Dextran 40
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here

Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
1 DEFINITION
Dextran 40 is derived by controlled hydrolysis and fractionation of polysaccharides elaborated by the fermentative action of certain strains of Leuconostoc mesenteroides (NRRL, B.512 F; NCTC, 10817) on a sucrose substrate. It is a Glucose polymer in which the linkages between glucose units are almost entirely of the α-1:6 type. Its weight average molecular weight is in the 35,000–45,000 range.
2 IDENTIFICATION
2.1 A. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197K
2.2 B.
Sample solutions: Prepare four solutions of Dextran 40 in water, in such a manner that the concentrations are accurately known and approximately evenly distributed in the range of 2%–0.5%.
Analysis: Using a capillary tube viscometer having dimensions such that the ow time of water is NLT 100 s, measure the ow times of water and of the Sample solution at 20°.
Calculate the viscosity numbers of each of the Sample solutions:
Result = {ln[(RD) × (t/t0)]}/C
RD = ratio of the density of the individual Sample solution to that of water
t = Sample solution ow time
t0 = water ow time
C = concentration of Dextran 40 in the Sample solution (g/mL)
Plot the viscosity numbers of each of the Sample solutions against their respective concentrations, draw the straight line of best t through the points, and extrapolate to zero concentration.
Acceptance criteria: The value of the intercept is 18–23 mL/g.
3 IMPURITIES
3.1 Chloride and Sulfate, Sulfate 〈221〉
A 1.5-g portion of Dextran 40 shows NMT 0.03%, which corresponds to 0.45 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid.
3.2 Limit of Nitrogenous Impurities (where it is labeled as intended for use in the preparation of injectables)
Sulfate solution: To 1000 mL of sulfuric acid add 5 g of anhydrous cupric sulfate and 500 g of potassium sulfate. Dissolve by heating, and store at 60°. [Note—If storage at 60° is not possible, prepare a smaller quantity of Sulfate solution on the day of use, adjusting the proportions accordingly.]
Indicator: Dilute a mixture of 20 mL of a 0.1% solution of bromocresol green in alcohol and 4 mL of methyl red TS with water to 100 mL. Sample solution: Transfer 0.2 g of Dextran 40, accurately weighed, to a micro-Kjeldahl ask. Add 4 mL of Sulfate solution. Analysis
Sample: Sample solution
Heat until the solution exhibits a clear green color and the sides of the ask are free from carbonaceous material. Cool, and transfer the solution to a steam distillation unit. Rinse the Kjeldahl ask three times with 5 mL of water, adding the washings to the solution. Add 15 mL of 45% sodium hydroxide solution, immediately close the distillation apparatus, and commence steam distillation without delay. Receive the distillate in 1 mL of Indicator in a 100-mL ask, keeping the end of the condensing tube below the liquid surface for 5 min and above the liquid surface for 1 min. Upon completing the distillation, remove the receiving ask, and rinse the end of the condensing tube with a small quantity of water, adding the rinse to the distillate. Titrate the distillate with 0.010 N hydrochloric acid until the color changes from blue to reddish violet. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction.
Acceptance criteria: The corrected volume of 0.010 N hydrochloric acid titrated does not exceed 0.14 mL (0.01%, as N).
3.3 Limit of Alcohol and Related Impurities
Standard solution: To 25.0 mL of the Sample solution add 0.5 mL of a 2.5% (w/v) solution of n-propyl alcohol.
Sample solution: Dissolve without heating 5.0 g of Dextran 40 in 100 mL of water, and distill the solution, collecting the rst 45 mL of the distillate. Dilute the distillate with water to 50.0 mL.
Chromatographic system
Mode: GC
Detector: Flame ionization
Column: 2-mm × 1.8-m; packed with S3
Temperatures
Column: 160°
Injection port: 240°
Detector: 210°
Carrier gas: Nitrogen
Flow rate: 25 mL/min
[Note—Injector seals may deteriorate after multiple injections of the Standard solution and Sample solution. Inspect the seals before making a series of injections.]
Injection volume: 1 µL
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution, Sample solution, and a 0.05% (w/v) solution of n-propyl alcohol and water
Acceptance criteria: After corrections for any impurities in the n-propyl alcohol solution and water, the total area of peaks from impurities in the Sample solution does not exceed the area of the n-propyl alcohol solution peak.
3.4 Antigenic Impurities (where it is labeled as intended for use in the preparation of injectables)
Sample solution: Prepare a sterile solution containing 100 mg/mL of Dextran 40 in sodium chloride injection.
Analysis: At intervals of about 48 h, inject three 0.5-mL doses into the peritoneal cavities of each of six guinea pigs. At 14 days after the rst intraperitoneal injection, inject 0.20 mL intravenously into each of three of the guinea pigs, and at 21 days treat the other three guinea pigs similarly. Observe the animals for 30 min after each intravenous injection and again 24 h later.
Acceptance criteria: The animals exhibit no evidence of anaphylactoid reactions, such as coughing, bristling of hair, or respiratory distress.
4 SPECIFIC TESTS
4.1 Optical Rotation, Specific Rotation 〈781S〉
Sample solution: 20 mg/mL of Dextran 40, heated, if necessary, on a water bath to dissolve
Acceptance criteria: +195° to +203°
4.2 pH 〈791〉
Sample solution: A solution (1 in 10)
Acceptance criteria: 4.5–7.0
4.3 Loss on Drying 〈731〉
Analysis: Dry at 105° for 5 h.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 7.0%
4.4 Bacterial Endotoxins Test 〈85〉
(where it is labeled as intended for use in the preparation of injectables): When tested in sodium chloride injection (1 in 10), it contains NMT 1.0 USP Endotoxin Unit/mL.
4.5 Color of Solution
Sample solution: A solution in water (1 in 10)
Blank solution: Water
Analysis: Absorbance at 375 nm in a 4-cm cell
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.20
4.6 Safety:
Inject intravenously 1.0 mL of a sterile solution (1 in 10) of 10% Dextran 40 in saline TS into each of ve mice weighing 18–20 g. The injection period is 10–15 s. If there are no deaths within 72 h, it meets the requirements of the test. If one or more animals die, continue the test using 10 mice weighing 20 ± 0.5 g. If all animals survive for 72 h, the requirements of the test are met.
Change to read:
4.7 Molecular Weight Distribution and Weight and Number Average Molecular Weights
Mobile phase: 7.1 g/L of anhydrous sodium sulfate in water, ltered and degassed
Calibration solutions: Separately prepare 20 mg/mL in Mobile phase, USP Dextran 4 Calibration RS, USP Dextran 10 Calibration RS, USP Dextran 40 Calibration RS, USP Dextran 70 Calibration RS, and USP Dextran 250 Calibration RS
Marker solution: 3 mg/mL each of dextrose and USP Dextran V0 Marker RS in Mobile phase
System suitability solution: 20 mg/mL of USP Dextran 40 RS (RB 1-Jul-2022) in Mobile phase
Sample solution: 20 mg/mL of Dextran 40 in Mobile phase
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: Refractive index
Column: Three 7.5-mm × 30-cm columns; packing L38
Column temperature: Constant temperature
Injection volume: 50 µL
System suitability
Samples: Calibration solutions, Marker solution, and System suitability solution
Suitability requirements
Elution prole: Prole shows two peaks: the rst due to the V0 marker, the second due to dextrose, Marker solution.
Tailing factor: NMT 1.3, for the dextrose peak, Marker solution
Relative standard deviation of the ratio V0:VT: Determine the void volume, V0 , of the system as the inection point of the ascending part
of the rst peak. Determine the total volume, VT , of the system as the maximum of the second peak. The relative standard deviation of the ratioV0:VT is NMT 1%, Marker solution.
Weight average molecular weight: Chromatograph each of the Calibration solutions separately. Divide each prole into at least 60 vertical sections of equal volume increments. (The actual number of sections is represented by the variable a in the equations below.) Record yi the height above the baseline, corresponding to each value of vi , the volume eluted at that section. For each value of vi, calculate the distribution coecient, Ki :
Result = (vi − V0)/(VT − V0)
Find appropriate values of b1, b2, b3, b4, and b5, using a suitable method1 that, when substituted in the equation:
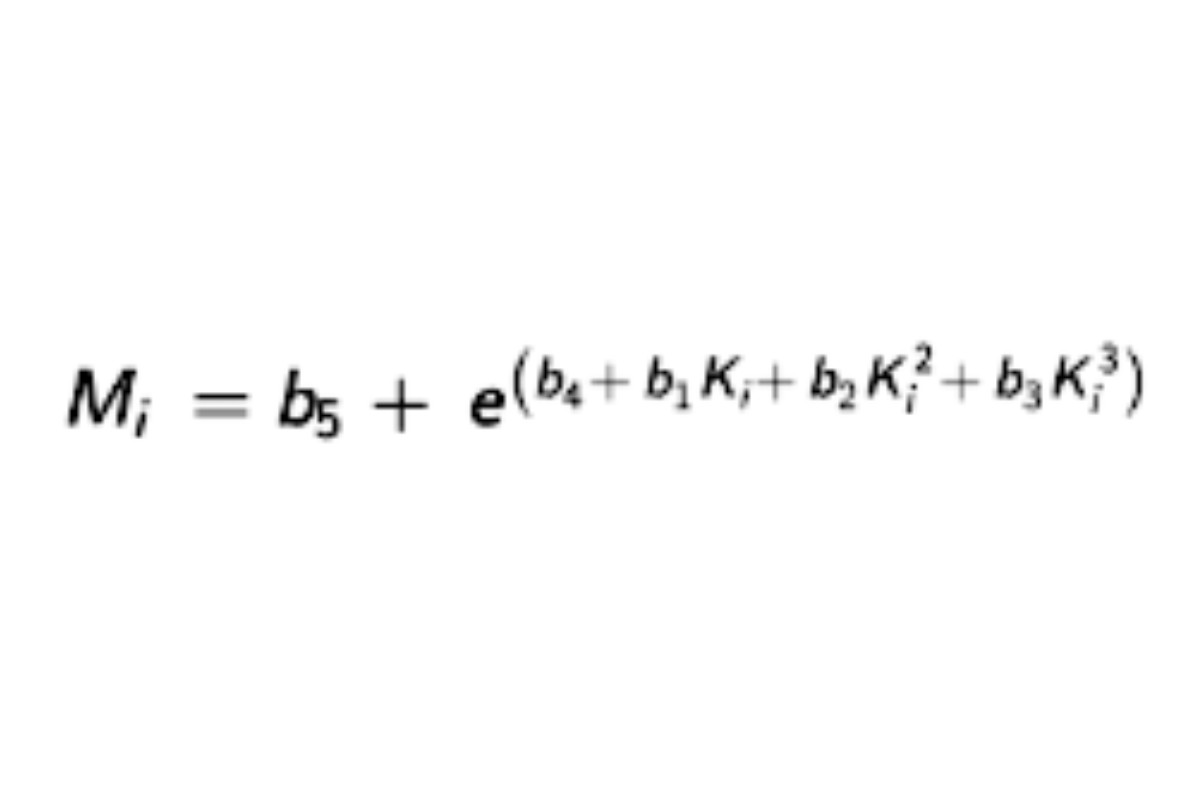
and the resulting values of Mi substituted, along with their corresponding values of yi in the equation:
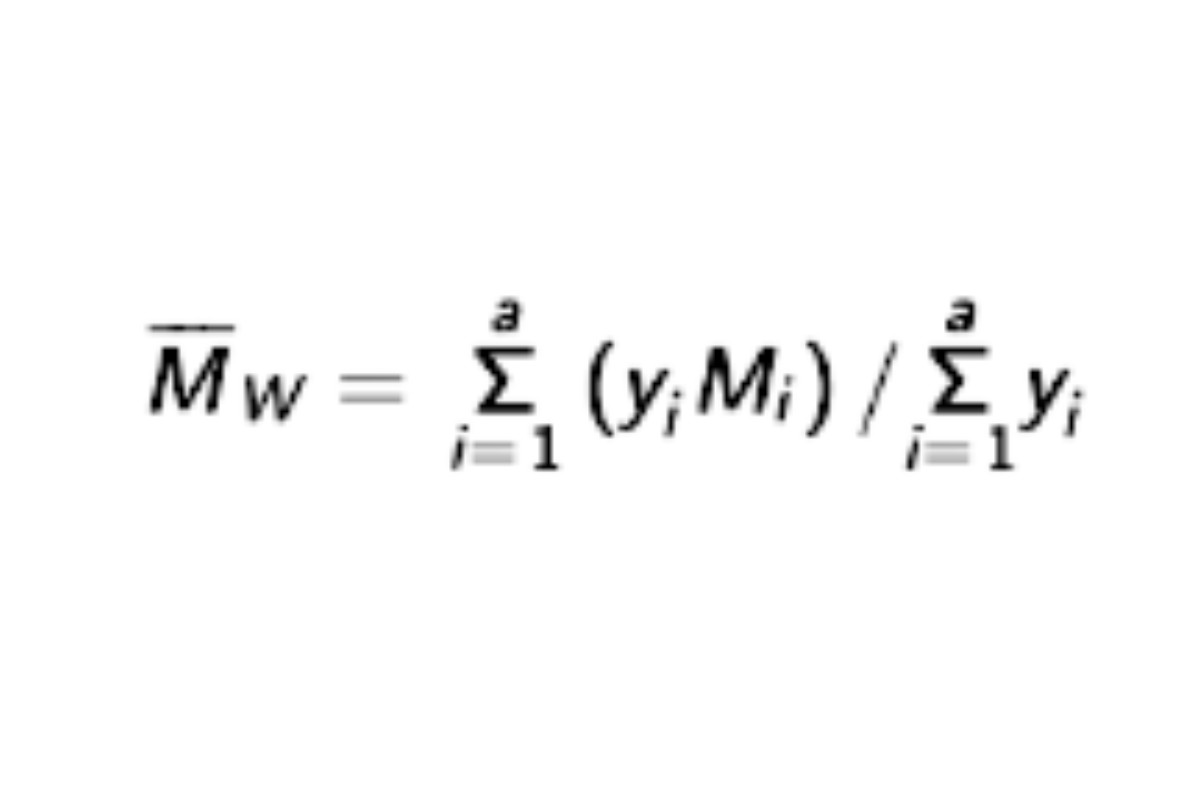
give values of weight average molecular weight, Mw , within 5% of the labeled values for each of the Calibration solutions and 180 ± 2 for dextrose. Using the System suitability solution, calculate Mw of the total molecular weight distribution using the same method, but inserting the now known values of b1, b2, b3, b4, and b5. See the USP Dextran 40 RS certicate for the range. (RB 1-Jul-2022)
Weight average molecular weight, high-fraction: Calculate Mw of the high-fraction dextran eluted through section n:
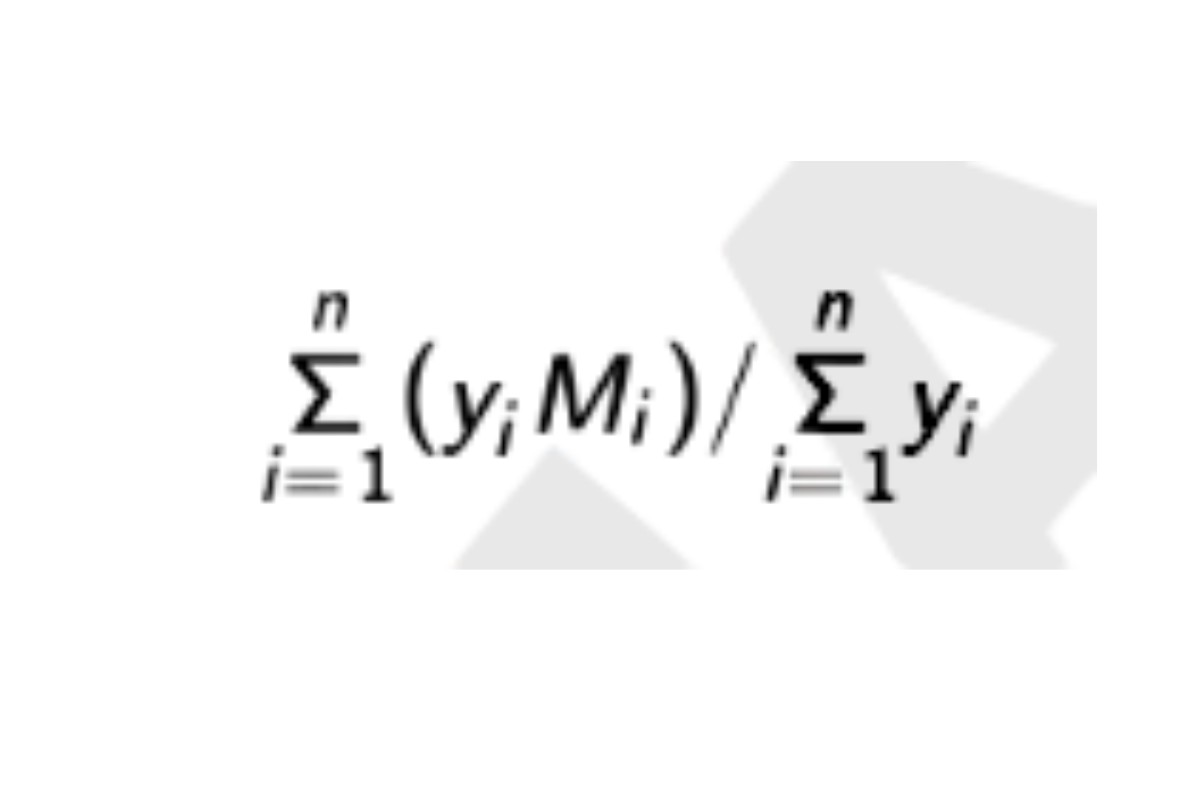
in which n is defined by the relations:
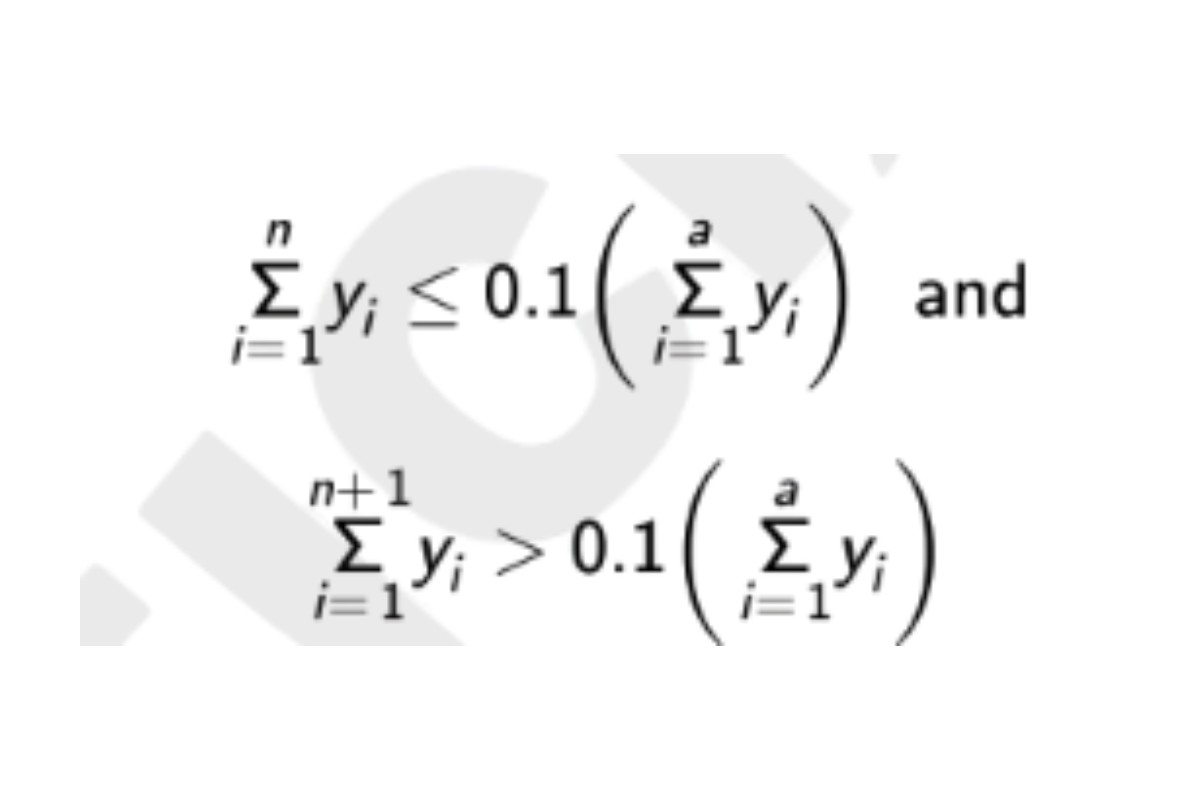
See the USP Dextran 40 RS certicate for the range, (RB 1-Jul-2022) System suitability solution. Weight average molecular weight, low-fraction: Calculate Mw of the low-fraction dextran eluted in and after section m:
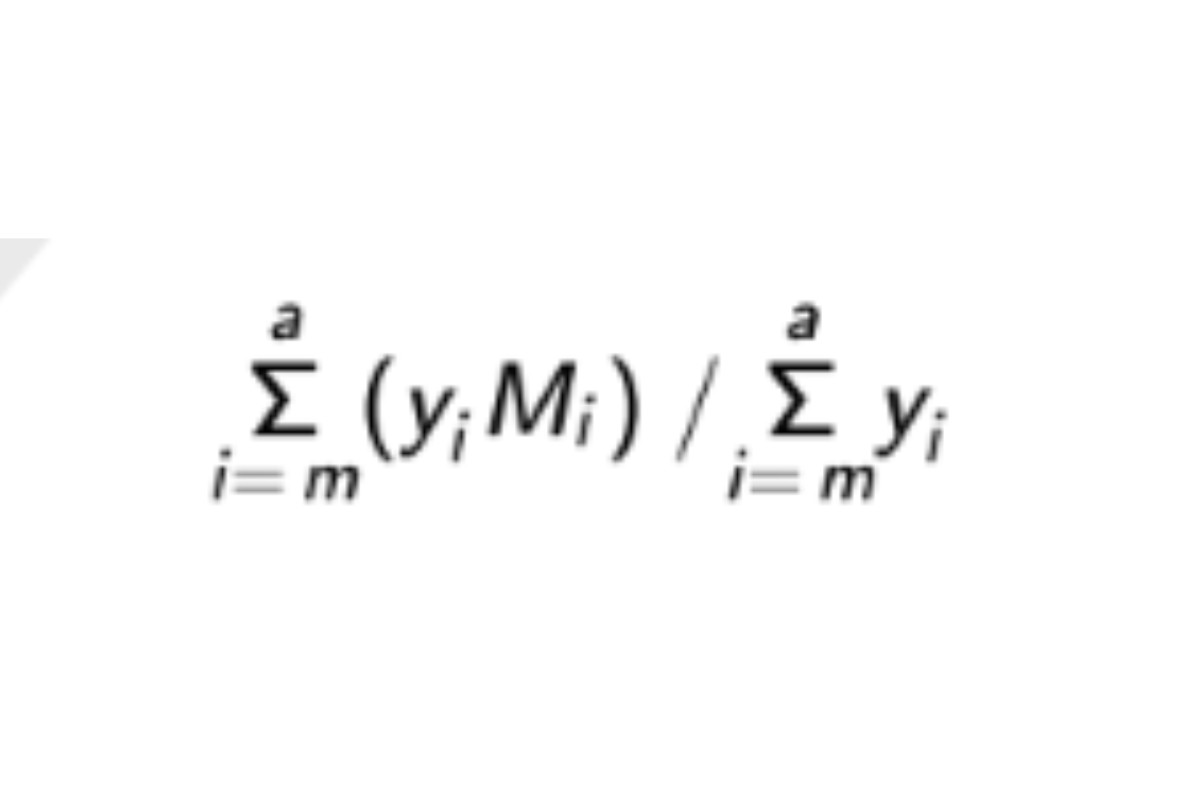
in which m is defined by:
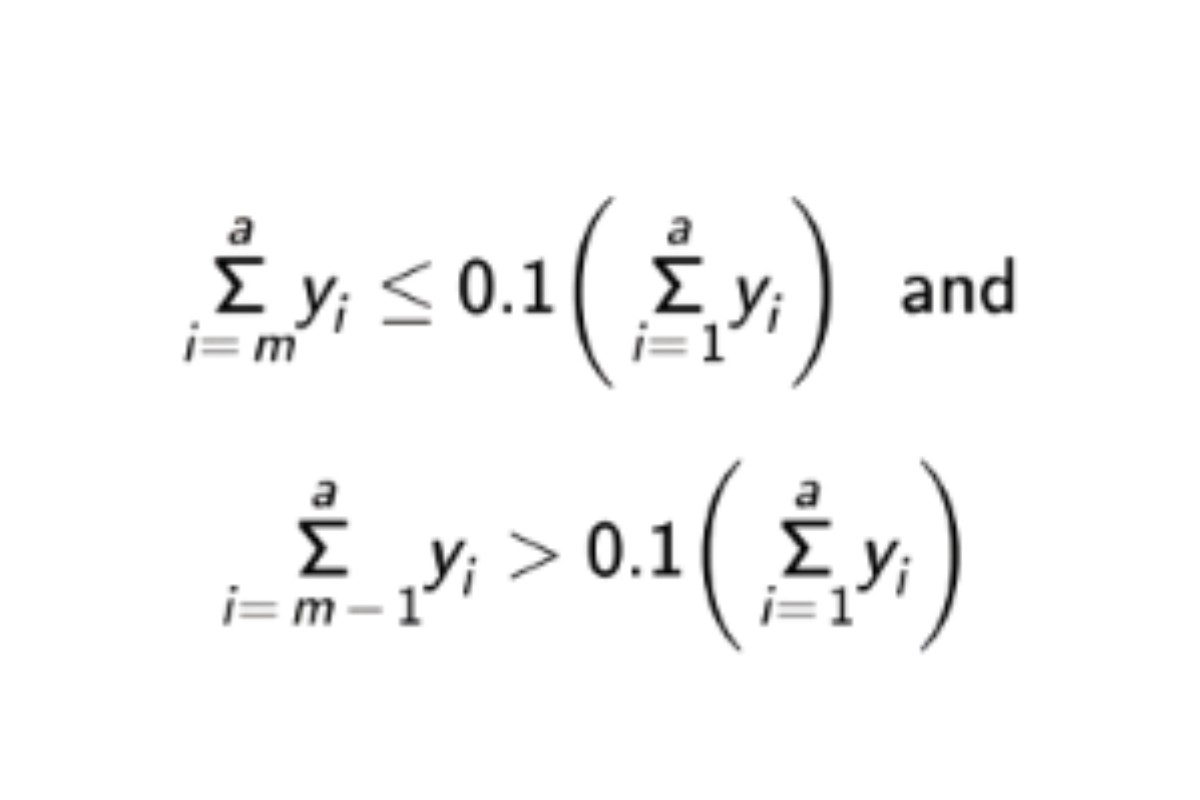
See the USP Dextran 40 RS certicate for the range, (RB 1-Jul-2022) System suitability solution.
5 Analysis
Sample: Sample solution
Calculate the weight average molecular weight, Mw, for the total molecular weight distribution, the high-fraction dextran, and the low fraction dextran. With the values of b1, b2, b3, b4, and b5 , obtained with the Calibration solutions in System suitability, calculate the number average molecular weight, Mn , of the total molecular weight distribution of the Sample solution by substituting the corresponding values of Mi , along with their corresponding values of yi, in the equation:
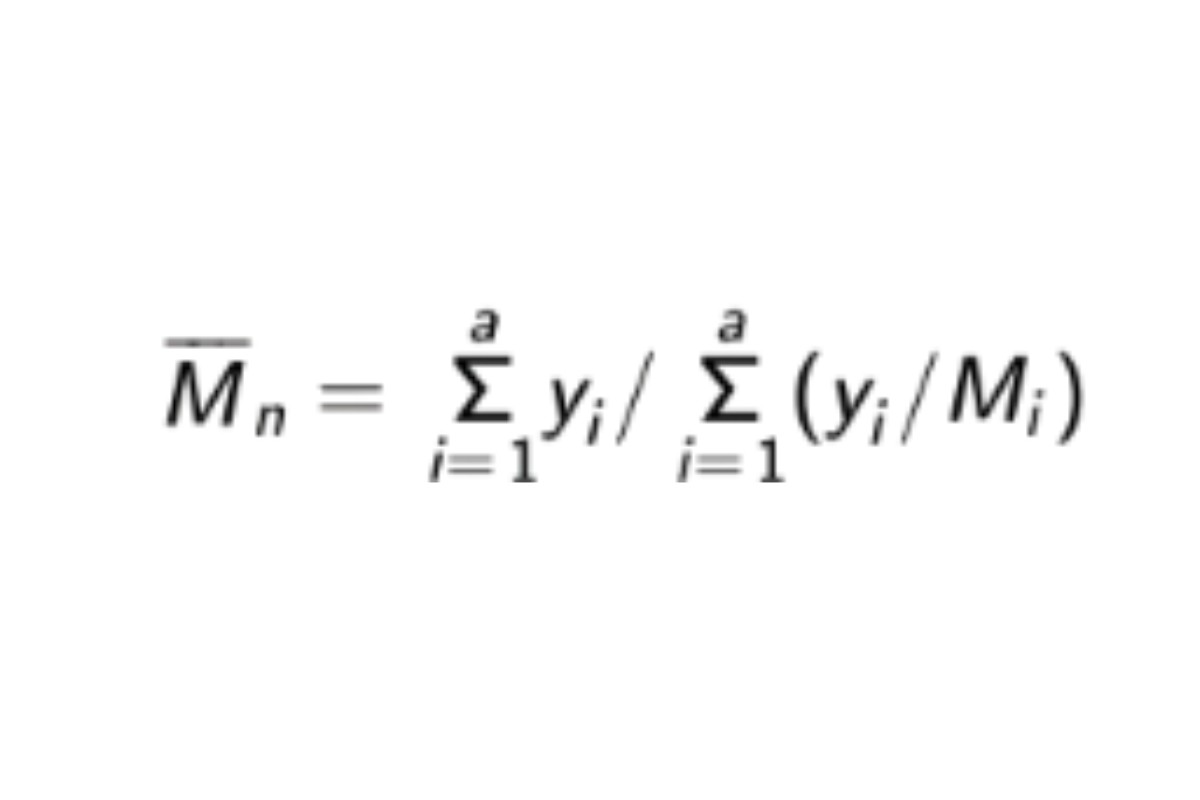
Acceptance criteria: The weight average molecular weight, Mw, of the total molecular weight distribution is 35,000–45,000. The weight average molecular weight, Mw, of the high-fraction dextran and of the low-fraction dextran are NMT 120,000 and NLT 5,000, respectively.
The number average molecular weight, Mn , is 16,000–30,000. Where Dextran 40 is labeled as intended for use in the preparation of injectables, the ratio Mw:Mn is in the 1.4–1.9 range.
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
6.1 Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in well-closed containers. Store at 25°; excursions are permitted between 15° and 30°.
6.2 Labeling:
Where it is intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms, the label states that it is sterile or must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms.
Change to read:
6.3 USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Dextran 40 RS
USP Dextran 4 Calibration RS
USP Dextran 10 Calibration RS
USP Dextran 40 Calibration RS
USP Dextran 70 Calibration RS
USP Dextran 250 Calibration RS
(RB 1-Jul-2022)
USP Dextran V0 Marker RS
The Gauss-Newton method, modied by Hartley [see D. Hartley Technometrics , 3 (1961)], and the G. Nilsson and K. Nilsson method [see G. Nilsson and K. Nilsson J. Chromat ., 101, 137 (1974)] are suitable methods. A curve-tting program capable of nonlinear regression may be used.


