Azithromycin
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
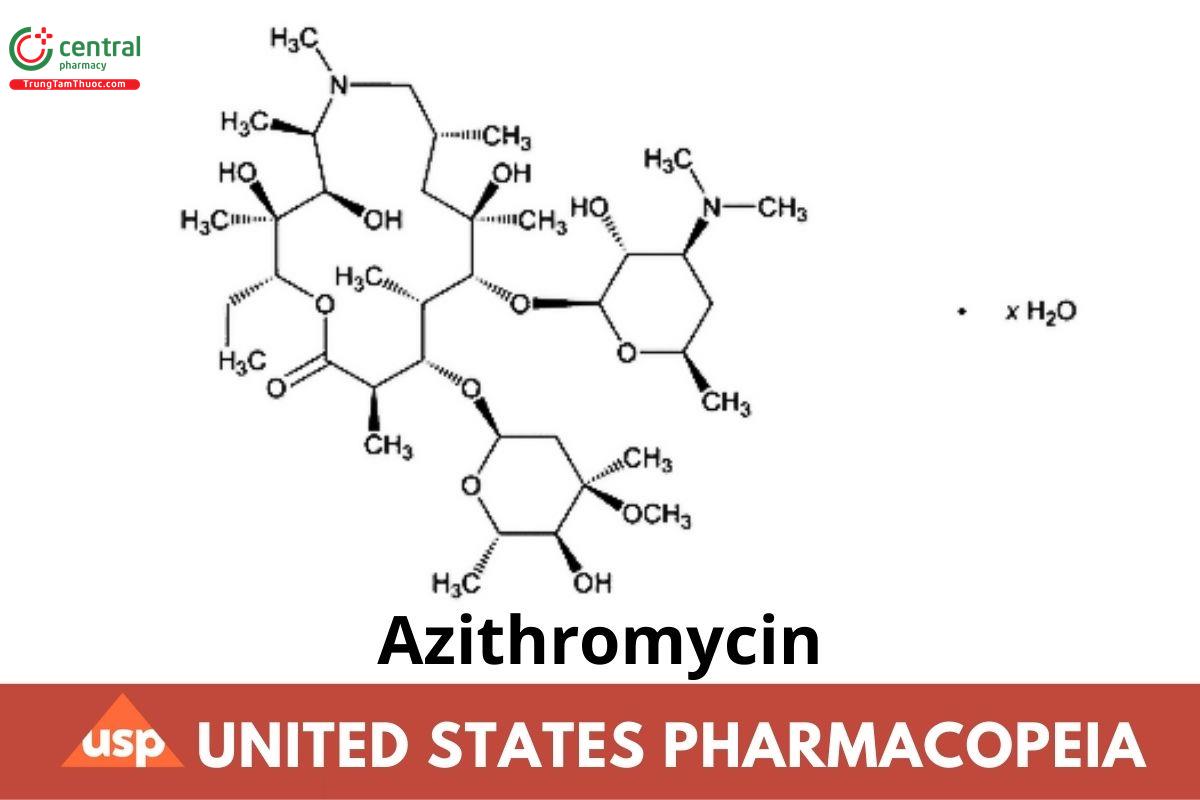
C38H72N2O12 749.00
C38H72N2O12 · H2O 767.01
C38H72N2O12 · 2H2O 785.03
1-Oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one, 13-[(2,6-dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-α-l-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-11-[[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-β-d-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-, [2R-(2R*,3S*,4R*,5R*,8R*,10R*,11R*,12S*,13S*,14R*(2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-13-[(2,6-Dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-α-l-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-11-[[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-β-d-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one; 9-Deoxo-9a-aza-9a-methyl-9a-homoerythromycin A
Anhydrous CAS RN: 83905-01-5.
Monohydrate CAS RN: 121470-24-4.
Dihydrate CAS RN: 117772-70-0.
1 DEFINITION
Azithromycin is anhydrous or contains 1 or 2 molecules of water of hydration. It contains the equivalent of NLT 945 µg/mg and NMT 1030 µg/mg of azithromycin (CH2N₂O₁₂), calculated on the anhydrous basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
A. SPECTROSCOPIC IDENTIFICATION TESTS (197), Infrared Spectroscopy: 197K: If a difference appears in the IR spectra of the analyte and the
Standard, dissolve equal portions of the test specimen and the USP Reference Standard in equal volumes of methanol. Evaporate the solutions to dryness on a water bath, and dry at 80° for 30 min under vacuum. Perform the test on the residues.
B. The retention time of the azithromycin peak of the Sample solution corresponds to that of the Standard solution, as obtained in the Assay.
3 ASSAY
PROCEDURE
Solution A: 10 M potassium hydroxide
Solution B: 6.7 g/L of dibasic potassium phosphate, adjusted with Solution A to a pH of 11.0
Solution C: 6.7 g/L of dibasic potassium phosphate, adjusted with phosphoric acid to a pH of 8.0
Mobile phase: Acetonitrile and Solution B (60:40)
Diluent: Acetonitrile and Solution C (60:40)
System suitability solution: 0.5 mg/mL each of USP Azithromycin RS and USP Azaerythromycin A RS prepared as follows. Dissolve USP Azithromycin RS and USP Azaerythromycin A RS first in acetonitrile, using 5% of the final volume, and then dilute with Diluent to volume.
Standard solution: 0.53 mg/mL of USP Azithromycin RS prepared as follows. Dissolve USP Azithromycin RS first in acetonitrile, using 2% of the final volume, and then dilute with Diluent to volume.
Sample solution: 0.53 mg/ml of Azithromycin prepared as follows. Dissolve Azithromycin first in acetonitrile, using 2% of the final volume, and then dilute with Diluent to volume.
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography (621), Systern Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 210 nm
Column: 4.6-mm x 25-cm, 5-µm packing 167
Column temperature: 40°
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Injection volume: 10 µL
System suitability
Samples: System suitability solution and Standard solution
[NOTE-The relative retention times for azaerythromycin A and azithromycin are 0.7 and 1.0, respectively.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 3.0 between azaerythromycin A and azithromycin, System suitability solution
Tailing factor: 0.8-1.5 for azithromycin, Standard solution
Relative standard deviation: NMT 1.10% for azithromycin, Standard solution
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the quantity, in µg, of azithromycin (C38H72N2O12) in each milligram of Azithromycin taken:
Result = (ru /rs ) × (Cs /Cu ) × P
ru = peak response from the Sample solution
rs = peak response from the Standard solution
Cs = concentration of USP Azithromycin RS in the Standard solution
Cu = concentration of Azithromycin in the Sample solution
P = potency of USP Azithromycin RS (µg/mg of azithromycin)
Acceptance criteria: 945–1030 µg/mg on the anhydrous basis
Acceptance criteria: 945-1030 µg/mg on the anhydrous basis
IMPURITIES
RESIDUE ON IGNITION (281): NMT 0.3%, moistening the charred residue with 2 mL of nitric acid and 5 drops of sulfuric acid
Change to read:
ORGANIC IMPURITIES
Solution A: 1.8 mg/mL of anhydrous dibasic sodium phosphate in water. Adjust with 1 N sodium hydroxide or 10% phosphoric acid to a pH of 8.9.
Solution B: Acetonitrile and methanol (3:1)
Solution C: 1.73 mg/mL of monobasic ammonium phosphate, Adjust with ammonia TS to a pH of 10.0 ± 0.05.
Solution D: Methanol, acetonitrile, and Solution C (7:6:7)
Mobile phase: See Table 1.
Table 1
Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) |
| 0 | 50 | 50 |
| 25 | 45 | 55 |
| 30 | 40 | 60 |
| 80 | 25 | 75 |
| 81 | 50 | 50 |
| 93 | 50 | 50 |
System suitability solution: 0.0165 mg/mL of USP Azithromycin Related Compound F RS and 0.027 mg/mL of USP
Desosaminylazithromycin RS in Solution D
Standard solution: 86 µg/mL of USP Azithromycin RS in Solution D
Sample solution: 8.6 mg/mL of Azithromycin in Solution D
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 210 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Column temperature: 60°
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Injection volume: 50 µL
System suitability
Samples: System suitability solution and Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Peak-to-valley ratio: NLT 1.4, System suitability solution Calculate the peak-to-valley ratio:
Result = HP /HV
HP = height above the baseline of the desosaminylazithromycin peak
HV = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating the desosaminylazithromycin and azithromycin related
compound F peaks
Tailing factor: 0.8–1.5, Standard solution
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Azithromycin taken:
Result = (ru /rs ) × (Cs /Cu ) × P × F1 × (100/F2 )
ru = peak response of each impurity from the Sample solution
rs = peak response of azithromycin from the Standard solution
Cs = concentration of USP Azithromycin RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
Cu = concentration of Azithromycin in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
P = potency of USP Azithromycin RS (µg/mg of azithromycin)
F1 = conversion factor, 0.001 mg/µg
F2 = relative response factor (see Table 2)
Acceptance criteria: See Table 2. Disregard peaks eluting before azithromycin N-oxide and after 3-deoxyazithromycin (azithromycin B). Disregard peaks with a response less than 0.1 times the response of the azithromycin peak in the Standard solution (0.1%).
Table 2
Name | Relative Retention Time | Relative Retention Time | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
| Azithromycin N-oxidea | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.5 |
| 3′-(N,N-Didemethyl)-3′-Nformylazithromycinb,c | 0.37 | 1.7 | 0.5 |
| Erythromycin A iminoetherd | 0.42 | 1.0 | 0.5 |
| 3′-(N,NDidemethyl)azithromycin(aminoazithromycin)e | 0.43 | 1.0 | 0.5 |
| Azithromycin related compound Fc,f | 0.51 | 3.8 | 0.5 |
| Desosaminylazithromycing | 0.54 | 1.0 | 0.3 |
| 3′-N-{[4-(Acetylamino)phenyl]sulfonyl}-3′,3′-didemethylazithromycinh | 0.55 | 12 | 0.15 |
| N-Demethylazithromycini | 0.61 | 1.0 | 0.7 |
| Erythromycin A oximej | 0.64 | 1.0 | 0.5 |
| Azithromycin C (3″-Odemethylazithromycin)k | 0.73 | 1.0 | 0.5 |
| 3′-De(dimethylamino)-3′-oxoazithromycinl | 0.76 | 1.5 | 0.5 |
| 3′-N-{[4-(Acetylamino)phenyl]sulfonyl}- 3′-demethylazithromycin (ERR 1-Dec-2023) m | 0.79 | 10 | 0.5 |
| Azaerythromycin An | 0.83 | 1.0 | 0.5 |
| Azithromycin impurity Po | 0.92 | 1.0 | 0.2 |
| Azithromycin | 1.0 | - | - |
| 2-Desethyl-2-propylazithromycinp | 1.23 | 1.0 | 0.5 |
| 3′-N-Demethyl-3′-N-[(4-methylphenyl)sulfonyl]azithromycinq | 1.26 | 5 | 0.5 |
| 3-Deoxyazithromycin (azithromycin B)r | 1.31 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Any individual, unidentied impurity | - | 1.0 | 0.2 |
| Total impurities | - | - | 3.0 |
a (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-13-[(2,6-Dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-α-l-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-11-[[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylazinoyl)-β-d-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one.
b (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-13-[(2,6-Dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-α-l-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-11-[[3-formamido-3,4,6-trideoxy-β-d-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one.
c The system may resolve two rotamers. The limit is for the sum of the two rotamers.
d (3R,4R,5S,6R,9R,10S,11S,12R,13S,15R,Z)-12-[[3,4,6-Trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-β-d-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-6-ethyl-4,5-dihydroxy-10-[(2,6- dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-α-l-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-3,5,9,11,13,15-hexamethyl-7,16-dioxa-2-azabicyclo[11.2.1]hexadec-1-en-8-one.
e (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-13-[(2,6-Dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-α-l-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-11-[[3-amino-3,4,6-trideoxy-β-d-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one.
f 3′-N-Demethyl-3′-N-formylazithromycin; (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-13-[(2,6-Dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-α-l-ribohexopyranosyl)oxy]-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy-3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-11-[[3-(N-methyl)formamido-3,4,6-trideoxy-β-d-xylohexopyranosyl]oxy]-1-oxa 6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one.
g (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-2-Ethyl-3,4,10,13-tetrahydroxy-3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-11-[[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-dimethylamino-βd-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one.
h (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-13-[(2,6-Dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-α-l-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-11-[[3-[N-(4-acetamidophenylsulfonyl)amino]-3,4,6-trideoxy-β-d-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one
i (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-13-[(2,6-Dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-α-l-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-11-[[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-methylamino-β-d-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one.
j (3R,4S,5S,6R,7R,9R,11S,12R,13S,14R,E)-6-[[3,4,6-Trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-β-d-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-4-[(2,6- dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-α-l-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-10-(hydroxyimino)-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyloxacyclotetradecan-2-one.
k (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-13-[(2,6-Dideoxy-3-C-methyl-α-l-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy-3,5,6,8,10,12,14- heptamethyl-11-[[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-dimethylamino-β-d-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one.
l (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-13-[(2,6-Dideoxy-3,3-dimethyl-α-l-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy-3,5,6,8,10,12,14- heptamethyl-11-[[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-oxo-β-d-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one.
m (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-13-[(2,6-Dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-α-l-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-11-[[3-[N-(4-acetamidophenylsulfonyl)-N-methylamino]-3,4,6-trideoxy-β-d-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-1-oxa-6- azacyclopentadecan-15-one. (ERR 1-Dec-2023)
n 9-Deoxo-9a-aza-9a-homoerythromycin A; 6-Demethylazithromycin.
o Specied unidentied impurity.
p (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-13-[(2,6-Dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-α-l-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-2-propyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-11-[[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-β-d-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one.
q (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-13-[(2,6-Dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-α-l-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-11-[[3-[N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)-N-methylamino]-3,4,6-trideoxy-β-d-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-1-oxa-6-
azacyclopentadecan-15-one.
r (2R,3R,4S,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-13-[(2,6-Dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-α-l-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-2-ethyl-4,10-dihydroxy3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-11-[[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-β-d-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one.
4 SPECIFIC TESTS
OPTICAL ROTATION (781S), Procedures, Specific Rotation
Sample solution: 20 mg/mL in dehydrated alcohol
Acceptance criteria: -45° to-49", at 20°
CRYSTALLINITY (695): Meets the requirements, except where it is labeled as amorphous, most of the particles do not exhibit birefringence and
extinction positions
PH (791)
Sample stock solution: 4 mg/mL in methanol
Sample solution: 2 mg/mL obtained by mixing equal volumes of Sample stock solution and water
Acceptance criteria: 9.0-11.0
WATER DETERMINATION (921), Method I
Where it is labeled as anhydrous: NMT 2.0%
Where it is labeled as the dihydrate: 4.0%-5.0%
Where it is labeled as the monohydrate: 1.8%-4.0%, except that it may be 4.0%-6.5% when the requirements of the Loss on Drying test are met
LOSS ON DRYING: Where it is labeled as Azithromycin monohydrate and has a water content of 4.0%-6.5% (see Thermal Analysis (891))
[NOTE-The quantity taken for this procedure may be adjusted, if necessary, for instrument sensitivity.]
Analysis: Determine the percentage of volatile substances by thermogravimetric analysis in an appropriately calibrated instrument, using about 10 mg of Azithromycin. Heat the specimen at the rate of 10°/min between ambient temperature and 150° in an atmosphere of nitrogen at a constant flow rate of about 35 mL/min. From the thermogram plot the derivatives of the loss on drying (percentage loss/min), and identify the inflection points of the two weight loss steps at about 70° and 130°.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 4.5% between ambient temperature and the inflection point at about 70°, and 1.8%-2.6% between the inflection point at about 70° and the inflection point at about 130°.
5 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
PACKAGING AND STORAGE: Preserve in tight containers.
LABELING: Label it to indicate whether it is anhydrous, the monohydrate, or the dihydrate. The amorphous form is so labeled. Where the quantity of azithromycin is indicated in the labeling of any preparation containing Azithromycin, this shall be understood to be in terms of anhydrous azithromycin (CHN2012).
USP REFERENCE STANDARDS (11)
USP Azaerthromycin A. RS
9-Deoxo-9a-aza-9a-homoerythromycin A;
6-Demethylazithromycin.
C37H70N2O12 734.97
USP Azithromycin RS
USP Azithromycin Related Compound F RS
3′-N-Demethyl-3′-N-formylazithromycin;
(2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-13-[(2,6-Dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-α-l-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-11-[[3-(N-methyl)formamido-3,4,6-trideoxy-β-d-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one.
C38H70N2O13 762.98
USP Decosamindazithromycin RS
(2R,3S,4R,5R,8R, 10R,11R,125,135,14R)-2-Ethyl-3,4,10,13-tetrahydroxy-3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-11-[[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-dimethylamino-B-D-xylo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one.
C30H58N2O9 590.80


