Calcium Ascorbate
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
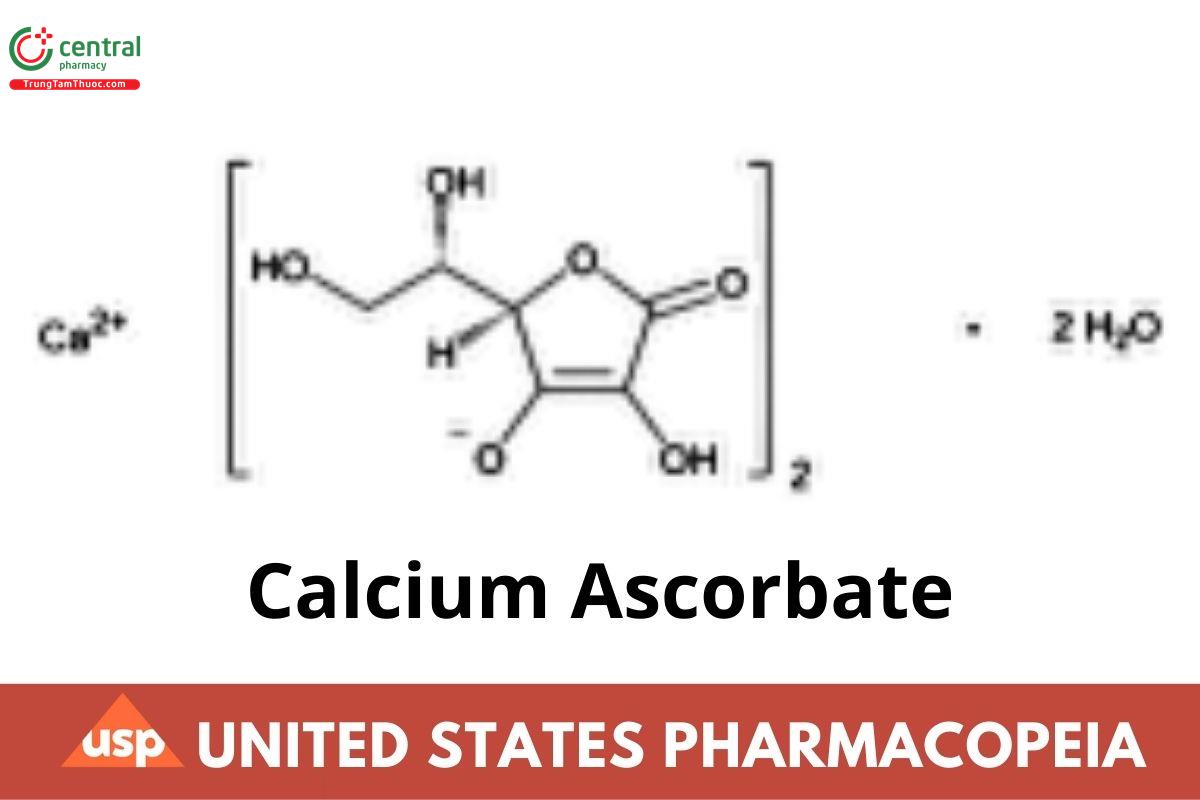
C12H14CaO12.2H2O 426.34
l-Ascorbic acid, calcium salt (2:1), dihydrate;
Calcium l-ascorbate (1:2), dihydrate [5743-28-2]; UNII:183E4W213W.
1 DEFINITION
Calcium Ascorbate contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 101.0% of calcium ascorbate dihydrate (C12H14CaO12.2H2O), calculated on the as-is basis. 12
2 IDENTIFICATION
Change to read:
A. Characteristic emission lines for calcium at 184.0, 315.9, and 317.9 nm from the Sample solution correspond to those from the Standard solution, as obtained in the Content of Calcium.
Change to read:
B. The retention time of the ascorbic acid peak of the Sample solution corresponds to that of the Standard solution, as obtained in the Assay.
C. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197M
3 ASSAY
Change to read:
Procedure
Mobile phase: 50 mM monobasic sodium phosphate, adjusted with phosphoric acid to a pH of 2.5
Diluent: Dissolve 73 g of metaphosphoric acid in 1.0 L of water.
Standard stock solution: 2 mg/mL of USP Ascorbic Acid RS in Diluent
Standard solution: 0.2 mg/mL of USP Ascorbic Acid RS in Mobile phase, from the Standard stock solution
Sample stock solution: Transfer 220 mg of Calcium Ascorbate to a 100-mL volumetric ask. Dissolve and dilute with Diluent to volume. Sample solution: 0.22 mg/mL of Calcium Ascorbate in Mobile phase, from the Sample stock solution
Blank: Diluent
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 245 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L96
Temperatures
Autosampler: 5°
Column: 10°
Flow rate: 0.8 mL/min
Injection volume: 10 µL
System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Tailing factor: NMT 2.0
Relative standard deviation: NMT 2.0% for the ascorbate peak
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of calcium ascorbate dihydrate (C12H14CaO12.2H2O) in the portion of sample taken: 12
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × (Mr1/2Mr2) × 100
rU = peak response of ascorbic acid from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of ascorbic acid from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Ascorbic Acid RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Calcium Ascorbate dihydrate in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Mr1 = molecular weight of calcium ascorbate dihydrate, 426.34
Mr2 = molecular weight of ascorbic acid, 176.12
Acceptance criteria: 98.0%–101.0% on the as-is basis
Add the following:
4 OTHER COMPONENTS
Content of Calcium
Stock aqua regia solution: A mixture of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid (3:1), prepared as follows. Add the nitric acid to the hydrochloric acid. [Note—Periodically vent the solution in an appropriate fume hood.]
Diluent: A mixture of Stock aqua regia solution and deionized water (1:9), prepared as follows. Add 1 volume of Stock aqua regia solution to 2 volumes of deionized water. Dilute with additional deionized water to volume, and mix well.
Standard stock solution: Using a commercially available calcium standard solution in 5% (v/v) nitric acid solution, pipet an appropriate amount of calcium standard solution into a volumetric flask and dilute with 5% (v/v) nitric acid solution to obtain a 1000-mg/L calcium solution.
Standard solution A: Dilute the Standard stock solution with Diluent to obtain a concentration of 5.0 mg/L.
Standard solution B: Dilute the Standard stock solution with Diluent to obtain a concentration of 30.0 mg/L.
Standard solution C: Dilute the Standard stock solution with Diluent to obtain a concentration of 60.0 mg/L.
Standard solution D: Dilute the Standard stock solution with Diluent to obtain a concentration of 100.0 mg/L.
Standard solution E: Dilute the Standard stock solution with Diluent to obtain a concentration of 150.0 mg/L.
Standard solution F: Dilute the Standard stock solution with Diluent to obtain a concentration of 250.0 mg/L.
Sample solution: Transfer 266 mg of Calcium Ascorbate (equivalent to about 25 mg of calcium) to a 250-mL Erlenmeyer ask. Cautiously add 25 mL of Stock aqua regia solution in 5-mL increments and swirl after each addition. Once bubbling stops, bring to a boil on a hot plate set at low to medium heat. Continue gently boiling until fumes cease (for about an hour). Remove from the heat source and let the solution cool to room temperature. Transfer the solution quantitatively to a 250-mL volumetric ask, dilute with deionized water to volume, and mix well. Pass about 30 mL through a nylon syringe filter of 5-µm pore size into a polypropylene centrifuge tube. Blank: Diluent
Instrumental conditions
(See Plasma Spectrochemistry 〈730〉.)
Mode: ICP-OES
Emission wavelength: About 315.9 nm or optimized wavelength for calcium. For Identification A, detect additional calcium emission lines at 184.0 and 317.9 nm. [Note—The operating conditions may be developed and optimized based on the manufacturer's recommendation. The wavelengths selected should be demonstrated experimentally to provide sufficient specificity, sensitivity, linearity, accuracy, and precision.]
System suitability
Sample: Standard solutions
Suitability requirements
Correlation coefficient: NLT 0.99, determined from the linear calibration constructed in the Analysis, Standard solutions A–F Relative standard deviation: NMT 2.0% from ve replicate analyses of Standard solution D
Analysis
Samples: Diluent, Standard solutions, and Sample solution
Construct a linear calibration curve using the intensity of the emission from the six Standard solutions. Determine the emission lines of calcium in each Standard solution and the Sample solution. Plot the emission values of calcium in the Standard solutions versus the concentration, in mg/L, of calcium, and draw the straight line best hitting the plotted points. From the graph, determine the concentration (C), in mg/L, of calcium in the Sample solution.
Calculate the percentage of calcium in the portion of Calcium Ascorbate taken:
Result = C × (V/W) × 100
C = concentration of calcium in the Sample solution (mg/L)
V = volume of the Sample solution (L)
W = sample weight (mg)
Acceptance criteria: 9.0%–10.0% on the as-is basis
5 IMPURITIES
Arsenic 〈211〉, Procedures, Procedure 1: NMT 3 µg/g
Limit of Fluoride
Prepare and store all solutions in plastic containers.
Buffer solution: 294 mg/mL of sodium citrate dihydrate in water
Standard stock solution: 1.1052 mg/mL of USP Sodium Fluoride RS in water
Standard solution: Transfer 20.0 mL of the Standard stock solution to a 100-mL volumetric ask containing 50.0 mL of Buffer solution, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Each milliliter of the Standard solution contains 100 µg of fluoride ion.
Sample solution: Transfer 2.0 g of Calcium Ascorbate to a beaker containing a plastic-coated stirring bar. Add 20 mL of water and 2.0 mL of hydrochloric acid, and stir until dissolved. Add 50.0 mL of Buffer solution and sufficient water to make 100 mL.
Electrode system: Use a fluoride-specic ion-indicating electrode and a silver–silver chloride reference electrode connected to a pH meter capable of measuring potentials with a minimum reproducibility of ± 0.2 mV (see pH 〈791〉).
Standard response line: Transfer 50.0 mL of Buffer solution and 2.0 mL of hydrochloric acid to a beaker, and add water to make 100 mL. Add a plastic-coated stirring bar, insert the electrodes into the solution, stir for 15 min, and read the potential, in mV. Continue stirring, and at 5- min intervals add 100, 100, 300, and 500 µL of the Standard solution, record the potential 5 min after each addition. Plot the logarithms of the cumulative fluoride ion concentrations (0.1, 0.2, 0.5, and 1.0 µg/mL) versus potential, in mV.
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Rinse and dry the electrodes, insert them into the Sample solution, stir for 5 min, and record the potential, in mV. From the potential and the Standard response line, determine the concentration (C), in µg/mL, of fluoride ion in the Sample solution.
Calculate the content, in ppm, of fluoride in the portion of Calcium Ascorbate taken:
Result = (C × V)/W
C = concentration of fluoride ion in the Sample solution (µg/mL)
V = volume of the Sample solution (mL)
W = weight of Calcium Ascorbate taken to prepare the Sample solution (g)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 10 ppm
6 SPECIFIC TESTS
Optical Rotation 〈781S〉, Procedures, Specific Rotation
Sample solution: 50 mg/mL in carbon dioxide-free water. [Note—Perform measurements immediately after preparation.] Acceptance criteria: +95° to +97°
pH 〈791〉
Sample solution: 100 mg/mL
Acceptance criteria: 6.8–7.4
Loss on Drying 〈731〉
Sample: 3 g
Analysis: Dry the Sample at 105° for 2 h.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.1%
7 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers.
Change to read:
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Ascorbic Acid RS
USP Calcium Ascorbate RS
USP Sodium Fluoride RS


