Dalteparin Sodium
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
DOWNLOAD PDF HERE
1 DEFINITION
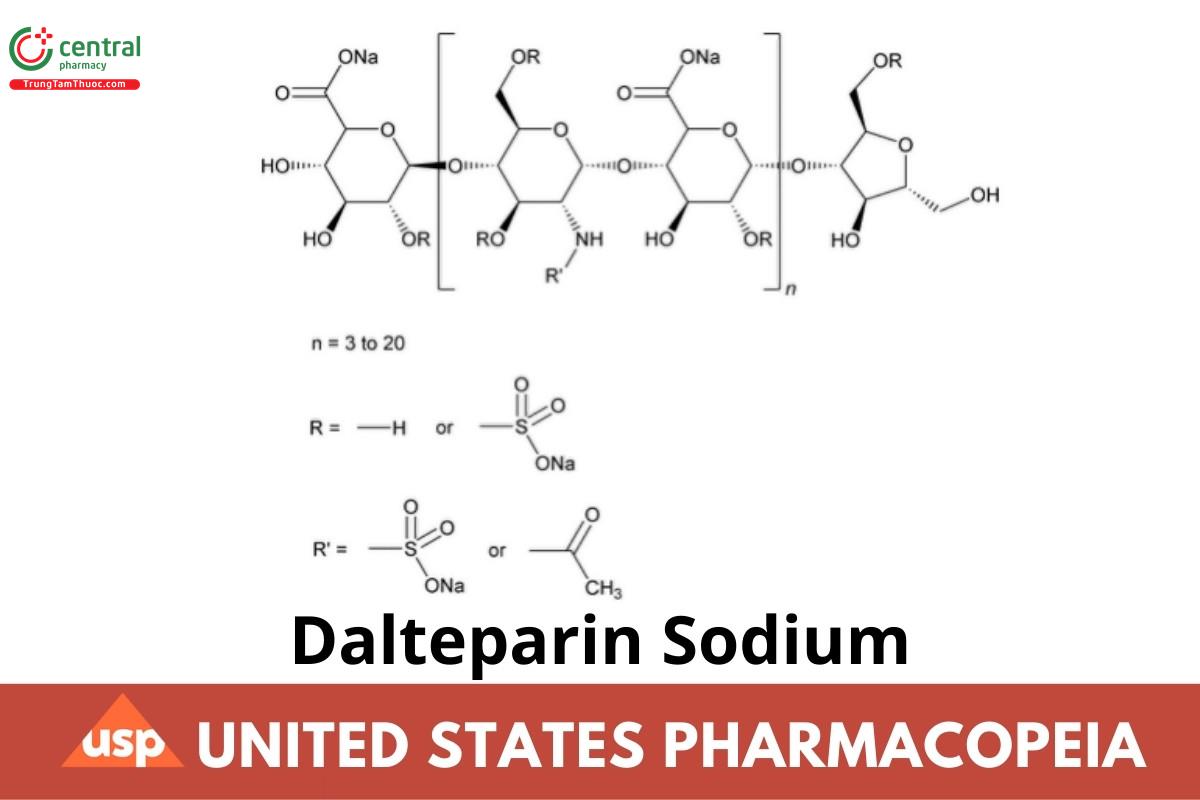
Dalteparin Sodium is the sodium salt of a low molecular weight heparin obtained by nitrous acid depolymerization of heparin from porcine intestine or intestinal mucosa. Heparin source material used in the manufacture of Dalteparin Sodium complies with the compendial requirements stated in the Heparin Sodium monograph. Dalteparin Sodium is produced by a validated manufacturing and purication procedure under conditions shown to minimize the presence of species containing the N–NO group. The majority of the components have a 2-O-sulfo-α-l-idopyranosuronic acid structure at the non-reducing end and a 6-O-sulfo-2,5-anhydro-d-mannitol structure at the reducing end of their chains. The weight-average molecular weight (Mw) ranges between 5600 and 6400 Da, with a characteristic value of about 6000 Da. The percentage of chains lower than molecular weight 3000 Da is NMT 13.0%, and the percentage of chains higher than molecular weight 8000 Da ranges between 15.0% and 25.0%. The degree of sulfation is NLT 1.8/disaccharide unit. The potency is NLT 110 and NMT 210 Anti-Factor Xa International Units (IU)/mg of activity, calculated on the dried basis. The anti-factor IIa activity is NLT 35 IU/mg and NMT 100 IU/mg, calculated on the dried basis. The ratio of anti-factor Xa activity to anti-factor IIa activity is between 1.9 and 3.2.
2 IDENTIFICATION
2.1 A. 1H NMR Spectrum
Standard solution: Dissolve 15 mg of USP Dalteparin Sodium RS in 0.7 mL of deuterium oxide with deuterated sodium 3- trimethylsilylpropionate. The sample is freeze-dried to remove exchangeable protons. Redissolve the sample and repeat the freeze-drying step twice more before transferring the sample into an NMR tube.
Sample solution: Dissolve 15 mg of Dalteparin Sodium in 0.7 mL of deuterium oxide (99.9%) with deuterated sodium 3- trimethylsilylpropionate. The sample is freeze-dried to remove exchangeable protons. Redissolve the sample and repeat the freeze-drying step twice more before transferring the sample into an NMR tube.
Instrumental conditions
(See Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy 〈761〉.)
Mode: NMR, pulsed (Fourier transform)
Frequency: NLT 500 MHz for 1H
Temperature: 30°
System suitability
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Transfer the Standard solution and the Sample solution to NMR tubes of 5 mm in diameter. Using a pulsed (Fourier transform) NMR spectrometer operating at NLT 500 MHz for 1H, acquire a free induction decay (FID) with NLT 32 scans using a 90° pulse, an acquisition time of NLT 2 s, and at least a 10-s delay. For each sample, an initial short spectrum is collected (1 scan), and the water resonance is then suppressed by selective irradiation during the relaxation delay. Final spectra are recorded over 32 scans. For all samples, the deuterated sodium 3-trimethylsilylpropionate methyl signal should be set to 0.00 ppm. Record the 1H NMR spectrum of the Standard solution. Collect the 1H NMR spectrum with a spectral window of at least 10 to −2 ppm and without spinning. The Standard solution shall be run at least daily when the Sample solution is being run. All spectra are phased, and linear baseline correction is applied to all spectra before peak identication.
Suitability requirements
Chemical shift: The deuterated sodium 3-trimethylsilylpropionate methyl signal should be set to 0.00 ppm for all samples.
Chemical shifts for system suitability: The ppm values for the methyl group of N-acetyl, the H-2 of N-sulfo glucosamine, the H-2 of glucuronic acid plus 3-O-sulfo glucosamine, the H-1 of iduronic acid, and the H-1 of 3-O-sulfo glucosamine of dalteparin in the Standard solution are present at 2.05, 3.28, 3.39, 5.01, and 5.51, respectively. Two additional signals, corresponding to the H-1 of the 2-O-sulfo iduronic acid linked to the terminal 2,5-anhydromannitol and the H-1 of 2-O-sulfo iduronic acid are located at 5.18–5.22 ppm. The ppm values of these signals do not differ by more than ±0.03 ppm, Standard solution.
[Note—Depending on specic sample makeup and instrument parameters, including the eld strength of the NMR instrument, the two signals associated with the H-1 of 2-O-sulfo iduronic acid at 5.18–5.22 ppm may appear well separated or as a main signal with a shoulder.]
Analysis
Sample: Sample solution
Record the 1H NMR spectra of the Sample solution.
Acceptance criteria: The ppm values for the methyl group of N-acetyl, the H-2 of N-sulfo glucosamine, the H-2 of glucuronic acid plus 3-O sulfo glucosamine, the H-1 of iduronic acid, the H-1 of the 2-O-sulfo iduronic acid linked to the terminal anhydromannitol and the H-1 of 2-O sulfo iduronic acid, and the H-1 of 3-O-sulfo glucosamine of dalteparin in the Sample solution are present at 2.05, 3.28, 3.39, 5.01, 5.18– 5.22, and 5.51, respectively. The ppm values of these signals do not differ by more than ±0.03 ppm.
Change to read:
2.2 B. Molecular Weight Distribution and Weight-Average Molecular Weight
(See Low Molecular Weight Heparin Molecular Weight Determinations 〈209〉.)
System suitability solution: 5 mg/mL of USP Dalteparin Sodium RS in Mobile phase. Filter using a nylon membrane of 0.45-µm pore size. System suitability
Sample: System suitability solution
Suitability requirements
Weight-average molecular weight (Mw): Take the mean of the calculated Mw from the duplicate injections of the System suitability solution, and round to the nearest 50 Da. The chromatographic system is suitable if the Mw of the USP Dalteparin Sodium RS is within 150 Da of the labeled value as stated in the USP Certicate for USP Dalteparin Sodium RS.
Analysis
Sample: Sample solution▲ (USP 1-Dec-2023)
Acceptance criteria: The weight-average molecular weight (Mw) ranges between 5600 and 6400 Da, with a characteristic value of about 6000 Da. The percentage of chains lower than the molecular weight 3000 Da (M3000) is NMT 13.0%, and the percentage of chains higher than the molecular weight 8000 Da (M8000) ranges between 15.0% and 25.0%.
2.3 C. Anti-Factor Xa to Anti-Factor IIa Ratio
(See Anti-Factor Xa and Anti-Factor IIa Assays for Unfractionated and Low Molecular Weight Heparins 〈208〉, Anti-Factor Xa and Anti-Factor IIa Assays for Low Molecular Weight Heparins.)
Acceptance criteria: The ratio of the numerical value of the anti-factor Xa activity, in Anti-Factor Xa IU/mg, to the numerical value of the anti-factor IIa activity, in Anti-Factor IIa IU/mg, as determined by the Anti-Factor Xa Activity and Anti-Factor IIa Activity assays, is NLT 1.9 and NMT 3.2, respectively.
Change to read:
2.4 D. Identification Tests—General 〈191〉, Chemical Identification Tests, Sodium:(USP 1-Dec-2023) Meets the requirements (USP 1-Dec-2023)
3 ASSAY
3.1 Anti-Factor Xa Activity
(See Anti-Factor Xa and Anti-Factor IIa Assays for Low Molecular Weight Heparins 〈208〉, Anti-Factor Xa Activity for Low Molecular Weight Heparin.)
Analysis: Proceed as directed in the chapter.
Acceptance criteria: The potency is NLT 110 and NMT 210 Anti-Factor Xa IU/mg on the dried basis.
4 OTHER COMPONENTS
Nitrogen Determination 〈461〉, Method II: 1.5%–2.5% on the dried basis
Sodium Content
Cesium chloride solution: 1.27 mg/mL of cesium chloride in 0.1 M hydrochloric acid
Standard solution A: 0.0025% of sodium chloride in Cesium chloride solution
Standard solution B: 0.0050% of sodium chloride in Cesium chloride solution
Standard solution C: 0.0075% of sodium chloride in Cesium chloride solution
Sample solution: Transfer 50.0 mg of Dalteparin Sodium to a 100-mL volumetric ask, and dissolve in and dilute with Cesium chloride solution to volume.
Analysis
Samples: Cesium chloride solution, Standard solution A, Standard solution B, Standard solution C, and Sample solution Concomitantly determine the absorbances of the Cesium chloride solution (blank), the Sample solution, and the Standard solutions at 330.3 nm, using a sodium hollow-cathode lamp and an air–acetylene ame. Using the absorbances of Standard solutions A, B, and C, determine the sodium content in the Sample solution after an appropriate blank correction.
Acceptance criteria: 10.5%–13.5% on the dried basis
5 IMPURITIES
Change to read:
5.1 Limit of Nitrites
Mobile phase: Dissolve 13.6 g of sodium acetate trihydrate in 900 mL of water in a 1000-mL volumetric ask. Adjust with orthophosphoric acid to a pH of 4.3, and dilute with water to 1000 mL. Filter through a nylon membrane of 0.45-µm pore size.
Nitrite standard stock solution: 0.05 g/L of nitrite prepared as follows. Dissolve 0.075 g of sodium nitrite in a 1000-mL volumetric ask with carbon dioxide-free water.
Nitrite standard solution: 500 ng/mL of nitrite prepared as follows. Dilute 1 mL of Nitrite standard stock solution in a 100-mL volumetric ask with carbon dioxide-free water.
Calibration standard solutions: Dilute Nitrite standard solution in carbon dioxide-free water to prepare four solutions with the nal nitrite concentrations of 2.5, 5, 15, and 25 ng/mL.
Sample solution: Weigh 80.0 mg of Dalteparin Sodium into a 20-mL volumetric ask, and dissolve in carbon dioxide-free water. Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: Electrochemical detector containing a working electrode (glassy carbon type) with the potential of +1.00 V against a silver–silver chloride reference electrode
Column: 3-mm × 15-cm; 5-µm packing L92
Column temperature: 30 ± 5°
Column regeneration: 1 M sodium chloride at 0.5 mL/min for about 1 h. After regeneration, wash the column with water and re-equilibrate with Mobile phase.
Flow rate: 0.5 mL/min
Injection volume: 25 µL
Run time: 10 min
System suitability
Samples: Calibration standard solutions and Sample solution
Suitability requirements
Column eciency: NLT 4000 theoretical plates for the nitrite peak for all Calibration standard (USP 1-Dec-2023) solutions and Sample solution runs
Tailing factor: Between 0.8 and 1.2 for all Calibration standard (USP 1-Dec-2023) solutions and Sample solution runs Relative standard deviation: Inject the 25-ng/mL Calibration standard solution at least six times. Calculate the relative standard deviation percentage (%RSD) of the nitrite peak areas of the last six injections. The %RSD is NMT 2%.
Analysis
Samples: Calibration standard solutions and Sample solution
Plot the areas of the nitrite peaks from the chromatograms of the Calibration standard solutions against respective concentrations of nitrite. Draw a best-t regression line through the points. The correlation coecient is NLT 0.995. Calculate the concentration of nitrite from the areas of the nitrite peak in the chromatogram of the Sample solution.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 5 ppm
• Boron
[Note—Use only plastic labware, avoid glass.]
Blank: 1% (v/v) solution of nitric acid in water
Calibration solution: Prepare a 11.4-µg/mL solution of USP Boric Acid RS in the Blank.
Standard solution A: Dissolve 0.2500 g of USP Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Boron Analysis RS in about 2 mL of water, add 100 µL of nitric acid, and dilute with the Blank to 10.00 mL.
Standard solution B: Dissolve 0.2500 g of USP Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Boron Analysis RS in about 2 mL of Blank, add 10 µL of a 5.7-mg/mL solution of USP Boric Acid RS, and dilute with the Blank to 10.00 mL. This solution contains 1 µg/mL of boron. Sample solution: Dissolve 0.2500 g of Dalteparin Sodium in about 2 mL of water, add 100 µL of nitric acid, and dilute with the Blank to 10.00 mL.
Analysis
Samples: Blank, Calibration solution, Standard solution A, Standard solution B, and Sample solution
Boron is determined by measurement of the emission from inductively coupled plasma (ICP) at 249.733 nm or a suitable wavelength. Use an appropriate apparatus with settings that have been optimized as directed by the manufacturer.
Calculate the content of boron in Dalteparin Sodium using the following correction factor (F):
F = (rSB − rSA ) × 2/(rC − rB)
rSB = response of boron from Standard solution
rSA = response of boron from Standard solution
rC = response of boron from the Calibration solution
rB = response of boron from the Blank
Acceptance criteria: NMT 1 ppm
6 SPECIFIC TESTS
6.1 Anti-Factor IIa Activity
(See Anti-Factor Xa and Anti-Factor IIa Assays for Low Molecular Weight Heparins 〈208〉, Anti-Factor IIa Activity for Low Molecular Weight Heparin.) Acceptance criteria: 35–100 Anti-Factor IIa IU/mg on the dried basis
6.2 Molar Ratio of Sulfate to Carboxylate
Mobile phase: Carbon dioxide-free water
Sample solution: 50 mg of Dalteparin Sodium in 10 mL of Mobile phase
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC Detector: Ion
Columns: One 1.5-cm × 2.5-cm column, packed with an anion-exchange resin packing L64, and one 1.5-cm × 7.5-cm column, packed with a cation-exchange resin packing L65.1 The outlet of the anion-exchange column is connected to the inlet of the cation-exchange column. Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Analysis
Sample: Sample solution
[Note—Regenerate the anion-exchange column and the cation-exchange column with 1 N sodium hydroxide and 1 N hydrochloric acid, respectively, between two injections.]
With the valve in the inject position, inject the Sample solution into the anion-exchange column, and collect the eluate from the cation exchange column in a beaker at the outlet until the ion detector reading returns to the baseline value. Quantitatively transfer the eluate to a titration vessel containing a magnetic stirring bar, and dilute with Mobile phase to about 60 mL. Position the titration vessel on a magnetic stirrer, and immerse the electrodes. Note the initial conductivity reading, and titrate with approximately 0.1 N sodium hydroxide added in 100-µL portions. [Note—Prepare the sodium hydroxide solution in Mobile phase.] Record the buret reading and the conductivity meter reading after each addition of the sodium hydroxide solution.
Plot the conductivity measurements on the y-axis against the volumes of sodium hydroxide added on the x-axis. The graph will have three linear sections—an initial downward slope, a middle slight rise, and a nal rise. For each of these sections, draw the best-t straight lines using linear regression analysis. At the points where the rst and second straight lines intersect and where the second and third lines intersect, draw perpendiculars to the x-axis to determine the volumes of sodium hydroxide taken up by the sample at those points. The point where the rst and second lines intersect corresponds to the volume of sodium hydroxide taken up by the sulfate groups (VS). The point where the second and third lines intersect corresponds to the volume of sodium hydroxide consumed by the sulfate and the carboxylate groups together (VT).
Calculate the molar ratio of sulfate to carboxylate:
Result = VS/(VT − VS)
Acceptance criteria: The molar ratio of sulfate to carboxylate is NLT 1.8.
pH 〈791〉: 5.5–8.0 for a 1.0% solution in water
Loss on Drying 〈731〉
Sample: 1 g
Analysis: Dry the Sample under vacuum at 70° for 6 h.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 10%
Change to read:
Bacterial Endotoxins Test 〈85〉: Where the label states that Dalteparin Sodium is sterile or must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms, the level of bacterial endotoxins are such that the requirement under the relevant dosage form monograph(s) in which Dalteparin Sodium is used can be met. (USP 1-Dec-2023)
7 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers, and store below 40°, preferably at room temperature.
Change to read:
Labeling: Label to state the number of Anti-factor Xa International Units of activity per milligram. Where it is intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms, the label states that it is sterile or must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms to ensure acceptable levels of bacterial endotoxins. (USP 1-Dec-2023)
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Boric Acid RS
USP Dalteparin Sodium RS
USP Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Boron Analysis RS
The procedure is based on analyses performed with two columns: one 1.5-cm × 2.5-cm packed with anion-exchange resin Dowex 1X8 (200– 400 mesh) and the other 1.5-cm × 7.5-cm packed with cation-exchange resin Dowex 50WX2 (100–200 mesh).


