Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
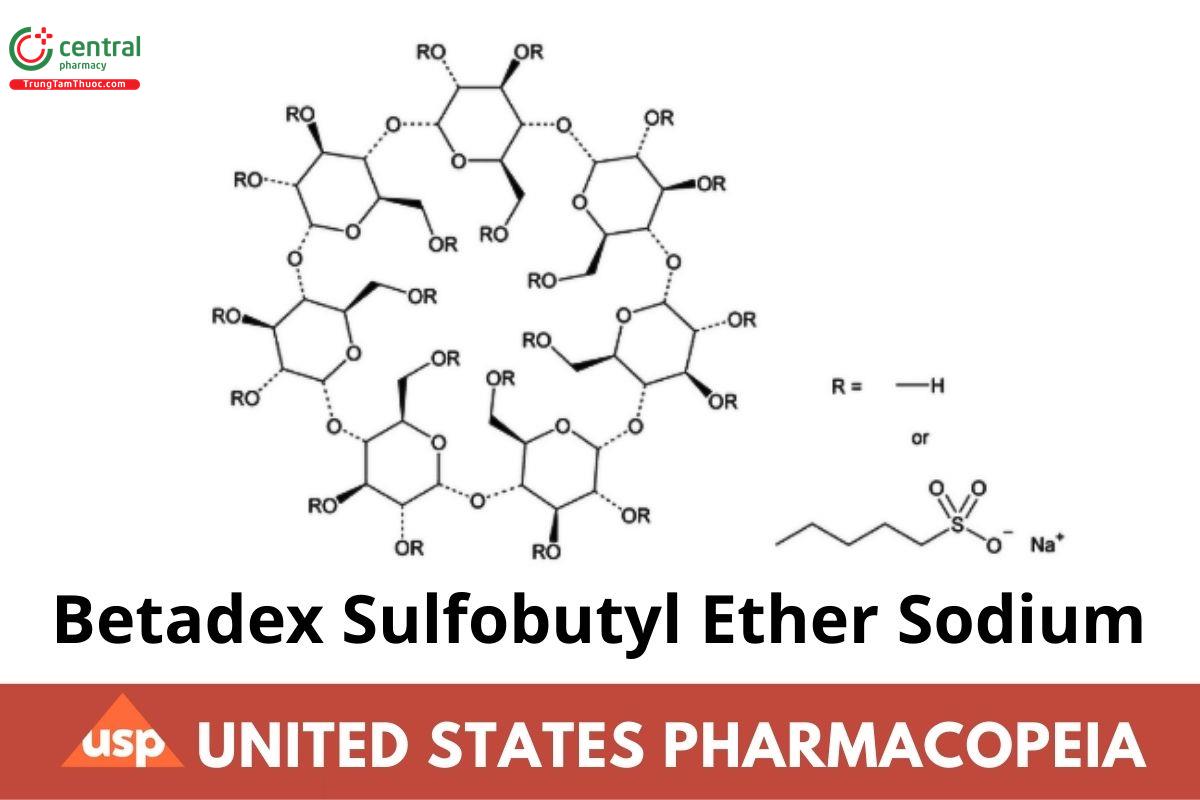
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
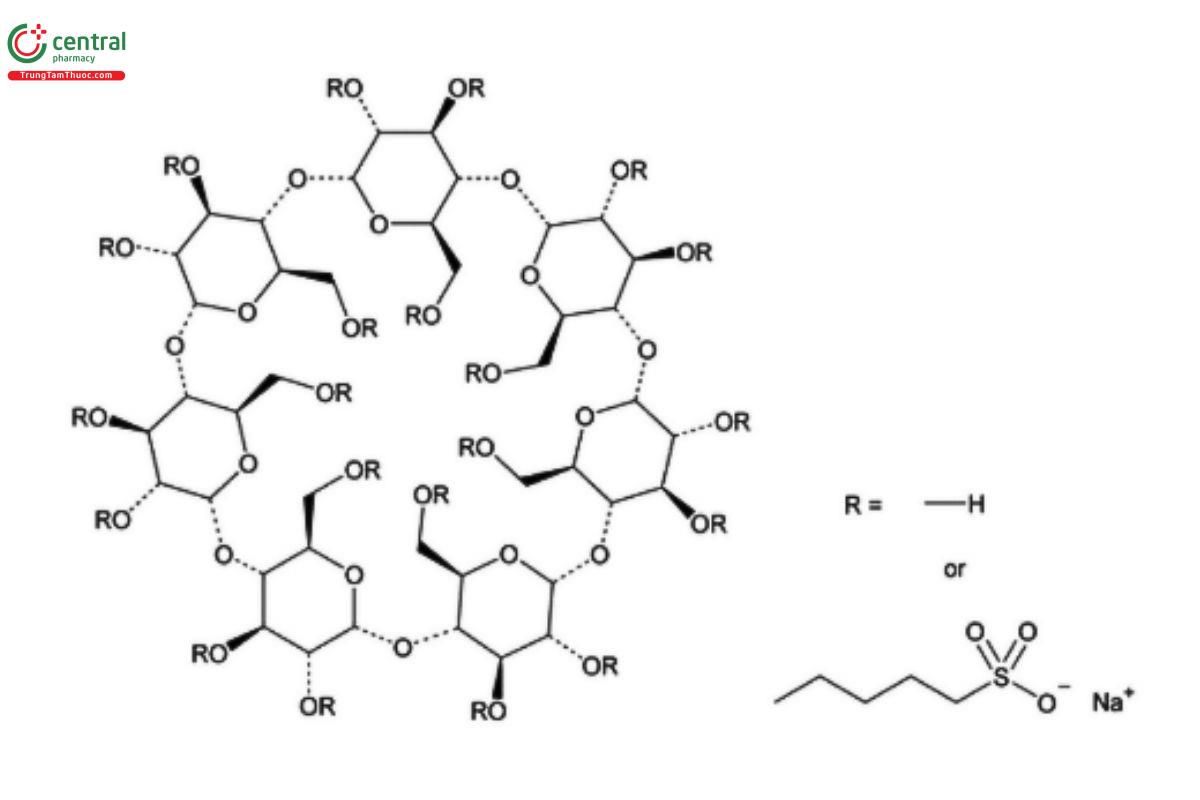
C24H70-nO35.(C4H8SO3Na)n 2163 when n = 6.5
Beta cyclodextrin sulfobutyl ethers, sodium salts;
Beta cyclodextrin sulfobutyl ether sodium CAS RN®: 182410-00-0.
1 DEFINITION
Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium is prepared by alkylation of betadex using 1,4-butane sultone under basic conditions. The average degree of substitution in betadex is NLT 6.2 and NMT 6.9. It contains NLT 95.0% and NMT 105.0% of C24H70-nO35.(C4H8SO3Na)n , (n = 6.2 - 6.9), calculated on the anhydrous basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
Change to read:
A. SPECTROSCOPIC IDENTIFICATION TESTS (197), Infrared Spectroscopy: 197K (CN 1-MAY-2020)
B. The retention time of the major peak of the Sample solution corresponds to that of the Standard solution, as obtained in the Assay.
C. It meets the requirements of the test for Average Degree of Substitution.
D. IDENTIFICATION TESTS GENERAL, Sodium (191).
3 ASSAY
3.1 PROCEDURE
Mobile phase: 0.1 M potassium nitrate in a mixture of acetonitrile and water (1:4)
Standard solution: 10 mg/mL of USP Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium RS in Mobile phase
Sample solution: 10 mg/mL of Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium in Mobile phase
3.1.1 Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography (621), System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: Refractive index
Detector temperature: 35 ± 2°
Column: 7.8-mm × 30-cm analytical column; packing L37. [Note—Rinse the column with a solution of acetonitrile and water (1:9) at the completion of the run series.]
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min
Injection size: 20 μL
3.1.2 System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation: NMT 2.0%
3.1.3 Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of betadex sulfobutyl ether sodium [C24H70-nO35.(C4H8SO3Na)n] in the portion of Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether
Sodium taken:
Result = (ru/rs) × (Cs /Cu) × 100
ru = peak response for betadex sulfobutyl ether sodium from the Sample solution
rs = peak response for betadex sulfobutyl ether sodium from the Standard solution
Cs = concentration of USP Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
Cu = concentration of Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: 95.0%–105.0% on the anhydrous basis
4 IMPURITIES
4.1 Limit of Beta Cyclodextrin (Betadex)
Solution A: 25 mM sodium hydroxide
Solution B: 250 mM sodium hydroxide and 1 M potassium nitrate
Mobile phase: See Table 1.
Table 1
| Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) |
| 0 | 100 | 0 |
| 4 | 100 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | 100 |
| 10 | 0 | 100 |
| 11 | 100 | 0 |
| 20 | 100 | 0 |
Standard solution: 2 µg/mL of USP Beta Cyclodextrin RS
Sample solution: 2 mg/mL of Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium
4.1.1 Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography (621), System Suitability, and lon Chromatography (1065).)
Mode: IC
Detector: Pulsed amperometry (amperometric cell with gold working electrode and silver reference electrode)
4.1.2 Column
Guard: 4.0-mm x 5-cm anion-exchange; packing L61
Analytical: 4.0-mm x 25-cm anion-exchange; packing L61
Column temperature: 50 ± 2°
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min
Injection size: 20 µL
Waveform for pulsed amperometric detector: See Table 2.
Table 2
| Time (s) | Voltage (V) |
| 0.00 | 0.10 |
| 0.30 | Start integration |
| 0.50 | 0.10 |
| 0.50 | Stop integration |
| 0.51 | 0.60 |
| 0.59 | 0.60 |
| 0.60 | −0.60 |
| 0.65 | −0.60 |
4.1.3 System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation: NMT 5.0%
4.1.4 Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of beta cyclodextrin (betadex) in the portion of Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium taken:
Result = (ru/rs) × (Cs /Cu) × F × 100
ru = peak response for beta cyclodextrin from the Sample solution
rs = peak response for beta cyclodextrin from the Standard solution
Cs = concentration of USP Beta Cyclodextrin RS in the Standard solution (μg/mL)
Cu = concentration of Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
F = conversion factor (10-3 mg/µg)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.1%
4.2 LIMIT OF 1,4-BUTANE SULTONE
Internal standard solution: 0.25 µg/mL of diethyl sulfone
Standard stock solution A: 0.5 µg/mL of 1,4-butane sultone
Standard stock solution B: 1.0 µg/mL of 1,4-butane sultone
Standard stock solution C: 2.0 µg/mL of 1,4-butane sultone
Sample stock solution: 250 mg/mL of Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium in the Internal standard solution
Blank solution, and Sample solutions A, B, C, and D: Follow Table 3 to place the quantities of Internal standard solution, each Standard stock solution, Sample stock solution, water, or methylene chloride in each glass test tube with a stopper. [NOTE-A screw-capped, 10-mL test tube is suitable.] Mix on a vortex mixer each test tube for 30 s, and allow it stand for at least 5 min or until complete separation of the phase. Extract the organic phase into a GC vial and seal. [NOTE-With great care take the minimum possible amount of aqueous phase.] Added quantities of 1,4-butane sultone in Sample solutions A, B, C, and D are 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, and 0 µg, respectively.
Table 3
| Sample Name0 | Solution 1 Added (mL) | Solution 2 Added (mL) | Methylene Chloride Added (mL) |
| Blank solution | Internal standard solution, 4.0 | Water, 1.0 | 1.0 |
Sample solution A | Sample stock solution, 4.0 | Standard stock solution A, 1.0 | 1.0 |
Sample solution B | Sample stock solution, 4.0 | Standard stock solution B, 1.0 | 1.0 |
Sample solution C | Sample stock solution, 4.0 | Standard stock solution C, 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Sample solution D | Sample stock solution, 4.0 | Water, 1.0 | 1.0 |
[Note—Prepare immediately before use.]
4.2.1 Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: GC
Detector: Flame ionization
Column: 0.32-mm × 25-m fused-silica capillary column; 0.5-μm layer of phase G46
4.2.2 Temperature
Detector: 270°
Injection port: 200°
Column: See the temperature program in Table 4.
Table 4
| Initial Temperature (°) | Temperature Ramp (°/min) | Final Temperature (°) | Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
| 100 | 10 | 200 | — |
| 200 | 35 | 270 | 5 |
Carrier gas: Helium, typically at 12 psi inlet pressure
Injection size: 1.0 μL
Injection type: Splitless injection for 0.5 min, then split at 50 mL/min. [Note—The use of an appropriate splitless injection liner is recommended.]
4.2.3 System suitability
Sample: Sample solution B
[Note—The relative retention times for diethyl sulfone and 1,4-butane sultone are 0.7 and 1.0, respectively.]
Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation: NMT 10.0%
4.2.4 Analysis
Samples: Blank solution, Sample solutions A, B, C, and D
Correct the ratio of peak responses of the 1,4-butane sultone to diethyl sulfone in Sample solution A, B, C, or D by subtracting the ratio of peak responses of the 1,4-butane sultone to ethyl sulfone in the Blank solution. Plot the corrected ratio of peak response of 1,4-butane sultone to peak response of diethyl sulfone in Sample solution A, B, C or D, versus the added quantity, in µg, of 1,4-butane sultone. Extrapolate the line joining the points on the graph until it meets the quantity axis. The distance between this point and the intersection of the axes represents the quantity of 1,4-butane sultone, A, in µg, in the 4-mL portion of Sample stock solution. Calculate the content of 1,4-butane sultone in the portion of Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium taken:
Result = A/(VExt x Cu x F )
A = determined above
VExt = volume of the Sample stock solution used in the extraction step, 4.0 mL
Cu = concentration of Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium in the Sample stock solution (mg/mL)
F = conversion factor (10-3 g/mg)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.5 ppm
4.3 LIMIT OF SODIUM CHLORIDE, 4-HYDROXYBUTANE-1-SULFONIC ACID, AND BIS (4-SULFOBUTYL) ETHER DISODIUM
Solution A: 5 mM sodium hydroxide, degas in a closed vessel for 15 min
Solution B: 25 mM sodium hydroxide, degas in a closed vessel for 15 min
Mobile phase: See Table 5.
Table 5
| Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) |
| 0 | 100 | 0 |
| 4 | 100 | 0 |
| 10 | 70 | 30 |
| 24 | 70 | 30 |
| 25 | 100 | 0 |
| 40 | 100 | 0 |
Column wash solution A: 50 mM sodium citrate
Column wash solution B: 150 mM sodium hydroxide
Standard solution: Prepare a solution having known concentrations of 8 μg/mL of USP Sodium Chloride RS, 4 μg/mL of 4-hydroxybutane-1- sulfonic acid, and 4 μg/mL of bis(4-sulfobutyl) ether disodium.
Sample solution: 4 mg/mL of Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium
4.3.1 Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability and Ion Chromatography 〈1065〉.)
Mode: IC
Detector: Conductivity
Range: 30 μS
Current: 100 mA
Column: [Note—At the end of each run, clean the column using Column wash solution A at a flow rate of 1 mL/min for 35 min then using
Column wash solution B at the same flow rate for 35 min.]
Guard: 4.0-mm × 5.0-cm anion-exchange; packing L61
Analytical: 4.0-mm × 25-cm anion-exchange; packing L61
Column temperature: 30°
Suppressor: Micromembrane anion autosuppressor or a suitable chemical suppression system
Suppressant: Autosuppression
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min
Injection size: 20 µL
4.3.2 System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
[ NOTE-Relative retention times are provided for information only. The relative retention times for 4-hydroxybutane-1-sulfonate ion, chloride ion, and bis(sulfobutyl) ether ion are 1.0, 1.4, and 8.6, respectively.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 2.0
Relative standard deviation: NMT 10.0%
4.3.3 Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of sodium chloride, 4-hydroxybutane-1-sulfonic acid, or bis(sulfobutyl) ether disodium in the portion of Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium taken:
Result = (ru/rs) × (Cs /Cu) × F x 100
ru = peak response for sodium chloride, 4-hydroxybutane-1-sulfonic acid, or bis(sulfobutyl) ether disodium from the Sample
rs = peak response for sodium chloride, 4-hydroxybutane-1-sulfonic acid, or bis(sulfobutyl) ether disodium from the Standard
Cs = concentration of sodium chloride, 4-hydroxybutane-1-sulfonic acid, or bis(sulfobutyl) ether disodium in the Standard solution (µg/mL)
Cu = concentration of Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
F = conversion factor (10−3 mg/μg)
4.3.4 Acceptance criteria
Sodium chloride: NMT 0.2%
4-Hydroxybutane-1-sulfonic acid: NMT 0.09%
Bis(sulfobutyl) ether disodium: NMT 0.05%
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
• Bacterial Endotoxins Test 〈85〉: The level of bacterial endotoxins is such that the requirement under the relevant dosage form monograph(s) in which Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium is used can be met. Where the label states that Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms, the level of bacterial endotoxins is such that the requirement under the relevant dosage form monograph(s) in which Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium is used can be met.
• Microbial Enumeration Tests 〈61〉 and Tests for Specified Microorganisms 〈62〉: The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 100 cfu/g, and the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 50 cfu/g. It meets the requirements of the test for absence of Escherichia coli.
5.1 Clarity of Solution
Sample solution: 30% (w/v) solution
Analysis: Examine the Sample solution using a light box against white and black backgrounds, and record the presence of any haze, fluorescence, fibers, specks, or other foreign matter.
Acceptance criteria: The solution is clear, and essentially free from particles of foreign matter.
5.2 Average Degree of Substitution
Run electrolyte: 30 mM benzoic acid and adjusted to a pH that is suitable for the instrument used by addition of 100 mM tris(hydroxymethyl) aminomethane buffer. [Note—Due to variation between capillaries, a single universally applicable electrolyte pH is not specified. Instead, the optimal pH associated with each individual capillary should be determined according to the instrumental manual.]
Standard solution: 10 mg/mL of USP Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium RS
Sample solution: 10 mg/mL of Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium
Capillary rinsing procedure: Use separate run electrolyte vials for capillary rinse and sample analysis. Perform pre-analysis rinses on a daily basis before each analysis: rinse the capillary with 0.1 N sodium hydroxide for 30 min, with water for NLT 2 h, and with Run electrolyte for NLT 1 h. Perform pre-injection rinses prior to each injection as follows. Rinse the capillary with 0.1 N sodium hydroxide for NLT 1 min, and with Run electrolyte for NLT 3 min. If a new capillary is being used, in addition to the regular rinses described above, a new capillary requires rinsing before its first use. Rinse the new capillary with 1 M sodium hydroxide for 1 h, followed by a 2-h water rinse.
5.2.1 Electrophoretic system
(See Capillary Electrophoresis 〈1053〉.)
Mode: High-performance CE
Detector: Inverse UV 200 nm, with a bandwidth of 20 nm. [NOTE-A detection wavelength of 205 nm with a bandwidth of 10 nm may be used as an alternative.]
Column: 50-µm x 50-cm fused silica column
Column temperature: 25°
Applied voltage: 0.00 to +30.00 kV linear ramp over 10 min, then at 30 kV for a further 20 min
Injection size: Equal volumes at 0.5 psi for 10 s
5.2.2 System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
[NOTE-See Table 6 for the approximate relative migration times for betadex sulfobutyl ether sodium peaks I-X (betadex sulfobutyl ether sodium peaks I, II, III, ..., X, contains beta cyclodextrin molecule with 1, 2, 3, ..., 10 sulfobutyl substituent(s), respectively). The relative migration times are for informational purposes only to aid in peak identification.]
Table 6
| Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium Peaks I–X | Relative Migration Time |
| I | 0.58 |
| II | 0.63 |
| III | 0.69 |
| IV | 0.77 |
| V | 0.83 |
| VI | 0.91 |
| VII | 1.00 |
| VIII | 1.10 |
| IX | 1.20 |
| X | 1.30 |
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 0.9, between betadex sulfobutyl ether sodium peak IX and betadex sulfobutyl ether sodium peak X
5.2.3 Analysis
Samples: Run electrolyte, water, Standard solution, and Sample solution
Inject the Standard solution and Sample solution by applying differential pressure of 0.5 psi, equivalent to 34 mbar, for 10 s, followed by injection of Run electrolyte at 0.5 psi for 2 s. [Note—Pressure injections should be made with a vial of water or Run electrolyte at the outlet end of the capillary.]
Record the electropherograms, and measure the peak responses for the individual betadex sulfobutyl ether sodium peaks (I to X).
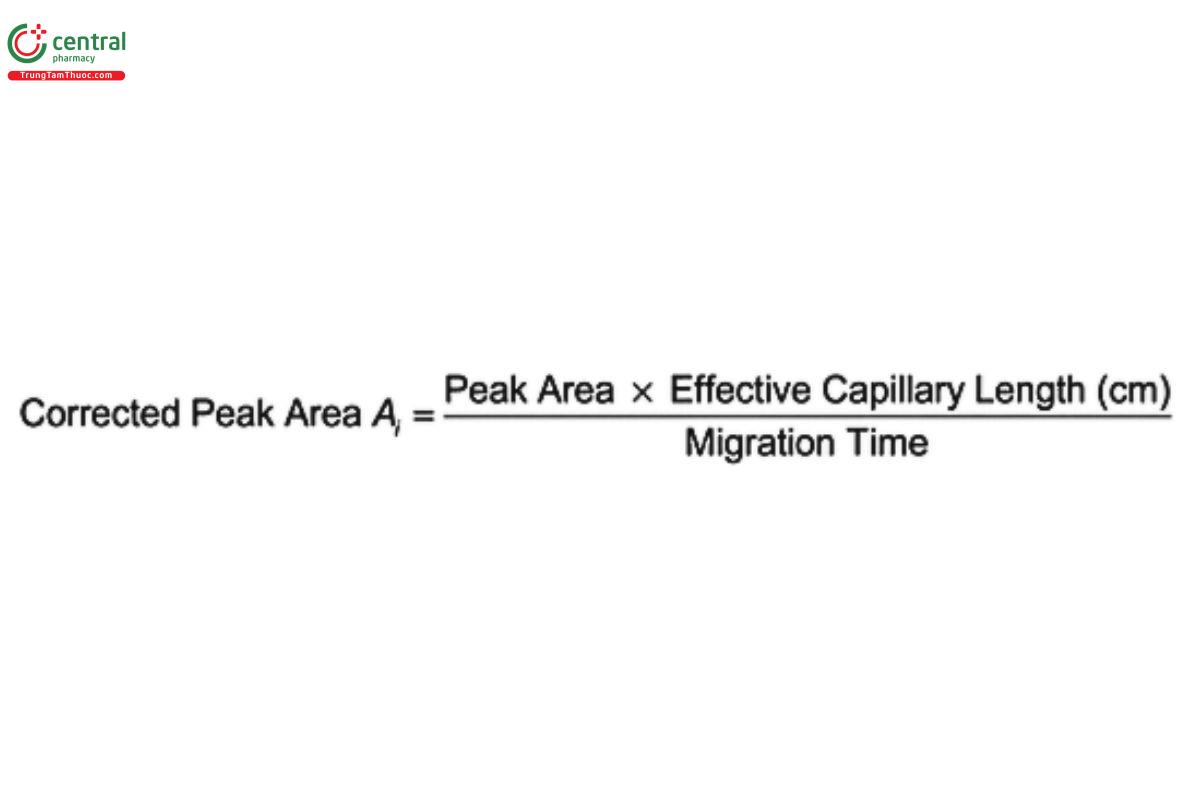
Calculate the corrected peak area, A , for each peak in the eletropherogram:
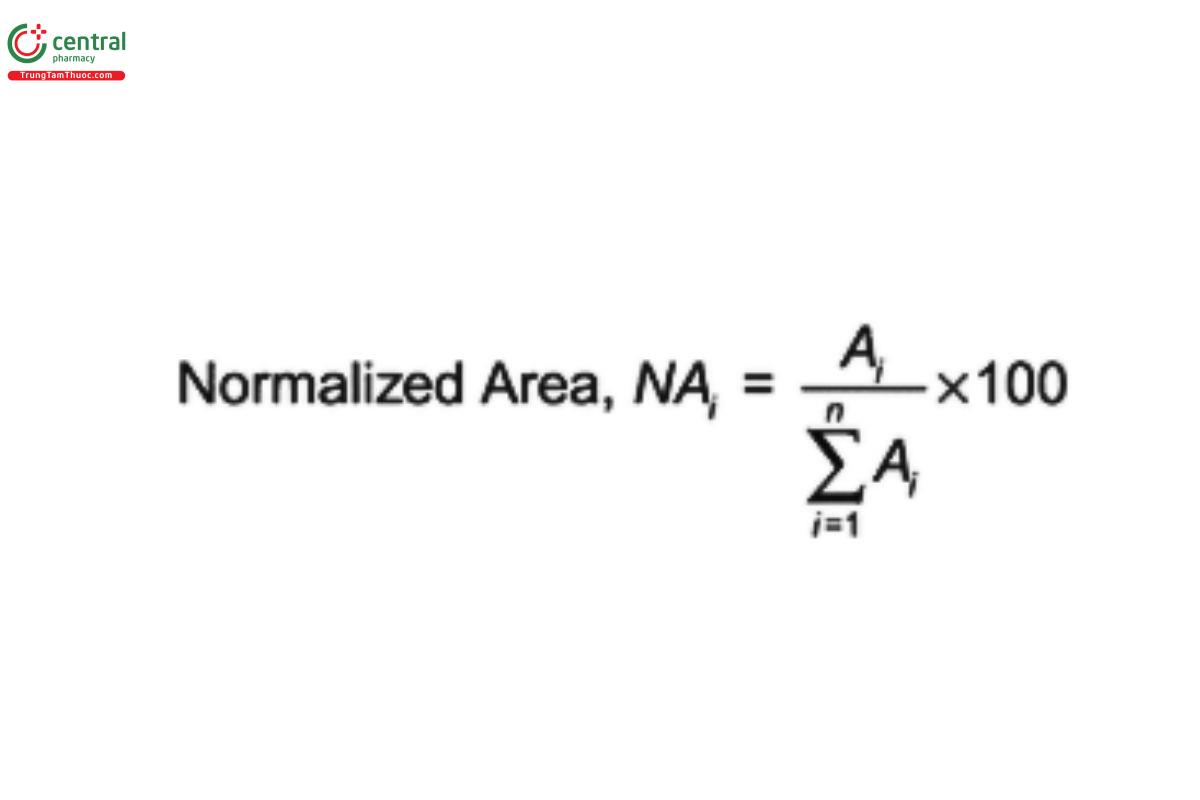
Normalize the corrected peak areas by presenting each as a percentage of the total corrected substitution envelope area:
n = highest level of substitution
Determine the average degree of substitution:
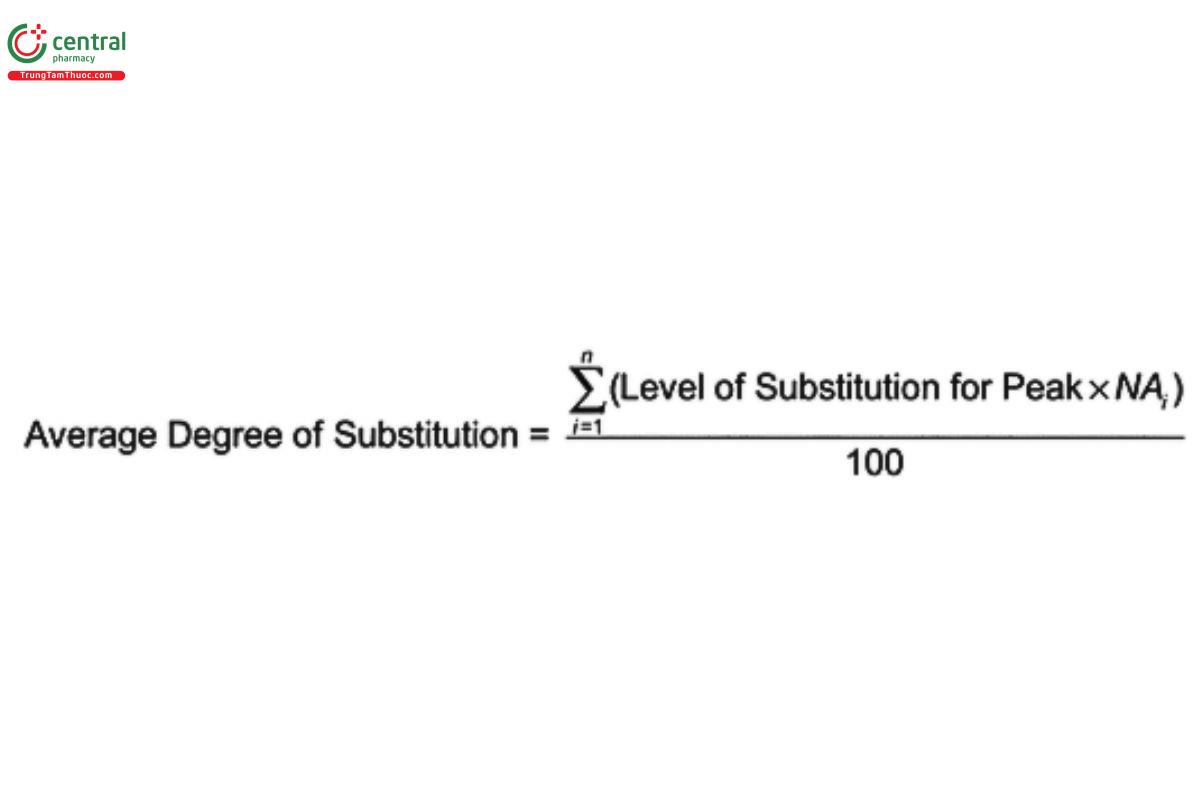
Acceptance criteria: 6.2–6.9 for average degree of substitution
For each of betadex sulfobutyl ether sodium peaks I–X, see limit range (% peak area) in Table 7
Table 7
| Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium Peaks I–X | Limit Range (% Peak Area) |
| I | 0–0.3 |
| II | 0–0.9 |
| III | 0.5–5.0 |
| IV | 2.0–10.0 |
| V | 10.0–20.0 |
| VI | 15.0–25.0 |
| VII | 20.0–30.0 |
| VIII | 10.0–25.0 |
| IX | 2.0–12.0 |
| X | 0–4.0 |
pH 〈791〉: 4.0–6.8, in a 30% (w/v) solution in carbon dioxide-free water
Water Determination, Method I 〈921〉: NMT 10.0%
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in well-closed containers, and store at room temperature. Protect from moisture.
Labeling: Label it to indicate its use in the manufacture of injectable dosage forms.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Beta Cyclodextrin RS
USP Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium RS
USP Sodium Chloride RS


