Bivalirudin
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
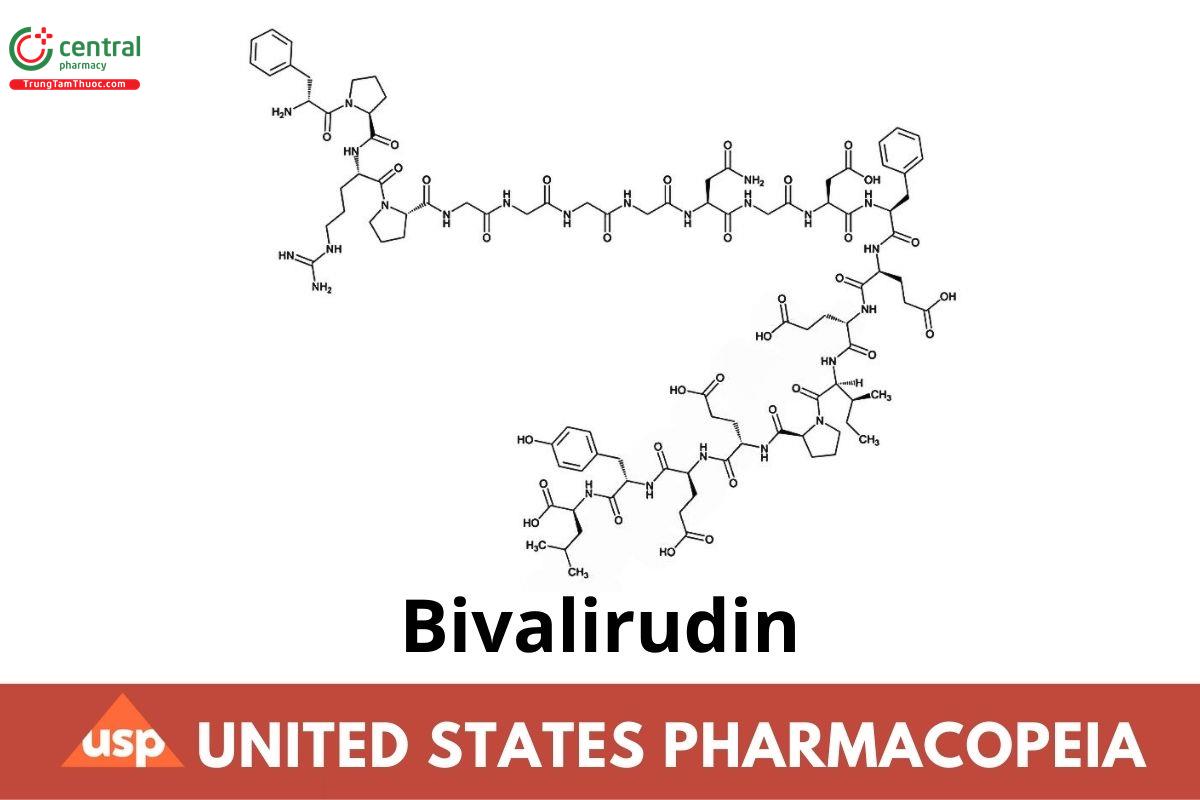
C98H138N24O33 2180.32
L-Leucine, D-phenylalanyl-L-prolyl-L-arginyl-L-prolylglycylglycylglycylglycyl-L-asparaginylglycyl-L-a-aspartyl-L-phenylalanyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-isoleucyl-L-prolyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-tyrosyl-;
D-Phenylalanyl-L-prolyl-L-arginyl-L-prolylglycylglycylglycylglycyl-L-asparaginylglycyl-L-a-aspartyl-L-phenylalanyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-isoleucyl-L-prolyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-tyrosyl-L-leucine CAS RN®: 128270-60-0.
1 DEFINITION
Bivalirudin is a synthetic 20 Amino acid peptide, which is a specific and reversible direct thrombin inhibitor. It contains NLT 96.0% and NMT 103.0% of bivalirudin (C98H138N24O33), calculated on the anhydrous, counter ion-free basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
2.1 A.
Solution A, Solution B, Mobile phase, System suitability solution, Standard solution A, Sample solution, Chromatographic system, and
System suitability: Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Identity sample solution: Mix equal volumes of Standard solution A and the Sample solution.
Acceptance criteria: The retention time of the major peak of the Sample solution corresponds to that of Standard solution A, as obtained in the Assay. The major peaks of the Identity sample solution co-elute.
2.2 B. The monoisotopic mass by Mass Spectrometry (736) is 2179.0 ± 1.0 mass units.
2.3 C. AMINO ACID CONTENT
For further discussion of the theory and applications, see Biotechnology-Derived Articles-Amino Acid Analysis (1052). [NOTE-Use a suitable, validated hydrolysis, separation, and calculation procedure, including amino acids used in the calculation.]
Standard solution: Standardize the instrument with a mixture containing equal molar per volume amounts of glycine and the L-form of the following amino acids: Lysine, threonine, alanine, leucine, histidine, serine, valine, tyrosine, Arginine, glutamic acid, Methionine, phenylalanine, aspartic acid, proline, isoleucine, and tryptophan, and half the molar per volume amount of the L-form of cystine.
Sample solution: Accurately weigh out 1.0 mg of bivalirudin in glass ampuls. Add a minimum of 1.0 mL of Hydrolysis Solution containing 4% phenol, freeze the sample ampul, and flame seal under vacuum. Hydrolyze at 110° for about 18 h. After hydrolysis, dry the test sample under vacuum to remove any residual acid. To the ampul add 2 mL of a buffer solution that is suitable for the amino acid analyzer, and pass through a filter of 0.45-um pore size.
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
First record and measure the peak responses for each amino acid in the Standard solution. Express the content of each amino acid in moles.
Calculate the mean nmol of the amino acids in the Sample solution:
Result = (nmol found in the Sample solution for arginine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, glycine, isoleucine, leucine, phenylalanine, proline, and tyrosine)/20
Divide the nmol of each amino acid by the Result to determine the amino acid ratios that must meet the Acceptance criteria.
Acceptance criteria: See Table 1.
Table 1
| Name | Acceptance Criteria |
| Glycine | Between 4.5 and 5.9 |
| Aspartic acid | Between 1.6 and 2.4 |
| Glutamic acid | Between 3.6 and 4.4 |
| Proline | Between 2.6 and 3.4 |
| Leucine, isoleucine, arginine, and tyrosine | Between 0.7 and 1.3 |
| Phenylalanine | Between 1.6 and 2.4 |
3 ASSAY
3.1 PROCEDURE
Buffer solution: Dissolve 13.6 g of sodium acetate trihydrate in 900 mL of water. Adjust with glacial acetic acid to a pH of 6.5 ± 0.1. Dilute with water to 1000 mL and pass through a filter of 0.2-µm pore size.
Solution A: Buffer solution and water (1:1)
Solution B: Buffer solution and acetonitrile (1:1)
Mobile phase: See Table 2.
Table 2
| Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) |
| 0 | 90 | 10 |
| 5 | 85 | 15 |
| 30 | 65 | 35 |
| 35 | 65 | 35 |
| 35.1 | 90 | 10 |
| 40 | 90 | 10 |
Standard solution A: 1.5 mg/mL of USP Bivalirudin RS in water
Standard solution B: 0.16 mg/mL of USP [Asp9]-Bivalirudin RS in water
System suitability solution: Standard solution A and Standard solution B (1:1)
Sample solution: 1.5 mg/mL of Bivalirudin in water. Prepare in triplicate.
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography (621), System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 215 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Temperatures
Autosampler: 2°-8°
Column: 40°
Flow rate: 1.2 mL/min
Injection volume: 40 µL
System suitability
Samples: Standard solution A and System suitability solution
[NOTE-The relative retention times for [Asp9]-bivalirudin and bivalirudin are 0.93 and 1.0, respectively.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 2.5 between the bivalirudin and [Asp9]-bivalirudin peaks, System suitability solution
Column efficiency: NLT 15,000 theoretical plates, Standard solution A
Relative standard deviation: NMT 1.5% for 3 replicate injections, Standard solution A
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution A and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of bivalirudin (C98H138N24O33) in the portion of Bivalirudin taken:
Result = (rU/rS) x (CS/CU) x 100
rU = peak response of bivalirudin from the Sample solution
rS = mean peak response of bivalirudin from Standard solution A
CS = concentration of USP Bivalirudin RS in Standard solution A (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Bivalirudin in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Take the percentage of Bivalirudin for each Sample solution. Average the results to report the acceptance criteria.
Acceptance criteria: 96.0%-103.0% on the anhydrous, counter ion-free basis
4 PRODUCT-RELATED SUBSTANCES AND IMPURITIES
4.1 PROCEDURE 1
[NOTE-Manufacturers should determine the suitability of their related substances method for their process-related and degradation impurities.
For any impurity peak equal to or above the limit for unspecified impurity peaks, identification and appropriate qualification is required.]
Buffer solution, Solution A, Solution B, Mobile phase, and Chromatographic system: Proceed as directed in the Assay.
System suitability solution: Prepare a solution containing 2.5 mg/mL of USP Bivalirudin RS spiked with 0.05 mg/mL of USP [Asp9]-Bivalirudin
RS and 0.05 mg/mL of USP [des-Glu13]-Bivalirudin RS in water.
Sample solution: 2.5 mg/mL of Bivalirudin in water
Blank: Water
System suitability
Sample: System suitability solution
[NOTE-See Table 3 for the relative retention times.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 2.5 between [Asp⁹]-bivalirudin and bivalirudin
Column efficiency: NLT 12,000 theoretical plates for the bivalirudin peak
Analysis
Sample: Sample solution
Record the chromatograms and measure the response of each peak from the Sample solution using the drop-down integration method with respect to the baseline. Exclude from the integration the peaks present in the Blank. Among all the integrated peaks, only those with a signal-to-noise ratio higher than 10 shall be used for the calculation.
Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Bivalirudin taken:
Result = (rU/rT) × 100
rU = peak response of each impurity
rT = sum of all the peak responses
Acceptance criteria
Individual impurities: See Table 3.
Table 3
| Name | Relative Retention Time | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
| Fragment [1–11]a | 0.49 | 0.5 |
| Fragment [12–20]b | 0.60 | 0.5 |
| Total fragmentsc | 0.44-0.65 | 1.8 |
| [Asp9]-bivalirudind | 0.93 | 0.4 |
| Bivalirudin | 1.00 | - |
| [des-Glu13]-bivalirudine | 1.25-1.29 | 0.4 |
| Unspecied impurities | - | 0.4 |
a D-Phenylalanyl-L-prolyl-L-arginyl-L-prolylglycylglycylglycylglycyl-L-asparaginylglycyl-L-a-aspartic acid.
b L-Phenylalanyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-isoleucyl-L-prolyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-tyrosyl-L-leucine.
c Peptide fragment peaks resulting from degradation.
d D-Phenylalanyl-L-prolyl-L-arginyl-L-prolylglycylglycylglycylglycyl-L-aspartylglycyl-L-a-aspartyl-L-phenylalanyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-isoleucyl-L-prolyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-tyrosyl-L-leucine and D-phenylalanyl-L-prolyl-L-arginyl-L-prolylglycylglycylglycylglycyl-L-B-aspartylglycyl-L-a-aspartyl-1-phenylalanyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-isoleucyl-L-prolyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-tyrosyl-L-leucine.
e D-Phenylalanyl-L-prolyl-L-arginyl-L-prolylglycylglycylglycylglycyl-L-asparaginylglycyl-L-α-aspartyl-L-phenylalanyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-isoleucyl-L-prolyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-tyrosyl-L-leucine.
4.2 PROCEDURE 2
[NOTE-Manufacturers should determine the suitability of their related substances method for their process-related and degradation impurities.
For any impurity peak equal to or above the limit for unspecified impurity peaks, identification and appropriate qualification is required.]
Solution A: Water and acetonitrile (15:85)
Solution B: 0.04% Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) (v/v) in Solution A
Solution C: 0.04% Trifluoroacetic acid in acetonitrile
Mobile phase: See Table 4.
Table 4
| Time (min) | Solution B (%) | Solution C (%) |
| 0 | 50 | 50 |
| 35 | 50 | 50 |
System suitability solution: Prepare a solution containing 3 mg/mL of USP Bivalirudin RS spiked with 0.015 mg/mL of USP [des-Glu13]-
Bivalirudin RS in Solution B.
Sample solution: 3 mg/mL of Bivalirudin in Solution B
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography (621), System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 207 nm
Column: 4.6-mm x 25-cm; 5-µm packing L3
Column temperature: 40°
Flow rate: 1.2 mL/min
Injection volume: 5 µL
System suitability
Sample: System suitability solution
[NOTE-See Table 5 for the relative retention times.]
Suitability requirements
Peak-to-valley ratio: NLT 1.25 for the ratio of the height of the [des-Glu¹³]-bivalirudin peak to the height of the valley between the [des-Glu13]-bivalirudin and bivalirudin peaks
Retention time: The bivalirudin peak elutes between 9.4 and 14.7 min.
Peak width: The bivalirudin peak width at half height should be NMT 0.45.
Analysis
Sample: Sample solution
Record the chromatograms and measure the response for each peak in the chromatogram of the Sample solution. Disregard any peak due to the solvent, the peak at relative retention time 0.2 (TFA), the peak at relative retention time ~0.91, the peak at relative retention time ~0.64, and any peak with an area less than 0.10% of that of Bivalirudin.
Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Bivalirudin taken:
Result = (rU/rT) × 100
rU = peak response of each impurity
rT = sum of all the peak responses
Acceptance criteria
Individual impurities: See Table 5.
Table 5
| Name | Relative Retention Time | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
| [des-Gly5]-bivalirudina | 0.75 | 0.4 |
| Bivalirudin | 1.00 | - |
| [endo-Gly5]-bivalirudinb | 1.36 | 0.5 |
| Unspecied impurities | - | 0.4 |
a D-Phenylalanyl-L-prolyl-L-arginyl-L-prolylglycylglycylglycyl-L-asparaginylglycyl-L-a-aspartyl-L-phenylalanyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-isoleucyl-L-prolyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-tyrosyl-L-leucine.
b D-Phenylalanyl-L-prolyl-L-arginyl-L-prolylglycylglycylglycylglycylglycyl-L-asparaginylglycyl-L-a-aspartyl-L-phenylalanyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-α-glutamyl-L-isoleucyl-L-prolyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-α-glutamyl-L-tyrosyl-L-leucine.
Total impurities: The sum of all impurities from Procedure 1 and Procedure 2 is NMT 2.5%.
5 OTHER COMPONENTS
TRIFLUOROACETIC ACID (TFA) IN PEPTIDES (503.1): Between 6.0% and 12.0%
6 SPECIFIC TESTS
6.1 BIOIDENTITY
Thrombin inhibition activity
Buffer solution: 50 mM tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane hydrochloride and 120 mM sodium chloride in water. Adjust to a pH of 7.40 ± 0.04. Add bovine serum Albumin to this solution to obtain a 1-mg/mL concentration and pass through a filter of 0.45-µm pore size.
Stop solution: Glacial acetic acid
Chromogenic substrate solution: 5 mM solution of H-D-cyclohexylalanyl-Ala-Arg-p-nitroanilide diacetate salt in water
Human thrombin solution: 10 µg/mL of human thrombin¹ in Buffer solution
Diluted human thrombin solution: Dilute Human thrombin solution with Buffer solution to obtain a 0.5-µg/mL solution. Thrombin from
alternate sources must be standardized in the substrate reaction. To perform standardization and determine the standardized volume of the Diluted human thrombin solution, prepare 6 replicates by adding 910 µL of Buffer solution to each sample tube followed by 30 µL of Chromogenic substrate solution. Add 60 µL of Diluted human thrombin solution, mix on a vortex mixer, and heat to 37° for 20 min ± 15 s in a water bath. Stop the reaction by adding 100 µL of Stop solution. Measure the absorbance at 405 nm for the 6 replicates. Use water to auto-zero.
Calculate the standardized volume (EC) of the Diluted human thrombin solution from the mean absorbance (AM) as follows:
EC = (0.45 × 60 μL)/AM
Standard solution: Prepare a 0.6-mg/mL solution of USP Bivalirudin RS in water. Dilute with Buffer solution to obtain a 5-µg/mL solution.
Sample solution: Prepare a 0.6-mg/mL solution of Bivalirudin in water. Make three independent preparations of this solution. Measure the absorbance of each of the 0.6-mg/mL solutions at 275 nm (A275), using the water to auto-zero.
Calculate the concentration of bivalirudin (C98H138N24O33), Cg, in mg/mL, in the solution:
CB = A275/ 0.62 From this concentration, dilute with Buffer solution to obtain a 5-µg/mL solution. Prepare triplicate dilutions from each independently prepared 0.6-mg/mL solution.
Blank, Control test solution, Sample test solution, and Standard test solution
Analysis: In each sample tube, add the Buffer solution first, then 30 µL of Chromogenic substrate solution (S), and then the Standard solution or Sample solution (if using). Mix on a vortex mixer and incubate for 10 min at 37° in a water bath. Add the appropriate volume (E) of Diluted human thrombin solution to give a final concentration of 0.095 NIH Units/mL and activate the chronometer immediately. Mix on a vortex mixer for a few seconds and heat to 37° for 20 min ± 15 s in a water bath. Stop the reaction by adding 100 µL of Stop solution. Measure the absorbance of all solutions at 405 nm using the water to auto-zero.
Prepare the solutions for the analysis as indicated in Table 6.
Table 6
| Blank | Control Test Solution | Sample Test Solution | Standard Test Solution | |
| Number of replicates | 1 | 6 | 3 | 3 |
| Total number of UV readings | 1 | 6 | 9 | 3 |
| Chromogenic substrate solution | 30 μL | 30 μL | 30 μL | 30 μL |
| Bivalirudin | 100 μL (Standard solution) | 0 | 100 μL (Sample solution) | 100 μL (Standard solution) |
| Diluted human thrombin solution | 0 | EC | EC | EC |
| Buffer solution | 1000 μL − 30 μL − 100 μL | 1000 μL − 30 μL − EC | 1000 μL − 30 μL − 100 μL − EC | 1000 μL − 30 μL − 100 μL − EC |
System suitability
Samples: Control test solution and Standard test solution
Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation of the absorbance: NMT 5% for 6 replicates, Control test solution
Mean absorbance: Between 0.428 and 0.473, Control test solution
Average inhibition: 44%-50%, Standard test solution
Analysis
Samples: Control test solution and Sample test solution
Determine the percentage of thrombin inhibition for each of the 9 sample readings of the sample tested:
Result = [1 - (rU/rS)] x 100
rU = absorbance response from the Sample test solution
rS = average absorbance response from the 6 readings of the Control test solution
The final inhibition percentage result is given as the average of these 9 values.
Acceptance criteria
Average inhibition: 42%-52%
Inhibition of each single Sample test solution: 41%-53%
Relative standard deviation of the inhibition of the Sample test solutions: NMT 10%, 9 readings
6.2 MICROBIAL ENUMERATION TESTS (61)
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 103 cfu/g and the total combined yeasts and molds count does not exceed 102 cfu/g.
6.3 BACTERIAL ENDOTOXINS TEST (85)
The level of bacterial endotoxins is such that the requirement under the relevant dosage form monograph(s) in which Bivalirudin is used can be met. Where the label states Bivalirudin must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms, the level of bacterial endotoxins is such that the requirement under the relevant dosage form monograph(s) in which Bivalirudin is used can be met.
6.4 WATER DETERMINATION (921), Method J, Method Ic: NMT 10.0%
7 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
PACKAGING AND STORAGE: Preserve in an airtight, closed container protected from light at a temperature between -20 ± 5°.
LABELING: Label it to state the strength, in milligrams, of Bivalirudin.
USP REFERENCE STANDARDS (11)
USP Bivalirudin RS
USP [Asp9-Bivalirudin RS
USP [des-Glu13]-Bivalirudin RSA (USP 1-Dec-2023)
1 Sigma-Aldrich, Catalog No. T6884, or suitable equivalent.


