Bacitracin
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
Bacitracin
CAS RN®: 1405-87-4; UNII: 58H6RWO52I.
1 DEFINITION
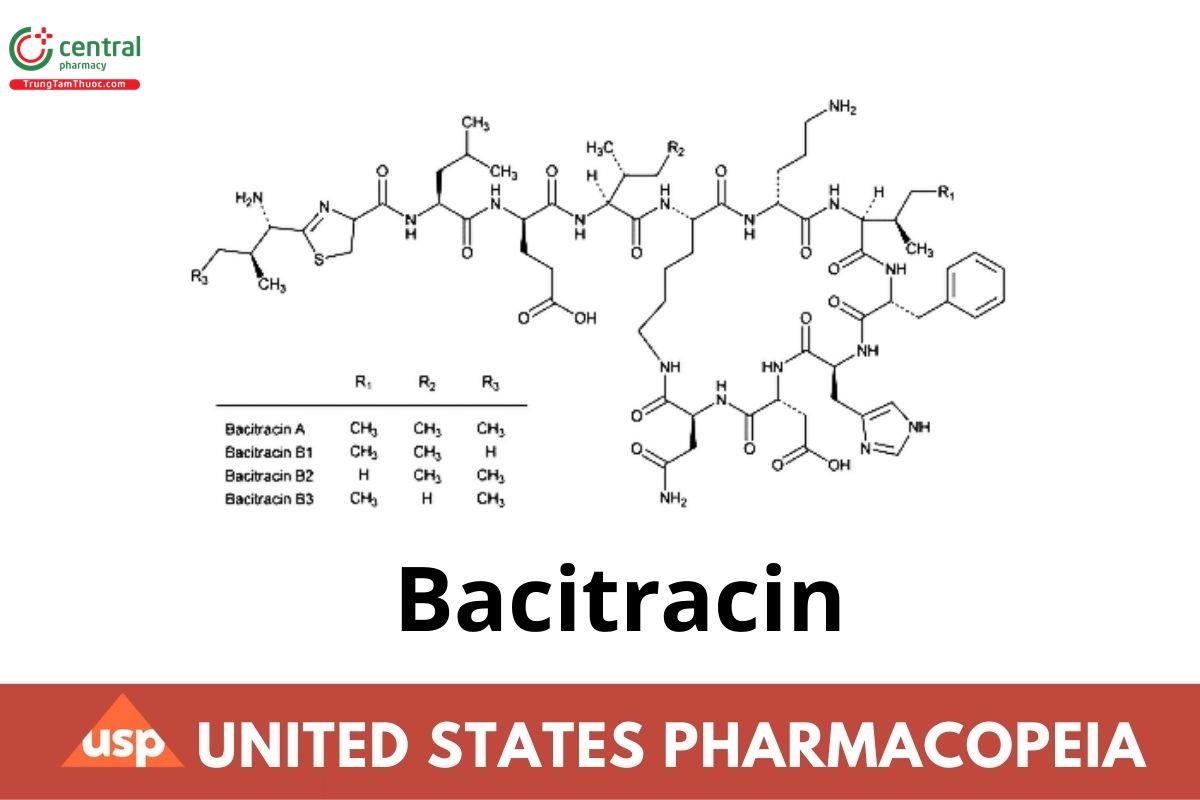
Bacitracin is a mixture of polypeptides produced by the growth of an organism of the licheniformis group of Bacillus subtilis (Fam. Bacillacaea),
the main components being bacitracins A, B₁, B₂, and B₃.
It has a potency of NLT 65 Bacitracin units/mg, calculated on the dried basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
A. Meets the requirements of the test for Composition of Bacitracin
Change to read:
B.
Sample: 0.2 g
Analysis: Ignite the Sample. Allow to cool. Dissolve the residue in 0.1 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid. Add 5 mL of water and 0.2 mL of sodium hydroxide TS 3.
Acceptance criteria: No white precipitate is formed.
3 ASSAY
Procedure
(See Antibiotics—Microbial Assays 〈81〉.)
Analysis: Proceed as directed in the chapter.
Acceptance criteria: NLT 65 Bacitracin units/mg on the dried basis
4 IMPURITIES
Residue on Ignition 〈281〉: NMT 0.5%
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
Composition of Bacitracin
Diluent: 40 g/L of edetate disodium in water adjusted with 8 N sodium hydroxide to a pH of 7.0
Solution A: 34.8 g/L of dibasic potassium phosphate in water
Solution B: 27.2 g/L of monobasic potassium phosphate in water
Solution C: Solution A and Solution B (2:9). The pH of the mixture is about 6.
Solution D: 0.1 mM edetate disodium in a mixture of Solution C and water (1:3)
Solution E: Methanol and acetonitrile (27:2)
Mobile phase: Solution D and Solution E (37:63)
System suitability solution: 2 mg/mL of USP Bacitracin Zinc RS in Diluent
Reporting threshold solution: 0.01 mg/mL of USP Bacitracin Zinc RS from System suitability solution in water
Peak identification solution: 2 mg/mL of USP Bacitracin Zinc RS in Diluent. Heat in a boiling water bath for 30 min, and cool to room temperature.
Sample solution: 2 mg/mL of Bacitracin in Mobile phase
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 254 and 300 nm. Quantitative analysis is performed at 254 nm; 300 nm is only used to identify the location of bacitracin F.
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; end-capped 5-µm packing L1
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Injection volume: 100 µL
System suitability
Samples: System suitability solution and Peak identification solution
Analyze the Peak identification solution at 300 nm. Identify bacitracin F, a known impurity, using the relative retention time provided in Table 1.
Analyze the System suitability solution at 254 nm. Identify the peaks of the most active components of bacitracin (bacitracins A, B₁, B₂, and B₃),
early-eluting peptides (those eluting before the bacitracin B₁ peak), and the impurity (bacitracin F) using the relative retention times in Table 1.
| Name | Nature of Component | Relative Retention Time |
| Bacitracin C₁ | Early-eluting peptides | 0.5 |
| Bacitracin C₂ | Early-eluting peptides | 0.6 |
| Bacitracin C₃ | Early-eluting peptides | 0.6 |
| Bacitracin B₁ | Active bacitracin | 0.7 |
| Bacitracin B₂ | Active bacitracin | 0.7 |
| Bacitracin B₃ | Active bacitracin | 0.8 |
| Bacitracin A | Active bacitracin | 1.0 |
| Bacitracin F | Impurity | 2.4 |
Suitability requirements
Peak-to-valley ratio: NLT 1.2, System suitability solution
The Peak-to-valley ratio is calculated as follows:
Result = Hₚ/Hᵥ
Hₚ = height above the baseline of the peak due to bacitracin B₁
Hᵥ = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating the bacitracin B₁ peak from the bacitracin B₂ peak
Analysis
Samples: Diluent, Reporting threshold solution, and Sample solution
Content of bacitracin A
Calculate the percentage of bacitracin A in the portion of Bacitracin taken:
Result = (rₐ/rₜ) × 100
rₐ = peak area of bacitracin A from the Sample solution
rₜ = sum of all peak areas above the reporting threshold from the Sample solution
Content of active bacitracin
Calculate the percentage of active bacitracin (bacitracin A, B₁, B₂, and B₃) in the portion of Bacitracin taken:
Result = [(rₐ + rB₁ + rB₂ + rB₃)/rₜ] × 100
rₐ = peak area of bacitracin A from the Sample solution
rB₁ = peak area of bacitracin B₁ from the Sample solution
rB₂ = peak area of bacitracin B₂ from the Sample solution
rB₃ = peak area of bacitracin B₃ from the Sample solution
rₜ = sum of all peak areas above the reporting threshold from the Sample solution
Limit of early-eluting peptides
Calculate the percentage of early-eluting peptides (peaks eluting before bacitracin B₁) in the portion of Bacitracin taken:
Result = (rₑ/rₜ) × 100
rₑ = sum of peak areas for all peaks before bacitracin B₁ from the Sample solution
rₜ = sum of all peak areas above the reporting threshold from the Sample solution
Limit of bacitracin F
Calculate the percentage of bacitracin F in the portion of Bacitracin taken:
Result = (rF/rₐ) × 100
rF= peak area of bacitracin F from the Sample solution
rₐ = peak area of bacitracin A from the Sample solution
Acceptance criteria: See Table 2. Disregard any peaks from the Sample solution that are observed in the Diluent chromatogram.
Disregard any peaks from the Sample solution that have a peak area less than bacitracin A in the Reporting threshold solution.
| Name | Acceptance Criteria, (%) |
| Content of bacitracin A | NLT 40.0 |
| Content of active bacitracin | NLT 70.0 |
| Limit of early-eluting peptides | NMT 20.0 |
| Limit of bacitracin F | NMT 6.0 |
pH 〈791〉
Sample solution: 10,000 Bacitracin units/mL in water
Acceptance criteria: 5.5–7.5
Loss on Drying 〈731〉
Sample: 100 mg
Analysis: Dry the Sample in a capillary-stoppered bottle under vacuum at a pressure not exceeding 5 mm of mercury at 60° for 3 h.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 5.0%
Sterility Tests 〈71〉: Where the label states that the Bacitracin is sterile, it meets the requirements.
Change to read:
Bacterial Endotoxins Test 〈85〉: The level of bacterial endotoxins is such that the requirement under the relevant dosage form monograph(s) in which Bacitracin is used can be met. Where the label states that Bacitracin must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms, the level of bacterial endotoxins is such that the requirement under the relevant dosage form monograph(s) in which Bacitracin is used can be met.
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in tight containers, and store below 8°.
Change to read:
Labeling: Where it is packaged for prescription compounding, label it to indicate that it is not sterile and that the potency cannot be assured for longer than 60 days after opening, and to state the number of Bacitracin Units/mg. Where Bacitracin must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms to ensure acceptable levels of bacterial endotoxins, it is so labeled.
Change to read:
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Bacitracin Zinc RS


