Butylene Glycol
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
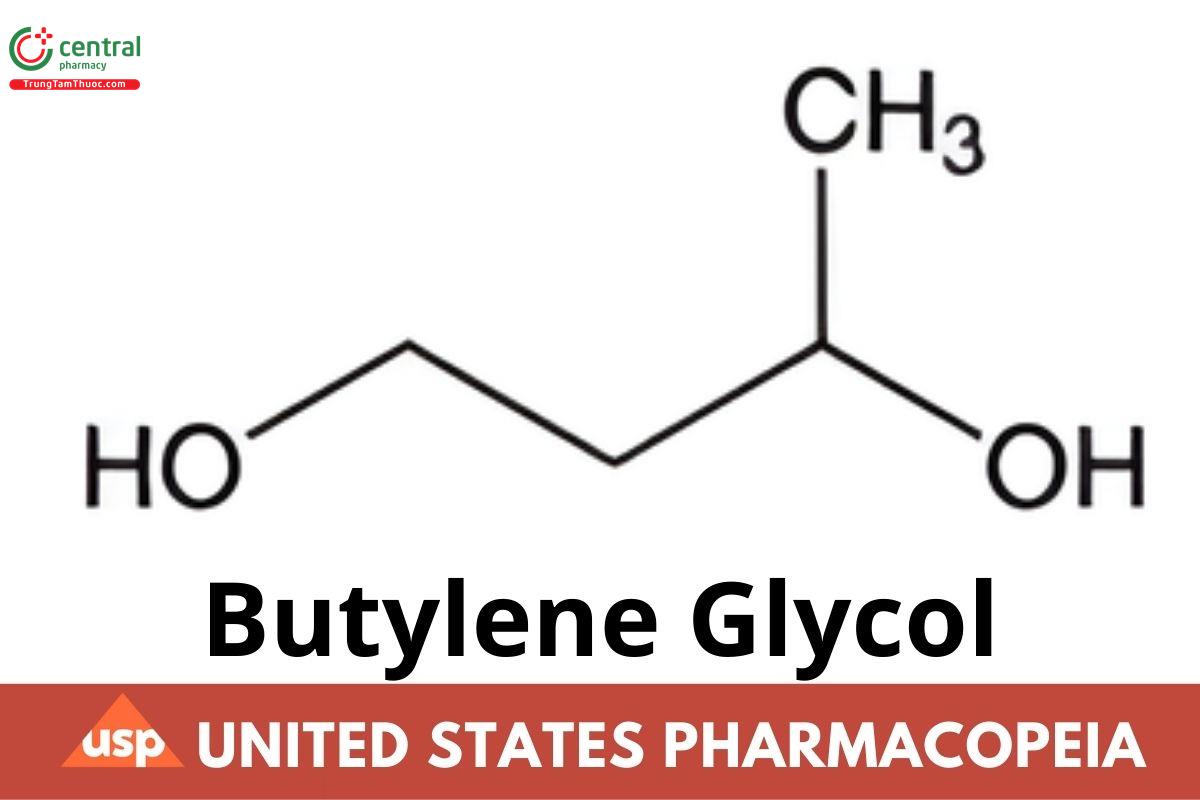
C4H10O2 (HOCH2CH2CH(OH)CH3) 90.12
Butane-1,3-diol;
1,3-Butylene glycol CAS RN®: 107-88-0.
1 DEFINITION
Butylene Glycol contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of butane-1,3-diol (C H O ), calculated on the anhydrous basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
Change to read:
A. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197F (CN 1-May-2020)
B. Chromatographic Identity
Analysis: Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Acceptance criteria: The retention time of butane-1,3-diol in the Sample solution corresponds to that in the Standard solution.
3 ASSAY
3.1 Procedure
Standard solution: 1.0 mg/mL of USP Butane-1,3-diol RS and 1.0 mg/mL of USP Propylene Glycol RS (internal standard) in methanol
Sample solution: 1.0 mg/mL of Butylene Glycol and 1.0 mg/mL of USP Propylene Glycol RS (internal standard) in methanol
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: GC
Detector: Flame ionization
Column: 0.53-mm × 30-m capillary; bonded with a 1.0-μm layer of phase G16 or G47
Temperatures
Detector: 240°
Injection port: 230°
Column: See Table 1.
Table 1
| Initial Temperature (°) | Temperature Ramp (°/min) | Final Temperature (°) | Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 0 | 40 | 3 |
| 40 | 10 | 80 | 0 |
| 80 | 5 | 130 | 2 |
| 130 | 10 | 170 | 0 |
| 170 | 25 | 240 | 0 |
Carrier gas: Hydrogen
Flow rate: 10 mL/min
Injection volume: 1.0 μL
Injection type: Split injection; split ratio is 2:1.
Liner: Single gooseneck liner with wool
3.2 System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
[Note—The relative retention times for propylene glycol and butane-1,3-diol are 1.00 and 1.22, respectively.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 15 between propylene glycol and butane-1,3-diol
Tailing factor: 0.8–2.0
Relative standard deviation: NMT 2% for the peak response ratio of butane-1,3-diol to the internal standard
3.3 Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of butane-1,3-diol in the portion of Butylene Glycol taken:
Result = (RU/RS) × (CS /CU) × 100
RU = peak response ratio of butane-1,3-diol to the internal standard (peak response of butane-1,3-diol/peak response of the internal standard) from the Sample solution
RS = peak response ratio of butane-1,3,-diol to the internal standard (peak response of butane-1,3-diol/peak response of the internal standard) from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Butane-1,3-diol RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Butylene Glycol in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: 98.0%–102.0% on the anhydrous basis
4 IMPURITIES
Residue on Ignition 〈281〉: NMT 0.05% determined on 2 g
Limit of Lead
[Note—For the preparation of all aqueous solutions and for the rinsing of glassware before use, use water that has been passed through a strong-acid, strong-base, mixed-bed ion-exchange resin. For digestion, use acid-cleaned, high-density polyethylene, polypropylene, polytef, or quartz tubes. Select all reagents to have as low a content of lead as practicable, and store all reagent solutions in borosilicate glass containers. Cleanse glassware before use by soaking in warm 8 N nitric acid for 30 min and rinsing with deionized water. Store final diluted solutions in acid-cleaned plastic or polytef tubes or bottles.]
Matrix modier solution: 200 mg/mL of magnesium nitrate. Just before use, transfer 1.0 mL of this solution to a 10-mL volumetric ask, and dilute with 5% nitric acid to volume.
Alternative matrix modier solution: Just before use, add 0.3 mL of commercially available 10,000 μg/mL palladium standard solution and 5mL of commercially available 10,000 μg/mL magnesium nitrate standard solution to 9.7 mL of 5% nitric acid, and mix well. [Note—Alternative matrix modier solution can be used to replace the Matrix modier solution. If the alternative solution is used, then the air-ashing step in the furnace program (see Table 2) can be omitted.]
Table 2
| Step | Temperature (°) | Ramp (s) | Hold Time (s) | Gas | Gas Flow Rate (mL/min) | Read (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | 200 | 20 | 30 | Argon | 300 | — |
| Char (ash) | 750 | 40 | 40 | Aira | 300 | — |
| Cool down | 20 | 1 | 60 | Argon | 300 | — |
| Atomize | 1800 | 0 | 10 | Argon | Stop flow | 10 |
| Clean | 2600 | 1 | 7 | Argon | 300 | — |
| Cool down | 20 | 1 | 5 | Argon | 300 | — |
a If Matrix modier solution is used, air ashing must be used in the experiment. If Alternative matrix modier solution is used, air can be substituted with argon.
Lead nitrate stock solution: Dissolve 159.8 mg of lead nitrate in 100 mL of water to which has been added 1 mL of nitric acid, and then dilute with water to 1000 mL. Prepare and store this solution in glass containers free from soluble lead salts.
Standard stock solution: Transfer 10.0 mL of Lead nitrate stock solution to a 100-mL volumetric ask, add 40 mL of water and 5 mL of nitric acid, and dilute with water to volume. Transfer 1.0 mL of this solution to a second 100-mL volumetric ask, dilute with 5% nitric acid to volume, and mix. This solution contains 0.1 μg/mL of lead.
Standard solutions: Transfer portions of Standard stock solution to four suitable containers, and dilute with 5% nitric acid to obtain Standard solutions having lead concentrations of 100, 50, 25, and 10 ng/mL, respectively.
Sample solution: [Note—Perform this procedure in a fume hood.] Transfer 1.5 g of Butylene Glycol to two digestion tubes, labeled “Sample solution” and “Temperature monitor solution”, and add 0.75 mL of nitric acid to each tube. Place a thermometer in the tube labeled
“Temperature monitor solution”, and use the Temperature monitor solution solely to monitor temperature to be within the ranges speci ed by the method. Warm both solutions slowly to 90°–95° to avoid spattering. Heat until all brown vapors have dissipated and the samples no longer have a rust-colored tint. This typically takes 20–30 min. Allow the samples to cool. Add 0.5 mL of 50% Hydrogen peroxide dropwise to both solutions, heat to 90°–95° for 5 min, and cool. Add a second 0.5-mL portion of 50% hydrogen peroxide dropwise to both solutions, and heat to 90°–100° for 5–10 min or until the solutions are clear. Cool, and transfer the Sample solution to a 10-mL volumetric ask. Rinse the tube labeled “Sample solution” with 5% nitric acid, add the rinsing to the volumetric ask, dilute with 5% nitric acid to volume, and mix.
Standard blank: 5% nitric acid
Sample blank: Transfer 1.5 g of water to a digestion tube, and proceed as directed for the Sample solution, beginning with “add 0.75 mL of nitric acid”.
Instrumental conditions
Mode: Graphite furnace atomic absorption with pyrolytically-coated graphite tubes and adequate means of background correction
Analytical wavelength: Lead emission line at 283.3 nm
Lamp: Lead hollow-cathode
Furnace program: See Table 2. [Note—The temperature program may be modied to obtain optimum furnace temperatures.]
If the Matrix modier solution is used, the furnace controller must be able to handle two gasows to facilitate air ashing. Argon is used as the purge gas for the furnace for all steps but the char. Oxygen ashing is used to avoid build up of residue during the char step.
Breathing-quality air is used as the alternative gas for the air ashing. The long (60 s) “Cool down” step prior to atomization ensures that the air used for the oxygen ashing (char) is cleared from the furnace.
Autosampler
Sample volume: 20 μL
Alternative volume: 5 μL of Matrix modier solution (or Alternative matrix modier solution)
Analysis
Samples: 5 μL of the Matrix modier solution (or Alternative matrix modier solution) added into each 20-μL aliquot of the four Standard
solutions; a mixture of 5 μL of the Matrix modier solution (or Alternative matrix modier solution) and 20 μL of the Sample solution; a mixture of 5 μL of the Matrix modier solution (or Alternative matrix modier solution) and 20 μL of the Standard blank; and a mixture of 5μL of the Matrix modier solution (or Alternative matrix modier solution) and 20 μL of the Sample blank. Use peak area measurements forall quantitations.
Using the Standard blank to set the instrument to zero, determine the integrated absorbances of the Standard solutions. Plot the integrated absorbances of the Standard solutions versus their contents of lead, in ng/mL, and draw the line besttting the four points to determine the calibration curve. Similarly determine the integrated absorbances of the Sample solution and the Sample blank. Correct the absorbance value of the Sample solution by subtracting from it the absorbance value obtained from the Sample blank.
Calculate the concentration of lead, in μg/g, in the portion of Butylene Glycol taken:
Result = [(V × CL)/W] × F
V = volume of the Sample solution, 10 mL
CL = concentration of lead in the Sample solution, as determined from the calibration curve (ng/mL)
W = weight of Butylene Glycol taken to prepare the Sample solution (g)
F = conversion factor, 10-3 μg/ng
Acceptance criteria: NMT 2 μg/g
Limit of 4-Hydroxy-2-butanone, Butane-2,3-diol, Ethylene Glycol, Butane-1,2-diol, Butane-1,4-diol, Diethylene Glycol, and Other Organic Impurities
System suitability solution: 1.0 mg/mL of USP Butane-1,3-diol RS, 1.0 mg/mL of USP Propylene Glycol RS, 0.01 mg/mL of 4-hydroxy-2-butanone, 0.01 mg/mL of butane-2,3-diol, 0.01 mg/mL of butane-1,2-diol, 0.01 mg/mL of USP Ethylene Glycol RS, 0.01 mg/mL of butane-1,4-diol, and 0.01 mg/mL of USP Diethylene Glycol RS in methanol
Sensitivity solution: 1.0 mg/mL of USP Butane-1,3-diol RS, 1.0 mg/mL of USP Propylene Glycol RS, 0.001 mg/mL of 4-hydroxy-2-butanone, 0.001 mg/mL of butane-2,3-diol, 0.001 mg/mL of butane-1,2-diol, 0.001 mg/mL of USP Ethylene Glycol RS, 0.001 mg/mL of butane-1,4-diol, and 0.001 mg/mL of USP Diethylene Glycol RS in methanol
Sample solution: 5 mg/mL of Butylene Glycol in methanol
Chromatographic system: Proceed as directed in the Assay.
System suitability
Samples: System suitability solution and Sensitivity solution
[Note—See Table 3.]
Table 3
| Name | Relative Retention Time |
|---|---|
| 4-Hydroxy-2-butanone | 0.91 |
| Butane-2,3-diol | 0.98 |
| Propylene glycol | 1.00 |
| Ethylene glycol | 1.05 |
| Butane-1,2-diol | 1.13 |
| Butane-1,3-diol | 1.22 |
| Butane-1,4-diol | 1.49 |
| Diethylene glycol | 1.54 |
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 1.5 between butane-2,3-diol and propylene glycol, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation: NMT 2% for the peak response ratio of butane-1,3-diol to propylene glycol, System suitability solution
Signal-to-noise ratio: NLT 20 for any of the following peaks: 4-hydroxy-2-butanone; butane-2,3-diol; ethylene glycol; butane-1,2-diol;
butane-1,4-diol; and diethylene glycol, Sensitivity solution
Analysis
Samples: System suitability solution and Sample solution
Identify each individual impurity peak in the Sample solution based on that in the System suitability solution.
Calculate the percentage of each individual impurity in the portion of Butylene Glycol taken:
Result = (rU/rT) × 100
rU= peak response of each individual impurity in the Sample solution
rT= sum of all the peaks in the Sample solution excluding those due to solvent or reagents
Acceptance criteria
Each individual impurity: NMT 0.1%
Total impurities: NMT 2.0%
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
Acidity and Alkalinity
Sample solution: A solution of Butylene Glycol (1 in 5)
Analysis: Perform a pH measurement.
Acceptance criteria: pH value is 5.5–7.0.
Water Determination, Method I〈921〉: NMT 0.5%
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in tight containers. Do not store above 50°. Protect from moisture.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Butane-1,3-diol RS
USP Diethylene Glycol RS
USP Ethylene Glycol RS
USP Propylene Glycol RS


