Colistin Sulfate
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
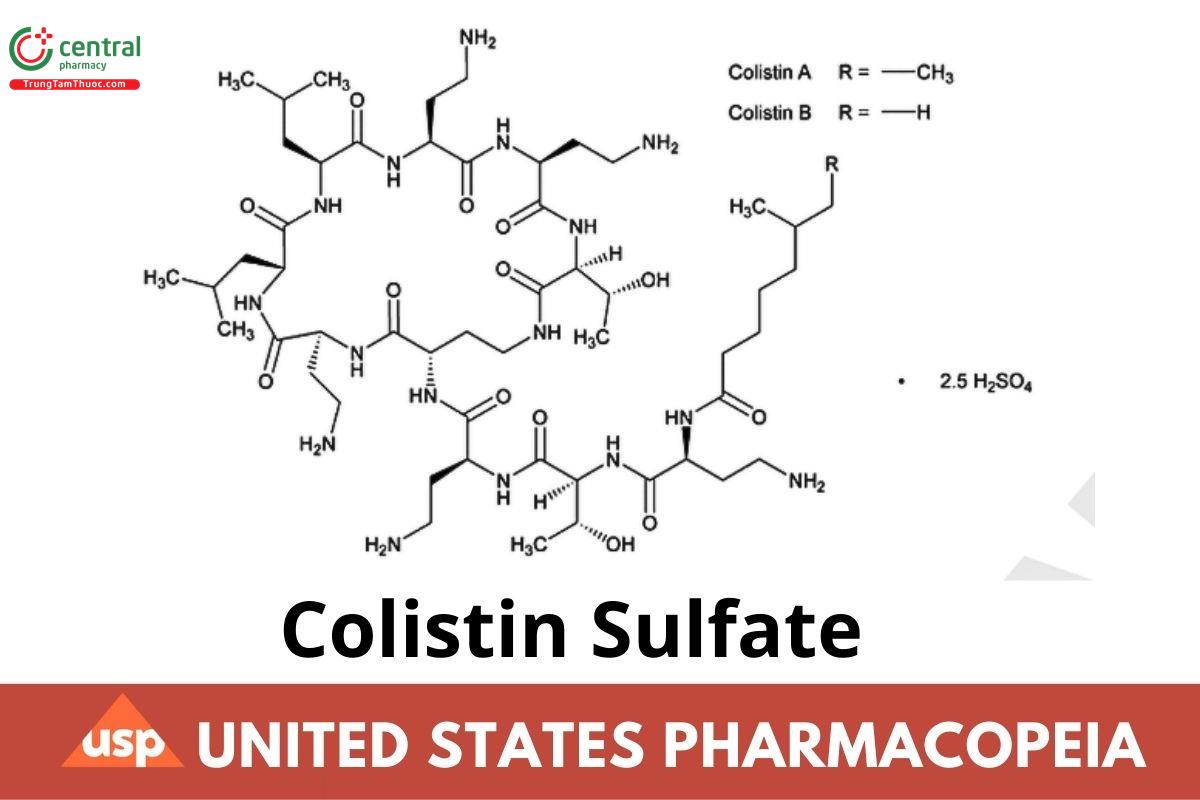
Colistin, sulfate;
Colistins sulfate
CAS RN®: 1264-72-8; UNII: WP15DXU577.
1 DEFINITION
Colistin Sulfate is the sulfate salt of an antibacterial substance produced by the growth of Bacillus polymyxa var. colistinus. It has a potency equivalent to NLT 500 µg of colistin/mg.
2 IDENTIFICATION
Delete the following:
A. Procedure
Add the following:
A. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197A or 197K
B. Identification Tests-General 〈191〉, Chemical Identification Tests, Sulfate: Meets the requirements
Delete the following:
C. Liquid Chromatographic Identification Test
Add the following:
C. The retention times of the colistin A and colistin B peaks of the Sample solution correspond to those of the Standard solution, as obtained in the test for Composition.
3 ASSAY
Change to read:
3.1 Procedure
Analysis: Proceed as directed for Colistin in Antibiotics-Microbial Assays 〈81〉.
Acceptance criteria: NLT 500 µg of colistin/mg
Add the following:
4 IMPURITIES
4.1 Organic Impurities
Solution A: 4.5 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate in 900 mL of water, adjusted with diluted phosphoric acid to a pH of 2.4 and diluted with water to 1000 mL
Mobile phase: Solution A and acetonitrile (78:22)
Diluent: Water and acetonitrile (80:20)
Sensitivity solution: 5 µg/mL of USP Colistin Sulfate RS in Diluent
Standard solution: 0.5 mg/mL of USP Colistin Sulfate RS in Diluent
Sample solution: 0.5 mg/mL of Colistin Sulfate in Diluent
Chromatographic system
- (See Chromatography (621), System Suitability.)
- Mode: LC
- Detector: UV 215 nm
- Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 3-µm packing L1
- Column temperature: 50°
- Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min
- Injection volume: 20 µL
System suitability
- Samples: Sensitivity solution and Standard solution
- [NOTE-See Table 1 for the relative retention times. Use the reference chromatogram provided with the lot of USP Colistin Sulfate RS to identify the peaks.]
- Suitability requirements
- Peak-to-valley ratio: NLT 1.1 for the ratio of the height of the peak that immediately follows the colistin B peak to the height of the valley. between the two peaks, Standard solution
- Resolution: NLT 2.0 between polymyxin E6 and 7-L-isoleucinepolymyxin E2; NLT 3.0 between 2,3-dehydro colistin A and colistin A, Standard solution
- Signal-to-noise ratio: NLT 10 for the colistin A peak, Sensitivity solution
Analysis
Sample: Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each individual impurity (for peaks other than colistin A; colistin B; polymyxins E3, E4, E6, E7; 7-L-valinepolymyxin E2; 7-L-isoleucinepolymyxin E2; 7-1-norvalinepolymyxin E1; colistin III; and 2,3-dehydro colistin A) in the portion of Colistin Sulfate taken:
Result = (rU/rT) × (1/F) × 100
rU = peak response of each individual impurity
rT = sum of all the peak responses
F = relative response factor
Reporting threshold: 0.35%
Acceptance criteria: See Table 1. The reporting threshold is 0.35%.
| Table 1 | |||
| Name | Relative Retention Time | Relative Response Factor | Acceptance Criteria (%) |
| 7-L-Valinepolymyxin E2a and polymyxin E4b | 0.28 | 1.0 | - |
| Polymyxin E6c | 0.39 | 1.0 | NMT 4.5 |
| 7-L-Isoleucinepolymyxin E2d | 0.42 | 1.0 | NMT 2.5 |
| Colistin Be | 0.50 | 1.0 | - |
| Polymyxin E3f | 0.56 | 1.0 | NMT 5.5 |
| 7-L-Norvalinepolymyxin E1g | 0.59 | 1.0 | NMT 4.5 |
| Colistin IIIh | 0.82 | 1.0 | NMT 8.5 |
| 2,3-Dehydro colistin Ai | 0.90 | 3.3 | NMT 1.5 |
| Colistin Aj | 1.00 | 1.0 | - |
| Polymyxin E7k | 1.1 | 1.0 | NMT 5.0 |
| Sum of 7-L-valinepolymyxin E2 and polymyxin E4 | - | - | NMT 3.0 |
| Sum of colistin A, colistin B, polymyxin E3, polymyxin E4, polymyxin E6, polymyxin E7, 7-L-valinepolymyxin E2, 7-L-isoleucinepolymyxin E2, 7-L-norvalinepolymyxin E1, colistin III, and 2,3-dehydro colistin A | - | - | NLT 86.0 |
| [N4-Dab5] Colistin Al | 1.3 | 1.0 | NMT 4.0 |
| Any individual impurity other than [N4-Dab5] Colistin A | - | 1.0 | NMT 2.5; the total number of impurities exceeding 1.0 is NMT 4 |
| Total impurities | - | - | NMT 11.0 |
a N2-(6-Methyl-1-oxoheptyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-d-leucyl-l- valyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonine, cyclic (10→4)-peptide.
b N2-(1-Oxoheptyl)-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-d-leucyl-l-leucyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l threonine, cyclic (10→4)-peptide.
c N2-[(6S)-3-Hydroxyl-6-methyl-1-oxooctyl]-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-d-leucyl-l-leucyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonine, cyclic (10→4)-peptide.
d N2-(6-Methyl-1-oxoheptyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-d-leucyl-l-isoleucyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonine, cyclic (10→4)-peptide.
e N2-(6-Methyl-1-oxoheptyl)-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-d-leucyl-l-leucyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonine, cyclic (10→4)-peptide.
f N2-(1-Oxooctyl)-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-d-leucyl-l-leucyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonine, cyclic (10→4)-peptide.
g N2-[(S)-6-Methyl-1-oxooctyl]-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-d-leucyl-l-norvalyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonine, cyclic (10→4)-peptide.
h N2-[(S)-6-Methyl-1-oxooctyl]-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-d-leucyl-l-isoleucyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonine, cyclic (10→4)-peptide.
i N2-[(S,E)-6-Methyloct-2-enoyl]-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-d-leucyl-l-leucyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonine, cyclic (10→4)-peptide.
j N2-[(S)-6-Methyl-1-oxooctyl]-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-d-leucyl-l-leucyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonine, cyclic (10→4)-peptide.
k N2-(7-Methyl-1-oxooctyl)-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-d-leucyl-l-leucyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonine, cyclic (10→4)-peptide.
l N2-[(S)-6-Methyl-1-oxooctyl]-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-4-[(S)-2-aminobutanoyl]-d-leucyl-l-leucyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-2,4-diaminobutanoyl-l-threonine, cyclic (10→4)-peptide.
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
5.1 pH 〈791〉
4.0–7.0, in 10 mg/mL solution
5.2 Loss on Drying 〈731〉
Sample: 100 mg
Analysis: Dry in a capillary-stoppered bottle under vacuum at a pressure NMT 5 mm of mercury at 60° for 3 h.
Sample: It loses NMT 7.0% of its weight.
Add the following:
5.3 COMPOSITION
Solution A, Mobile phase, Diluent, Sensitivity solution, Standard solution, Sample solution, Chromatographic system, and System suitability: Proceed as directed in the test for Organic Impurities.
Analysis
Sample: Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each individual component (colistin A; colistin B; polymyxins E3, E4, E6, E7; 7-L-valinepolymyxin E2; 7-L-isoleucinepolymyxin E2; 7-1-norvalinepolymyxin E1; colistin III; and 2,3-dehydro colistin A) in the portion of Colistin Sulfate taken:
Result = (rU/rT) × (1/F) × 100
rU = peak response of each individual component
rT = sum of all the peak responses
F = relative response factor
Acceptance criteria: See Table 1 (USP 1-Dec-2022)
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
PACKAGING AND STORAGE: Preserve in tight containers.
USP REFERENCE STANDARDS (11)
USP Colistin Sulfate RS


