Carbomer Interpolymer
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
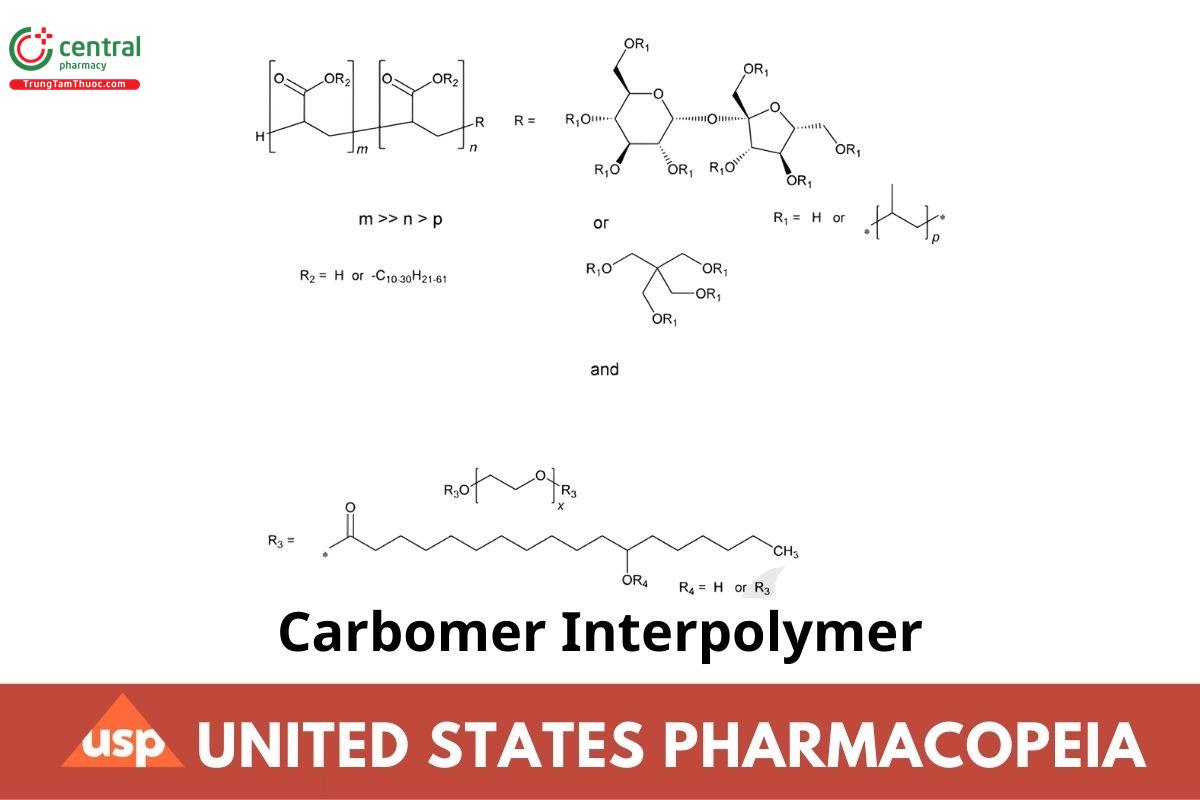
1 DEFINITION
Carbomer Interpolymer is a carbomer homopolymer or copolymer that contains a block copolymer of polyethylene glycol and a long-chain alkyl acid ester. Carbomer Interpolymer contains NLT 52.0% and NMT 62.0% of carboxylic acid (–COOH) groups, calculated on the dried basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
A. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197A or 197K. Exhibits bands at or near (±10) wavenumbers (cm−1). (See Table 1.)
Table 1
| Sampling Mode | Peak Maxima | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transmission | 1710ᵃ | 1454 | 1414 | 1245 | 1172 | 801 |
| ATR (germanium crystal) | 1702ᵃ | 1452 | 1412 | 1260–1140ᵇ | 797 | |
| ATR (diamond crystal) | 1698ᵃ | 1451 | 1412 | 1260–1140ᵇ | 795 | |
a Strongest absorption band.
b Represents a doublet peak with 2 maxima occurring between 1260 and 1140 cm–1.
c Zinc selenide (ZnSe) and thallium bromoiodide (KRs-5) have similar refractive indices as diamond so give similar peak maxima.
[Note-If peak shifting occurs during testing using the method found in 197A causing the test to fail, follow the method found in 197K.]
• B.
Sample: 2.5 g
Analysis: Spread the Sample with a spatula over a 20-mesh stainless steel screen placed over the mouth of an 800-mL beaker. The beaker should contain 500 mL of water at 25°, and the sample should be evenly dispersed on the surface of the water without agitation. The Sample should be added within 1 min.
Acceptance criteria: The powders wet out in NMT 60 min.
• C.
Sample: 5 g
Analysis: Add the Sample to 500 mL of water, stir, and adjust with 1 N sodium hydroxide to a pH of 7.5, or use the method described in Viscosity—Rotational Methods.
Acceptance criteria: A viscous gel is formed.
3 ASSAY
Carboxylic Acid Content
Sample: 400 mg, previously dried under vacuum at 80° for 1 h
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry 〈541〉.)
Mode: Direct titration
Electrode: Calomel–glass or silver/silver chloride
Titrant: 0.25 N sodium hydroxide VS
Endpoint detection: Potentiometric
Analysis: Slowly add the Sample to 400 mL of water in an 800–1000-mL beaker, while stirring continually at 1000 ± 10 rpm. The stirrer shaft is set at an angle of about 60° and to one side of the beaker, and the propeller is positioned near the bottom of the beaker. Continue stirring for 15 min. Allow the polymer dispersion to stand for 30 min. Transfer the beaker to a magnetic stirring device. Place an approximately 7.62-cm stirring bar into the solution, and adjust the mixer speed to obtain moderate mixing. Add 1 g of potassium chloride, and titrate with Titrant. After each addition of Titrant, allow 1 min for mixing before recording the pH.
Calculate the carboxylic acid content as a percentage of carboxylic acid groups in the portion of Carbomer Interpolymer taken:
Result = [(V × NA/W) × F] × 100
V = Titrant volume consumed (mL)
NA = actual normality of the Titrant (mEq/mL)
W = Sample weight (mg)
F = equivalency factor for the carboxylic acid (–COOH) group, 45.02 mg/mEq
Acceptance criteria: 52.0%–62.0%
4 IMPURITIES
4.1 Limit of Ethyl Acetate and Cyclohexane
[Note-This test is required only for those Carbomer Interpolymers where the labeling indicates that ethyl acetate or a mixture of ethyl acetate and cyclohexane was used in the polymerization process.]
Diluent: 166 mL/L of Dimethyl sulfoxide in water
Standard stock solution: 7 mg/g of cyclohexane and ethyl acetate in dimethyl sulfoxide
Standard solution A: Transfer 50 ± 1 mg of Carbomer Interpolymer to a 20-mL headspace vial, and add 6 mL of Diluent to the vial. Weigh the vial. Using a syringe, add 10 μL of the Standard stock solution to the vial. Weigh the vial. Calculate the weight of the added Standard stock solution. Seal the vial with a Te on-lined butyl rubber septum and aluminum crimp cap. Shake the vial for 1 h.
Standard solution B: Transfer 50 ± 1 mg of Carbomer Interpolymer to a 20-mL headspace vial, and add 6 mL of Diluent to the vial. Weigh the vial. Using a syringe, add 20 μL of the Standard stock solution to the vial. Weigh the vial. Calculate the weight of the added Standard stock solution. Seal the vial with a Teflon-lined butyl rubber septum and aluminum crimp cap. Shake the vial for 1 h.
Standard solution C: Transfer 50 ± 1 mg of Carbomer Interpolymer to a 20-mL headspace vial, and add 6 mL of Diluent to the vial. Weigh the vial. Using a syringe, add 50 μL of the Standard stock solution to the vial. Weigh the vial. Calculate the weight of the added Standard stock solution. Seal the vial with a Teflon-lined butyl rubber septum and aluminum crimp cap. Shake the vial for 1 h.
Sample solution: Transfer 50 ± 1 mg of Carbomer Interpolymer to a 20-mL headspace vial, and add 6 mL of Diluent to the vial. Seal the vial with a Teflon-lined septum and aluminum crimp cap. Shake for 1 h.
4.1.1 Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: GC, equipped with a headspace injector
Detector: Flame ionization
Column: 0.53-mm × 30-m fused silica; coated with 3.0-μm stationary phase G43
Temperatures
Injection port: 140°
Detector: 250°
Column: See Table 2.
Table 2
| Initial Temperature (°) | Temperature Ramp (°/min) | Final Temperature (°) | Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | – | 40 | 10 |
| 40 | 30 | 240 | 5 |
Carrier gas: Helium
Flow rate: 5 mL/min (at a linear velocity of 35 cm/s programmed in constant pressure mode)
Injection volume: 1 mL (gaseous phase)
Injection type: Split, split ratio, 5:1
[Note-The following headspace conditions may be used: a vial pressure of 10 psi, a loop fill pressure (if equipped) of 7 psi, and a transfer line temperature of 105°.]
Vial temperature: The vials are maintained at a temperature of 80° for 45 min before headspace injection.
4.1.2 System suitability
Sample: Standard solution B
4.1.3 Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation: NMT 15% from 3 injections
4.1.4 Analysis
Samples: Standard solution A, Standard solution B, Standard solution C, and Sample solution
The detector response factor (RF) of each Standard solution is determined by:
RF = (WSS × CSS )/(rS − rU )
WSS = weight of the Standard stock solution in each Standard solution (g)
CSS = concentration of ethyl acetate or cyclohexane in the Standard stock solution (mg/g)
rS = peak area of ethyl acetate or cyclohexane in each Standard solution
rU = peak area of ethyl acetate or cyclohexane in the Sample solution
Average three RF to obtain RF . Calculate the percentage of ethyl acetate or cyclohexane in the portion of Carbomer Interpolymer taken:
Result = [(RFavg × rU )/WU ] × 100
RFavg = average of three RF
rU = peak area of ethyl acetate or cyclohexane in the Sample solution
WU = weight of Carbomer Interpolymer in the Sample solution (mg)
4.1.5 Acceptance criteria
Ethyl acetate: NMT 0.35%
Cyclohexane: NMT 0.15%
Change to read:
4.2 Limit of Benzene
Diluent: 166 mL/L of dimethyl sulfoxide in water
Standard stock solution: 1.2 μg/g of benzene in dimethyl sulfoxide
Standard solution A: Transfer 50 ± 1 mg of Carbomer Interpolymer to a 20-mL headspace vial, and add 6 mL of Diluent to the vial. Weigh the vial. Using a syringe, add 10 μL of the Standard stock solution to the vial. Weigh the vial. Calculate the weight of the added Standard stock solution. Seal the vial with a Teflon-lined butyl rubber septum and aluminum crimp cap. Shake the vial for 1 h.
Standard solution B: Transfer 50 ± 1 mg of Carbomer Interpolymer to a 20-mL headspace vial, and add 6 mL of Diluent to the vial. Weigh the vial. Using a syringe, add 50 μL of the Standard stock solution to the vial. Weigh the vial. Calculate the weight of the added Standard stock solution. Seal the vial with a Teflon-lined butyl rubber septum and aluminum crimp cap. Shake the vial for 1 h.
Standard solution C: Transfer 50 ± 1 mg of Carbomer Interpolymer to a 20-mL headspace vial, and add 6 mL of Diluent to the vial. Weigh the vial. Using a syringe, add 100 μL of the Standard stock solution to the vial. Weigh the vial. Calculate the weight of the added Standard stock solution. Seal the vial with a Teflon-lined butyl rubber septum and aluminum crimp cap. Shake the vial for 1 h.
Sample solution: Transfer 50 ± 1 mg of Carbomer Interpolymer to a 20-mL headspace vial, and add 6 mL of Diluent to the vial. Seal the vial with a Teflon-lined septum and aluminum crimp cap. Shake for 1 h.
4.2.1 Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: GC, equipped with a headspace injector
Detector: Flame ionization
Column: 0.53-mm × 30-m fused silica; coated with 3.0-μm stationary phase G46
Temperatures
Injection port: 140°
Detector: 250°
Column: See Table 3.
Table 3
| Initial Temperature (°) | Temperature Ramp (°/min) | Final Temperature (°) | Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | – | 40 | 10 |
| 40 | 30 | 240 | 5 |
Carrier gas: Helium
Flow rate: 5 mL/min (at a linear velocity of 35 cm/s programmed in constant pressure mode)
Injection volume: 1 mL (gaseous phase)
Injection type: Split, split ratio, 0.5: 1
[Note-The following headspace conditions may be used: a vial pressure of 10 psi, a loop fill pressure (if equipped) of 7 psi, and a transfer line temperature of 105°.]
Vial temperature: The vials are maintained at a temperature of 80° for 45 min before headspace injection.
4.2.2 System suitability
Sample: Standard solution B
4.2.3 Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation: NMT 15% from 3 injections
4.2.4 Analysis
Samples: Standard solution A, Standard solution B, Standard solution C, and Sample solution
The detector response factor (RF) of each Standard solution is determined by:
RF = (WSS × CSS)/(rS − rU)
WSS = weight of the Standard stock solution in each Standard solution (g)
CSS = concentration of benzene in Standard stock solution (μg/g)
rS = peak area of benzene in each Standard solution
rU = peak area of benzene in the Sample solution
Average three RF to obtain RF . Calculate the percentage of benzene in the portion of Carbomer Interpolymer taken:
Result = [(RFavg × r )/W ] × 100
RFavg = average of three RF
rU =peak area of benzene in the Sample solution
WU = weight of Carbomer Interpolymer in the Sample solution (μg (ERR 1-Dec-2021) )
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.0002%, corresponding to NMT 2 μg/g
4.3 Limit of Acrylic Acid
Solution A: Methanol
Solution B: Dissolve 6.80 g of monobasic potassium phosphate in 300 mL of water, dilute with water to 500 mL. Dilute 100 mL of this solution with water to 1 L, adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 3.0 ± 0.1. Filter and degas.
Mobile phase: See Table 4.
| Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) | Flow Rate (mL/min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 95 | 1.0 |
| 8 | 5 | 95 | 1.0 |
| 9 | 10 | 90 | 1.5 |
| 19 | 10 | 90 | 1.5 |
| 20 | 5 | 95 | 1.0 |
| 25 | 5 | 95 | 1.0 |
Standard solution A: 2 μg/g of Acrylic acid (w/w)
Standard solution B: 50 μg/g of acrylic acid (w/w)
Standard solution C: 100 μg/g of acrylic acid (w/w)
Sample solution: Transfer 100 mg of Carbomer Interpolymer to a tared serum vial. Add water to obtain a total weight of 10 g of solution. Cap the vial, and shake by mechanical means for 2 h. Add 2 drops of sodium hydroxide solution (50% w/v), and shake by hand for 15 s. Add 1.0mL of calcium chloride solution (100 mg/mL), and shake until the gel collapses. Record the weight of all additions of water, sodium hydroxide, and calcium chloride. Centrifuge for 15 min, and use the clear supernatant.
4.3.1 Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 200 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 15-cm; 5 μm packing L1
Flow rate: See Table 4.
Injection volume: 10 μL
4.3.2 System suitability
Sample: Standard solution B
4.3.3 Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation: NMT 5% from 3 injections
4.3.4 Analysis
Samples: Standard solution A, Standard solution B, Standard solution C, and Sample solution
Analyze each Standard solution, and plot the peak area versus concentration. Plot should be linear with an r2 equal or greater than 0.9990. The slope of the calibration curve (area/ppm acrylic acid) is the response factor. Calculate the percentage of free acrylic acid in the portion of Carbomer Interpolymer taken:
Result (wt%) = (rU/RF)/CU × F × 100
rU = peak response of acrylic acid from the Sample solution
RF = response factor [peak area/(μg/g)]
CU = concentration of Carbomer Interpolymer in the Sample solution (mg/g)
F = unit conversion factor, 10–3 (mg/μg)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.25%
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
Loss on Drying 〈731〉
Analysis: Dry under vacuum at 80° for 1 h.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 2.0%
Viscosity-Rotational Methods 〈912〉
5.1 Carbomer Interpolymer A
Sample: 2.50 g of Carbomer Interpolymer, previously dried under vacuum at 80° for 1 h (0.5% aqueous dispersion)
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry 〈541〉.)
Mode: Direct titration
Electrode: Calomel–glass or silver/silver chloride
Titrant: 180 mg/mL of sodium hydroxide
Endpoint detection: pH
Analysis: Carefully add the Sample to 500 mL of water in an 800-mL beaker,1 while stirring continuously at 1000 ± 10 rpm, with the stirrer shaft set to one side of the beaker at an angle of 60° and the propeller positioned near the bottom of the beaker. Allow 45–90 s for addition of the Sample at a uniform rate, being sure that loose aggregates of powder are broken up, and continue stirring at 1000 ± 10 rpm for 15 min. [Note-Proper dispersion of the carbomer resin is imperative for accurate viscosity readings.] Remove the stirrer, and place the beaker containing the dispersion in a 25 ± 0.1° water bath for 30 min. Insert the stirrer to a depth necessary to ensure that air is not drawn into the dispersion, and while stirring at 300 ± 25 rpm, titrate to a pH of 7.3–7.8. Stir 2–3 min until neutralization is complete.
[Note-After neutralization, care must be taken to avoid high shearing because aggressive mixing will break the polymer chains and reduce the viscosity readings.] Then determine the final pH. [Note-If the pH is below 7.3, raise it with additional Titrant. If it is above 7.8, discard the mucilage, and prepare another batch, using a smaller amount of Titrant for titration.]
Return the beaker containing the neutralized mucilage to the 25 ± 0.1° water bath for 1 h. Measure the mucilage pH again, making certain that it is between 7.3 and 7.8. Equip a suitable rotational viscometer 2 with a suitable spindle at a spindle immersion depth as defined in Table 5, perform the viscosity determination without delay to avoid the slight viscosity changes that occur 75 min after neutralization.
The spindle rotates at 20 rpm. Follow the instrument manufacturer's directions to measure the apparent viscosity.
5.2 Carbomer Interpolymer B
Sample: 5.00 g of Carbomer Interpolymer, previously dried under vacuum at 80° for 1 h (1.0% aqueous dispersion)
Analysis: Proceed as directed for Carbomer Interpolymer A, except for the following:
1. Adjust the pH of the dispersion to 5.8–6.3.
2. Interpolymer type B may foam, and efforts should be made to remove the foam to the extent feasible. After mixing for 2 min at 1000± 10 rpm, lower the speed to 300 ± 25 rpm, and set the timer for 13 min. Scrape the resin from the sides of the beaker and stirrer shaft with a spatula or rubber policeman.
3. If foam persists during temperature equilibration in the water bath, it may be removed by carefully directing an air stream at the surface of the dispersion.
5.3 Carbomer Interpolymer C
Sample: 2.50 g of Carbomer Interpolymer, previously dried under vacuum at 80° for 1 h
Analysis: Proceed as directed for Carbomer Interpolymer B.
Acceptance criteria: See Table 5.
Table 5
| Viscosity Ranges (mPa·s) | Spindle No. | Aa (cm) | Bb (cm) | Cc (cm) | Dd (cm) | Ee (cm) | Multiplier |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100–400 | 1 | 5.6 | 2.2 | 0.3 | 2.7 | 6.1 | 5 |
| 400–1,600 | 2 | 4.7 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 2.7 | 4.9 | 20 |
| 1,000–4,000 | 3 | 3.5 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 2.7 | 4.9 | 50 |
| 2,000–8,000 | 4 | 2.7 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 2.7 | 4.9 | 100 |
| 4,000–16,000 | 5 | 2.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 2.7 | 4.9 | 200 |
| 10,000–40,000 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 3.0 | 4.9 | 500 |
| 40,000–160,000 | 7 | – | – | 0.3 | – | 5.5 | 2,000 |
a Cylinder diameter.
b Cylinder height.
c Shaft diameter.
d Distance from the top of the cylinder to the lower tip of the shaft.
e Spindle immersion depth.
Table 6
| Carbomer Interpolymer | Viscosity Specifications (mPa·s) |
|---|---|
| A | 45,000–65,000 |
| B | 47,000–77,000 |
| C | 8,500–16,500 |
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Product is hygroscopic. Preserve in tight containers away from direct sources of moisture.
Labeling: Label it to indicate whether it is Type A, B, or C. Also label it to state the measured viscosity, giving the viscosity measurement parameters, the concentration of the solution, and the type of equipment used; the solvent or solvents used in the polymerization process; and the nominal and measured residual solvent levels for each solvent.
1 A beaker size of 600–1000 mL is ideal for this method. However, the minimum inside diameter of the beaker should be 83 mm.
2 Available as a Brookfield RV viscometer, or equivalent.


