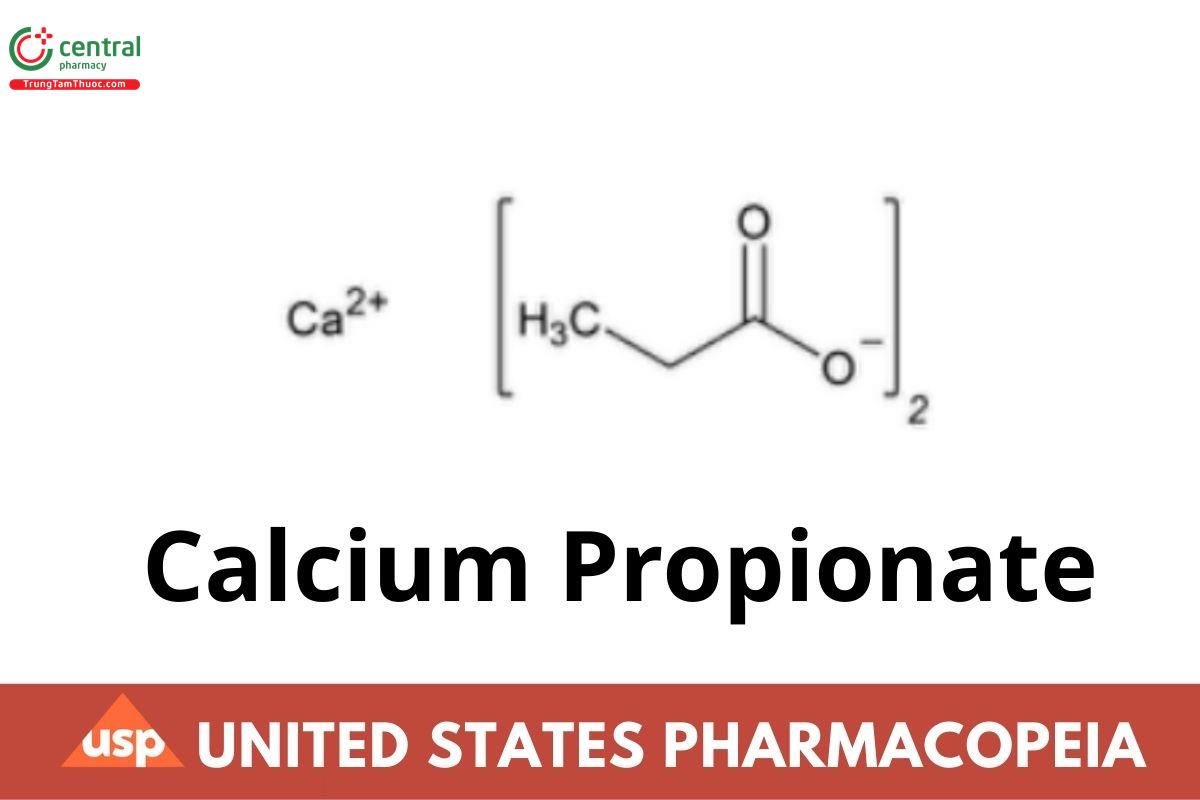
Calcium Propionate
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
DOWNLOAD PDF HERE
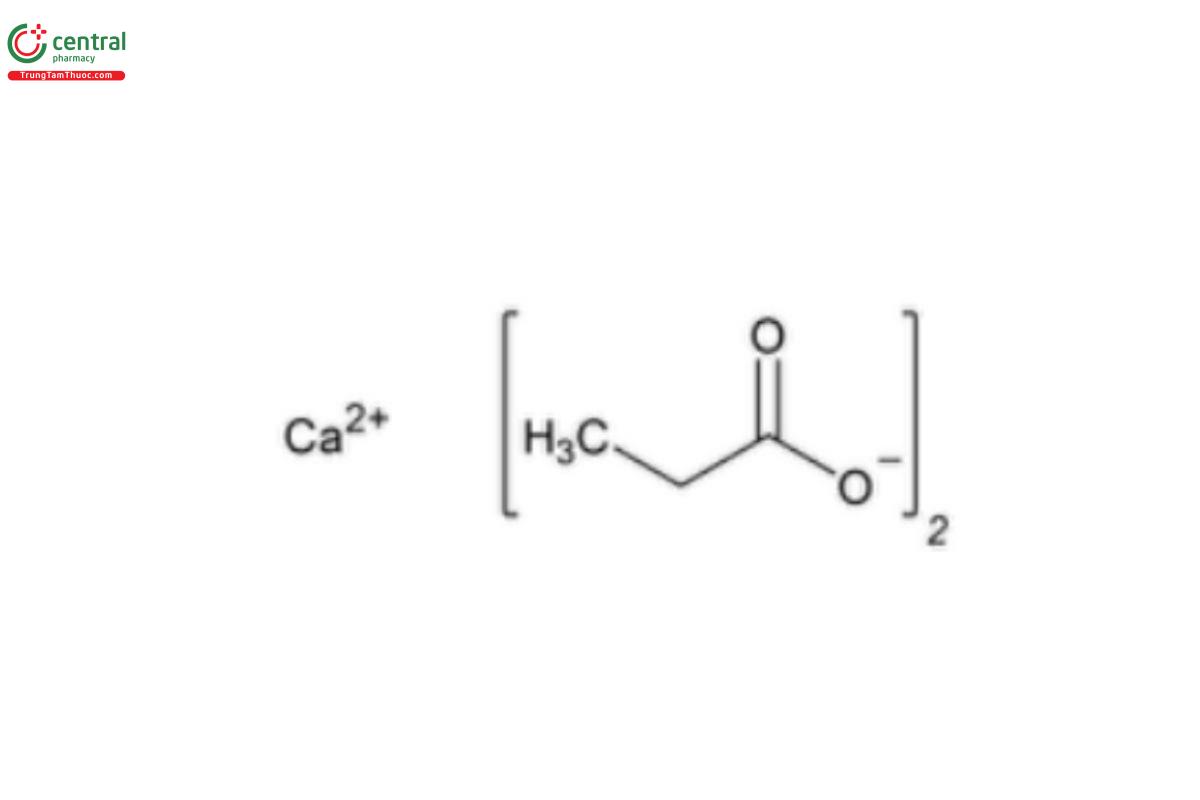
C6H10CaO4 186.22
Propanoic acid, calcium salt;
Calcium propionate (NF 1-May-2023) CAS RN®: 4075-81-4.
Change to read:
1 DEFINITION
Calcium Propionate contains NLT 97.0% (NF 1-May-2023) and NMT 102.0% (NF 1-May-2023) of calcium propionate (C6H10CaO4), calculated on the anhydrous basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
2.1 Change to read:
A. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197A (NF 1-May-2023)
2.2 Add the following:
B. Chromatographic Identity
Analysis: Examine the chromatograms obtained in the Assay.
Acceptance criteria: The retention time of the major peak of the Sample solution corresponds to that of the Standard solution. (NF 1-May-2023)
3 ASSAY
Change to read:
Procedure
Solution A: 10 mM potassium phosphate, monobasic, with the pH adjusted to 2.5 using phosphoric acid
Solution B: Acetonitrile
Mobile phase: See Table 1.
Table 1
| Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) |
| 0 | 100 | 0 |
| 3.0 | 100 | 0 |
| 15.0 | 70 | 30 |
| 25.0 | 50 | 50 |
| 26.0 | 100 | 0 |
| 35.0 | 100 | 0 |
Diluent: 2% (v/v) phosphoric acid in water
System suitability solution: 2.5 mg/mL of USP Calcium Propionate RS and 0.008 mg/mL of Acrylic acid in Diluent
Standard solution: 2.5 mg/mL of USP Calcium Propionate RS in Diluent
Sample solution: 2.5 mg/mL of Calcium Propionate in Diluent
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 210 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-μm packing L1
Column temperature: 45°
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min
Injection volume: 20 μL
Run time: 35 min
System suitability
Samples: System suitability solution and Standard solution
[Note—The approximate relative retention times for related substances are listed in Table 2.]
Table 2
| Name | Relative Retention Time |
| Calcium acetate | 0.5 |
| Calcium acrylate | 0.95 |
| Calcium propionate | 1.0 |
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 1.5 between the calcium propionate peak and the acrylic acid peak, System suitability solution
Tailing factor: NMT 2, determined from the calcium propionate peak, Standard solution
Relative standard deviation: NMT 1%, determined from the calcium propionate peak, Standard solution
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of calcium propionate in the portion of sample taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
rU= peak area of calcium propionate from the Sample solution
rS= peak area of calcium propionate from the Standard solution
CS= concentration of USP Calcium Propionate RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU= concentration of Calcium Propionate in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: 97.0%–102.0% on the anhydrous basis (NF 1-May-2023)
4 IMPURITIES
Add the following:
Organic Impurities
Mobile phase, Diluent, System suitability solution, and Chromatographic system: Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Sensitivity solution: 0.01 mg/mL of USP Calcium Propionate RS in Diluent
Standard solution: 0.02 mg/mL of USP Calcium Propionate RS in Diluent
Sample solution: 20 mg/mL of Calcium Propionate in Diluent
System suitability
Samples: System suitability solution, Sensitivity solution, and Standard solution
[Note—The approximate relative retention times for related substances are listed in Table 2.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 1.5 between the calcium propionate peak and the acrylic acid peak, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation: NMT 5.0%, determined from the calcium propionate peak, Standard solution
Signal-to-noise ratio: NLT 10, determined from the calcium propionate peak, Sensitivity solution
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
[Note—The peak eluting at RRT 0.3 is the calcium ion peak. This peak and the peaks eluting before it are excluded from integration. These
peaks are not from organic impurities of Calcium Propionate.]
Calculate the percentage of each individual impurity in the portion of sample taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × (1/F) × 100
rU= peak area of each individual impurity from the Sample solution
rS= peak area of calcium propionate from the Standard solution
CS= concentration of USP Calcium Propionate RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU= concentration of Calcium Propionate in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
F = relative response factor (see Table 3)
Acceptance criteria: See Table 3.
Table 3
| Name | Relative Response Factor | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
| Calcium acetate | 1.0 | 0.2 |
| Calcium acrylate | 92.4 | 0.1 |
| Calcium propionate | - | - |
| Any unidentified individual impurity | 1.0 | 0.1 |
| Total impurities | - | 1.0 (NF 1-May-2023) |
Change to read:
Limit of Fluoride
Buffer: 294.1 mg/mL of sodium citrate dihydrate
Standard solution: 2.21 mg/mL of USP Sodium Fluoride RS. [Note—Store solution in a plastic bottle.] On the day of use, transfer 5.0 mL of the resulting solution to a 1000-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Each milliliter of this solution contains 5 μg of fluoride ion.
Electrode system: Use a fluoride-specific, ion-indicating electrode and a silver–silver chloride reference electrode connected to a pH meter capable of measuring potentials with a minimum reproducibility of ±0.2 mV (see pH 〈791〉).
Standard response line: Transfer 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 5.0, 10.0, and 15.0 mL of the Standard solution to separate 250-mL plastic beakers. Add 50 mL of water, 5 mL of 1 N hydrochloric acid, 10 mL of Buffer, and 10 mL of 0.2 M edetate disodium to each beaker, and mix. Transfer each solution to separate 100-mL volumetric flasks, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Transfer a 50-mL portion of each solution to separate 125-mL plastic beakers, and read the potential, in mV, of each solution using the electrode system. Construct a calibration curve by plotting potential, in mV, versus logarithm of μg of fluoride per 100 mL of solution.▲ (NF 1-May-2023)
Sample: 1.0 g
Analysis: Transfer the Sample to a 150-mL glass beaker, add 10 mL of water, and, while stirring continuously, slowly add 20 mL of 1 N hydrochloric acid to dissolve the Sample. Boil rapidly for 1 min. Transfer to a 250-mL plastic beaker, and cool rapidly in ice water. Add 15 mL of Buffer and 10 mL of 0.2 M edetate disodium, and mix. Adjust the pH to 5.5 ± 0.1 with 1 N hydrochloric acid or 1 N sodium hydroxide, if necessary. Transfer to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Transfer a 50-mL portion of this solution to a 125- mL plastic beaker, and record the potential using the electrode system. Determine the concentration of fluoride, in μg/mL, in the Sample.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 30 μg/g
Limit of Lead
25% Sulfuric acid solution: Cautiously add 100 mL of sulfuric acid to 300 mL of water with constant stirring while cooling in an ice bath.
Standard solutions: On the day of use, transfer 5.0, 10.0, and 20.0 mL of standard lead solution TS to three separate 100-mL volumetric flasks, add 10 mL of 3 N hydrochloric acid to each, and dilute with water to volume corresponding to 0.5-, 1.0-, and 2.0-μg/mL standards.
Sample blank: Add 5 mL of 25% Sulfuric acid solution into an evaporating dish. Within a hood, place the dish on a steam bath to evaporate most of the water. Place the dish on a burner, and slowly pre-ash the sample by expelling most of the sulfuric acid. Place the dish in a
muffle furnace that has been set at 525°, and ash the sample until the residue appears free from carbon. Cool, and cautiously wash down the inside of the evaporation dish with water. Add 5 mL of 1 N hydrochloric acid. Place the dish on a steam bath, and evaporate to dryness.
Add 1.0 mL of 3 N hydrochloric acid and approximately 5 mL of water, and heat briefly on a steam bath to dissolve any residue. Transfer the solution quantitatively to a 10-mL volumetric flask, dilute to volume, and mix.
Sample solution: Place 10 g of Calcium Propionate, to the nearest 0.1 mg, into an evaporating dish. Add a suffcient amount of 25% Sulfuric acid solution, and distribute the sulfuric acid uniformly through the sample. Proceed as directed under Sample blank beginning with “Within
a hood...”.
Instrumental conditions
(See Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy 〈852〉.)
Mode: Atomic absorption
Analytical wavelength: 283.3 nm
Lamp: Lead electrodeless discharge
Flame: Air–acetylene
Slit width: 0.7 nm
Instrument blank: Water
Standard curve
Samples: Standard solutions and Sample blank
Plot: Corrected absorbance values versus their corresponding concentration (μg/mL). [Note—Determine corrected absorbance values by subtracting the absorbance of the Sample blank from the absorbance of the Standard solutions.]
Analysis
Samples: Sample blank and Sample solution
[Note—Determine corrected absorbance values by subtracting the absorbance of the Sample blank from the absorbance of the Sample
solution.]
From the Standard curve, determine the lead concentration in the Sample solution.
Calculate the lead content in the portion of Calcium Propionate taken:
Result = (CS× V)/W
CS= concentration of lead from the Standard curve (μg/mL)
V = final volume of the sample (mL)
W = weight of the sample taken (g)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 2 μg/g
Magnesium (as MgO)
Magnesium standard solution: Dissolve 50.0 mg of magnesium metal in 1 mL of hydrochloric acid in a 1000-mL volumetric
ask, dilute with
water to volume, and mix.
Sample solution: Place 400.0 mg of Calcium Propionate, 5 mL of 2.7 N hydrochloric acid, and about 10 mL of water in a small beaker, and dissolve the Calcium Propionate by heating on a hot plate.
Analysis: Evaporate the Sample solution to a volume of about 2 mL, and cool. Transfer the residual liquid to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Dilute 7.5 mL of this solution with water to 20 mL, add 2 mL of 1 N sodium hydroxide and 0.05 mL of a 1:1000 solution of thiazole yellow, and mix. Allow to stand for 10 min, and shake. Any color produced does not exceed that produced by 1.0 mL of Magnesium standard solution in the same volume as that of a control containing 2.5 mL of the Sample solution (corresponding to 10 mg of Calcium Propionate) and the quantities of the reagents used in the test.
Acceptance criteria: The solution passes the test (about 0.4%).
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
Water-Insoluble Substances
Sample: 10 g
Analysis: Dissolve the Sample in 100 mL of hot water, pass through a tared ltering crucible, wash the insoluble residue with hot water, and dry at 105° to constant weight.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.2%
pH 〈791〉: 7.5–10.5, in a solution (1 in 10)
Water Determination 〈921〉, Method I: NMT 5.0%
Delete the following:
Loss on Drying 〈731 (NF 1-May-2023)
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Store in tightly closed containers. No storage requirements specified.
Change to read:
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Calcium Propionate RS (NF 1-May-2023)
USP Sodium Fluoride RS


