
Calculate the percentage of isopropanolamines, expressed as NH(C3H6OH)2, in the portion of Diisopropanolamine taken:
Result = {[(VS− VB ) × N × F]/W} × 100
VS = Titrant volume consumed by the Sample (mL)
VB = Titrant volume consumed by the Blank (mL)
N = actual normality of the Titrant (mEq/mL)
F = equivalency factor, 0.1332 g/mEq
W = Sample weight (g)
Acceptance criteria: 98.0%–102.0% on the anhydrous basis
4 IMPURITIES
Limit of Triisopropanolamine
Indicator solution: 1.5 mg/mL of methyl orange and 0.8 mg/mL of xylene cyanole FF
Sample: 20 g
Blank: 100 mL of methanol
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry 〈541〉.)
Mode: Direct titration
Titrant: 0.5 N alcoholic sulfuric acid VS
Endpoint detection: Visual
Analysis: To a glass-stoppered, 500-mL conical ask add 100 mL of methanol and 6–8 drops of Indicator solution, and neutralize with 0.1 N alcoholic sulfuric acid or 0.1 N alcoholic potassium hydroxide. The neutral solution is amber when viewed by transmitted light and is red brown when viewed by reflected light. Add the Sample, cautiously add 75 mL of acetic anhydride, and swirl to dissolve. Allow to stand at room temperature for 30 min. Cool to room temperature, if necessary. Titrate with Titrant. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction.
Calculate the percentage of triisopropanolamine in the portion of Diisopropanolamine taken:
Result = {[(VS − VB ) × N × F]/W} × 100
VS = Titrant volume consumed by the Sample (mL)
VB = Titrant volume consumed by the Blank (mL)
N = actual normality of the Titrant (mEq/mL)
F = equivalency factor, 0.1914 g/mEq
W = Sample weight (g)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 1.0% by weight
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
Water Determination, Method I〈921〉
Solvent: A mixture of 5.0 mL of glacial acetic acid and 25 mL of methanol
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.50%
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers. No specific storage conditions are required.


