Castor Oil
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
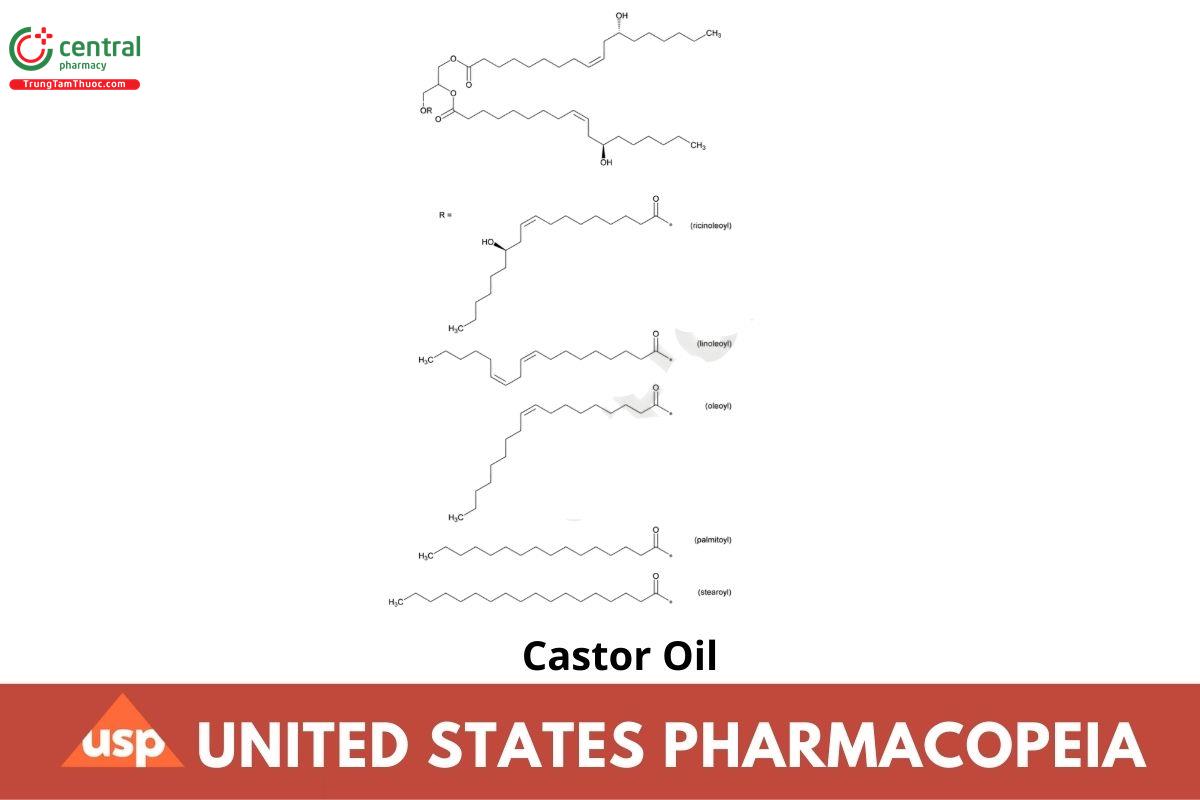
Triricinolein (glyceryl triricinoleate or triricinoleoyl-glycerol) predominates
CAS RN®: 8001-79-4].2S (USP41)
Change to read:
1 DEFINITION
Castor Oil is the fixed oil obtained from the seed of Ricinus communis L. (Family Euphorbiaceae). Castor Oil consists of NLT 90.0% of the triglyceride of ricinoleic acid.2S (USP41) It contains no added substances.
2 IDENTIFICATION
Add the following:
A. Identity by Fatty Acid Composition
Diluent: n-Heptane
Standard solution 1: 0.2 mg/mL each of methyl palmitate, methyl stearate, methyl oleate, methyl linoleate, methyl linolenate, methyl cis-11-eicosenoate, and methyl ricinoleate from, respectively, USP Methyl Palmitate RS, USP Methyl Stearate RS, USP Methyl Oleate RS, USP
Methyl Linoleate RS, USP Methyl Linolenate RS, methyl cis-11-eicosenoate, and USP Methyl Ricinoleate RS in Diluent
Standard solution 2: 4 mg/mL each of methyl stearate and methyl ricinoleate from USP Methyl Stearate RS and USP Methyl Ricinoleate RS in
Diluent
Sample solution: Transfer 140 mg of Castor Oil to a 10-mL screw-cap test tube, add 3.0 mL of Diluent, and mix well. Add 0.5 mL of 0.5 M sodium methoxide in methanol,1and mix with the sample. Allow the reaction to proceed at room temperature for 2 h. After 2 h, add 5 mL of water, and mix. Separate the organic layer (the upper layer), and remove the lower layer. Place an aliquot of the organic layer into an autosampler vial.
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: GC
Detector: Flame ionization
Column: 0.25-mm × 15-m fused silica capillary; bonded with a 0.25-μm layer of phase G7
Temperatures
Injection port: 240°
Detector: 250°
Column: See Table 1 for the oven program.
Table 1
| Initial Temperature (°) | Temperature Ramp (°/min) | Final Temperature (°) | Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) | Total Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 | 0 | 80 | 1 | 1 |
| 80 | 30 | 140 | 0 | 3 |
| 140 | 3 | 150 | 0 | 6.3 |
| 150 | 1 | 155 | 0 | 11.3 |
| 155 | 2 | 165 | 0 | 16.3 |
| 165 | 3 | 220 | 10 | 45 |
Column mode: See Table 2 for the pressure program.
Table 2
| Pressure (psi) | Pressure Ramp (psi/min) | Hold Time (min) | Total Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0 | 16 | 16 |
| 4 | 5 | 9 or 0 | 26.2 or 17.2 |
| 3 | 10 | 19 or 28 | 45 |
a If considerable discrimination of late-eluting compounds is observed, the hold time can be adjusted from 9 to 0 min. Thus the total time should be 17.2 min. The next step of the hold time should be 28 min.
Carrier gas: Hydrogen
Injection volume: 0.5 μL
Injection type: Split ratio, 60:1
Liner: Single taper, low-pressure drop with deactivated wool
Run time: 45 min
System suitability
Sample: Standard solution 1
[Note—See Table 3 for relative retention times.]
Table 3
| Component | Relative Retention Time |
|---|---|
| Methyl palmitate (C16:0) | 0.62 |
| Methyl stearate (C18:0) | 0.98 |
| Methyl oleate (C18:1) | 1.00 |
| Methyl linoleate (C18:2) | 1.08 |
| Methyl linolenate (C18:3) | 1.19 |
| Methyl cis-11-eicosenoate (C20:1) | 1.63 |
| Methyl ricinoleate | 2.68 |
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 1.5 between the methyl stearate and methyl oleate peaks
Relative standard deviation: NMT 2.0% for the peak area ratio of methyl ricinoleate to methyl linoleate
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution 1, Standard solution 2, and Sample solution
The peak of methyl cis-11-octadecenoate, which is an isomer of methyl oleate, can be resolved from the methyl oleate peak with a
resolution of about 1 and a relative retention time of 1.01 with respect to methyl oleate.
Calculate the relative response factor (F) for methyl ricinoleate:
F = (rS/rR) x (CR/CS)
rS = peak area of methyl stearate from Standard solution 2
rR = peak area of methyl ricinoleate from Standard solution 2
CR = concentration of USP Methyl Ricinoleate RS in Standard solution 2 (mg/mL)
CS = concentration of USP Methyl Stearate RS in Standard solution 2 (mg/mL)
Correct the peak area of methyl ricinoleate in the Sample solution by multiplying by F.
Calculate the percentage of each fatty acid component in the portion of sample taken:
Result = (rU/rT) × 100
rU = peak area of each individual fatty acid methyl ester, except for the uncorrected peak area of methyl ricinoleate (or corrected peak area of methyl ricinoleate) in the Sample solution
rT = sum of all the peak areas, excluding the solvent and methyl ricinoleate peaks and including the corrected peak area of methyl ricinoleate in the Sample solution
Acceptance criteria: Castor Oil exhibits the composition pro
le of fatty acids shown in Table 4.
Table 4
| Component | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|
| Palmitic acid (C16:0) | ≤2.0 |
| Stearic acid (C18:0) | ≤2.5 |
| Oleic acid (C18:1) | 2.5–6.0 |
| Linoleic acid (C18:2) | 2.5–7.0 |
| Linolenic acid (C18:3) | ≤1.0 |
Add the following:
B. Distinction from Most Other Fixed Oils: It is only slightly soluble in solvent hexane (distinction from most other fixed oils), but it yields a clear liquid with an equal volume of alcohol (foreign fixed oils).2S (USP41)
Add the following:
C. Identification of Refined Castor Oil or Virgin Castor Oil by Using Ultraviolet Absorption
Sample solution: Dissolve 1.0 g of Castor Oil in alcohol, and dilute with alcohol to 100 mL.
Instrumental conditions
(See Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy 〈857〉.)
Mode: UV-Vis
Analytical wavelength: 270 nm
Cell: 1 cm
Analysis: Determine the UV-Vis absorbance using the Instrumental conditions.
Acceptance criteria
Refined Castor Oil: The absorbance is within the range of 0.7–1.5.
Virgin Castor Oil: The absorbance is NMT 0.7.2S (USP41)
3 ASSAY
Add the following:
Triglyceride Composition
[Note—The fatty acid radicals are designated as linoleic (L), oleic (O), palmitic (P), ricinoleic (R), and stearic (S), and the common abbreviations for triglycerides used are as follows: triricinolein (glyceryl triricinoleate or triricinoleoyl-glycerol) (RRR), diricinoleoyl-linoleoyl-glycerol (RRL), diricinoleoyl-oleoyl-glycerol (RRO), diricinoleoyl-palmitoyl-glycerol (RRP), and diricinoleoyl-stearoyl-glycerol (RRS).]
Solution A: Methanol
Solution B: 2-Propanol
Mobile phase: See Table 5.
Table 5
| Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100 | 0 |
| 20 | 50 | 50 |
| 23 | 0 | 100 |
| 25 | 100 | 0 |
| 35 | 100 | 0 |
Diluent: 2-Propanol
System suitability solution: 2.0 mg/mL of USP Castor Oil RS in Diluent
Sample solution: 2.0 mg/mL of Castor Oil in Diluent
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: Evaporative light-scattering
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-μm packing L1
Temperatures
Column: 25°
Detector: 40°
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min
Injection volume: 5 μL
Run time: 35 min
[Note—Depending on the different settings of the detector, the temperature and Flow rate can be adjusted as long as system suitability
requirements are met.]
System suitability
Sample: System suitability solution
[Note—See Table 6 for relative retention times.]
| Component | Relative Retention Time |
|---|---|
| RRR | 1.0 |
| RRL | 1.6 |
| RRO | 1.8 |
| RRS | 2.0 |
a RRP coelutes with RRO, and the percentage of RRP is about 10 times less than that of RRO.
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 5.0 between the RRR and RRL peaks; NLT 2.0 between the RRL and RRO peaks; NLT 3.0 between the RRO and RRS peaks
Tailing factor: 0.8–1.8 for the RRR peak
Relative standard deviation: NMT 2% for the RRR peak
Analysis
Samples: System suitability solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each of the triglycerides in the portion of sample taken:
Result = (rU/rT) × 100
rU = peak area of each individual triglyceride
rT = sum of all the peak areas, excluding the solvent peak
Acceptance criteria: Castor Oil exhibits the composition profile of triglycerides shown in Table 7.
Table 7
| Component | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|
| RRR | ≥90.0 |
| RRL | 2.0–4.0 |
| RRO | 2.5–5.0 |
| RRS | 0.2–0.8 |
4 IMPURITIES
Delete the following:
Heavy Metals 〈231〉, Method II: NMT 10 ppm (Official 1-Jan-2018)
SPECIFIC TESTS
Specific Gravity 〈841〉: 0.957–0.961
Delete the following:
2/14/25, 3:37 AM USP-NF Castor Oil
Distinction from Most Other Fixed Oils: It is only partly soluble in solvent hexane (distinction from most other fixed oils), but it yields a clear liquid with an equal volume of alcohol (foreign fixed oils). 2S (USP41)
Delete the following:
Fats and Fixed Oils 〈401〉, Free Fatty Acids: The free fatty acids in 10 g require NMT 3.5 mL of 0.10 N sodium hydroxide for neutralization. 2S
(USP41)
Add the following:
Fats and Fixed Oils 〈401〉, Procedures, Acid Value: NMT 2.02S (USP41)
Change to read:
Fats and Fixed Oils 〈401〉, Procedures, Hydroxyl Value
Free acid determination: The acid value (A) is determined from Fats and Fixed Oils 〈401〉, Procedures, Acid Value.2S (USP41)
Hydroxyl value determination
Sample: 2 g
Blank: 5.0 mL of a freshly prepared mixture of acetic anhydride and pyridine (1:3)
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry 〈541〉.)
Mode: Residual titration
Titrant: 0.5 N alcoholic potassium hydroxide VS
Endpoint detection: Visual
Analysis: Transfer the Sample to a glass-stoppered, 250-mL conical flask. Add 5.0 mL of a freshly prepared mixture of acetic anhydride and pyridine (1:3), and swirl to mix. Connect the flask to a reflux condenser, and heat on a steam bath for 2 h. Add 10 mL of water through the condenser, swirl to mix, heat on a steam bath for an additional 10 min, and allow to cool to room temperature. Add through the condenser 15 mL of normal butyl alcohol that has been neutralized previously to phenolphthalein, remove the condenser, and wash the tip of the condenser and the sides of the flask with an additional 10 mL of neutralized normal butyl alcohol. Add 1 mL of phenolphthalein TS, and titrate with Titrant to a faint pink endpoint.
Calculate the hydroxyl value in the portion of Oil taken:
Result = (VB − VT ) × [(Mr × N)/W] + A
VB = volume of Titrant consumed by the Blank (mL) 2S (USP41)
VT = volume of Titrant consumed by the Sample in the hydroxyl value determination (mL)
Mr = milliequivalent weight of potassium hydroxide, 56.11 mg/mEq
N = actual normality of the Titrant
W = sample weight from the hydroxyl value determination (g)
A = acid value from the test for Fats and Fixed Oils, Acid Value2S (USP41)
Acceptance criteria: 160–168
Add the following:
Fats and Fixed Oils 〈401〉, Procedures, Peroxide Value: NMT 10.02S (USP41)
Delete the following:
Fats and Fixed Oils, Iodine Value〈401〉: 83–88 2S (USP41)
Delete the following:
Fats and Fixed Oils 〈401〉, Procedures, Saponification Value: 176–1822S (USP41)
Add the following:
Fats and Fixed Oils 〈401〉, Procedures, Unsaponifiable Matter: NMT 0.8%2S (USP41)
Add the following:
Water Determination 〈921〉: NMT 0.3%2S (USP41)
5 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Change to read:
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in tight containers, avoid exposure to excessive heat, and protect from light.2S (USP41)
Add the following:
Labeling: Where Castor Oil is intended for use in the manufacture of injectable dosage forms, it is so labeled. Where Castor Oil must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms to ensure acceptable levels of bacterial endotoxins, it is so labeled.2S (USP41)
Add the following:
OTHER REQUIREMENTS: For Castor Oil intended for use in injectable dosage forms, which is specified in the Labeling section, the following specifications must be met:
Water Determination 〈921〉: NMT 0.2%
Fats and Fixed Oils 〈401〉, Procedures, Acid Value: NMT 0.8
Fats and Fixed Oils 〈401〉, Procedures, Peroxide Value: NMT 5.0
Ultraviolet Absorption
Sample solution: Dissolve 1.0 g of Castor Oil in alcohol, and dilute with alcohol to 100 mL.
Instrumental conditions
(See Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy 〈857〉.)
Mode: UV-Vis
Analytical wavelength: 270 nm
Cell: 1 cm
Analysis: Determine the UV-Vis absorbance using the Instrumental conditions described above.
Acceptance criteria: The absorbance is within the range of 0.7–1.5.
Bacterial Endotoxins Test 〈85〉: The level of bacterial endotoxins is such that the requirement under the relevant dosage form monograph(s) in which Castor Oil is used can be met. Where the label states that Castor Oil must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms, the level of bacterial endotoxins is such that the requirement under the relevant dosage form monograph(s) in which
Castor Oil is used can be met.
Fats and Fixed Oils 〈401〉, Procedures, Saponification Value: 176–1822S (USP41)
Add the following:
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Castor Oil RS
USP Methyl Linoleate RS
USP Methyl Linolenate RS
USP Methyl Oleate RS
USP Methyl Palmitate RS
USP Methyl Ricinoleate RS
USP Methyl Stearate RS2S (USP41)
1 0.5 M sodium methoxide in methanol is available from Sigma-Aldrich (www.sigmaaldrich.com), product #403067. Any other equivalent reagent can be used as well.


