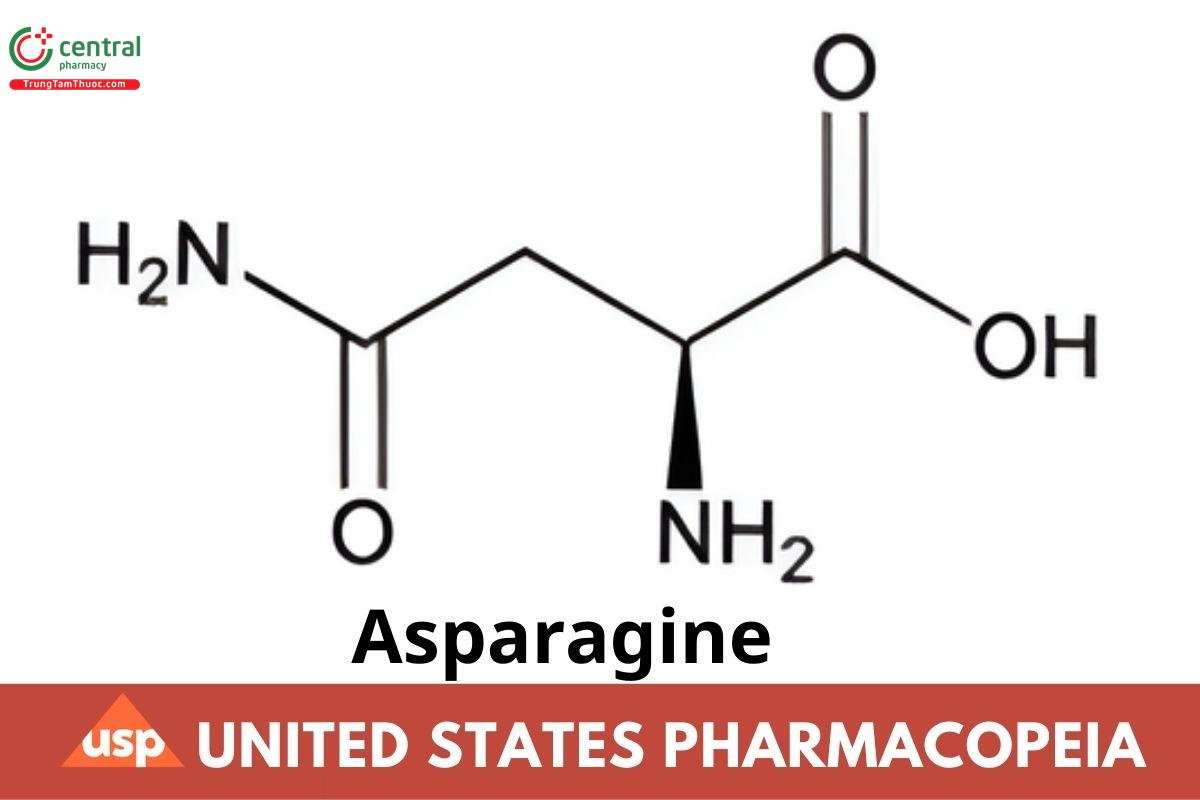
Asparagine
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
C4H8N2O3 132.12
C4H8N2O3 · H2O 150.13
C4H8N2O3 132.12
l-Asparagine;
l-α-Aminosuccinamic acid, monohydrate CAS RN®: 5794-13-8.
Anhydrous CAS RN®: 70-47-3.
1 DEFINITION
Asparagine is anhydrous, or contains one molecule of water of hydration. It contains NLT 95.5% and NMT 102.0% of asparagine (C H N O ), as l-asparagine, calculated on the dried basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
2.1 A. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197K
[Note—Use USP Asparagine Anhydrous RS and USP Asparagine Monohydrate RS for the evaluation of the anhydrous and monohydrate forms of
Asparagine, respectively.]
2.2 B. Chromatographic Identity
Analysis: Examine the chromatograms obtained in the Assay.
Acceptance criteria: The retention time of the major peak of the Sample solution corresponds to that of the Standard solution.
3 ASSAY
3.1 Procedure
Mobile phase: Dissolve 13.61 g of potassium phosphate, monobasic and 2.16 g of sodium 1-octanesulfonate in about 900 mL of water.
Adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 2.2, and dilute with water to 1 L. Add 5.0 mL of acetonitrile, and mix well.
Diluent: Water
System suitability solution: 1.5 mg/mL of USP Asparagine Anhydrous RS and 0.075 mg/mL of USP Aspartic Acid RS in Diluent
Standard solution: 1.5 mg/mL of USP Asparagine Anhydrous RS in Diluent
Sample solution: 1.5 mg/mL of Asparagine Anhydrous in Diluent or 1.7 mg/mL of Asparagine Monohydrate in Diluent
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 210 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-μm packing L1
Column temperature: 25°
Flow rate: 0.7 mL/min
Injection volume: 20 μL
Run time: 20 min
3.2 System suitability
Samples: System suitability solution and Standard solution
[Note—See Table 1 for relative retention times.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 5 between the asparagine and aspartic acid peaks, System suitability solution
Tailing factor: NMT 2.0 determined from the asparagine peak, Standard solution
Relative standard deviation: NMT 1% determined from the asparagine peak, Standard solution
3.3 Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of asparagine (C4H8N2O3) in the portion of sample taken:
Result = (rU/rS ) × (CS /CU) × 100
r = peak area of asparagine from the Sample solution
r = peak area of asparagine from the Standard solution
C = concentration of USP Asparagine Anhydrous RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
C = concentration of Asparagine in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: 95.5%–102.0% on the dried basis
4 IMPURITIES
Residue on Ignition 〈281〉
Sample: 1.0 g
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.1%
Change to read:
Lead 〈251〉, Procedures, Procedure 1 (CN 1-Jun-2023)
Sample: 1 g
Control: 5 mL of Diluted standard lead solution (5 μg of lead)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 5 ppm
Organic Impurities
Mobile phase, Diluent, System suitability solution, and Chromatographic system: Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Sensitivity solution: 0.005 mg/mL of USP Asparagine Related Compound A RS, USP Asparagine Anhydrous RS, and USP Aspartic Acid RS in Diluent
Standard solution: 0.01 mg/mL of USP Asparagine Related Compound A RS, USP Asparagine Anhydrous RS, and USP Aspartic Acid RS in Diluent
Sample solution: 2.0 mg/mL of Asparagine Anhydrous in Diluent or 2.3 mg/mL of Asparagine Monohydrate in Diluent
System suitability
Samples: System suitability solution, Sensitivity solution, and Standard solution
[Note—See Table 1 for relative retention times.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 5 between the asparagine and aspartic acid peaks, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation: NMT 5.0% determined from the aspartic acid peak, Standard solution
Signal-to-noise ratio: NLT 10 determined from the aspartic acid peak, Sensitivity solution
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of asparagine related compound A in the portion of sample taken:
Result = (rU/rS ) × (CS /CU) × 100
rU = peak area of asparagine related compound A from the Sample solution
rS = peak area of asparagine related compound A from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Asparagine Related Compound A RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Asparagine in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Calculate the percentage of aspartic acid in the portion of sample taken:
Result = (rU/rS ) × (CS /CU) × 100
rU = peak area of aspartic acid from the Sample solution
rS = peak area of aspartic acid from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Aspartic Acid RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Asparagine in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Calculate the percentage of each individual unidenti
ed impurity in the portion of sample taken:
Result = (rU/rS ) × (CS /CU) × 100
rU = peak area of each individual unidentied impurity from the Sample solution
rS = peak area of asparagine from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Asparagine Anhydrous RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Asparagine in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: See Table 1.
| Name | Relative Retention Time | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Asparagine related compound Aa | 0.4 | 1.0 |
| Asparagine | 1.0 | — |
| Aspartic acid | 1.6 | 1.0 |
| Each individual unidentified impurity | — | 0.5 |
| Total impurities | — | 3.0 |
a 2,2'-(3,6-Dioxopiperazine-2,5-diyl)diacetamide.
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
Optical Rotation 〈781S〉, Procedures, Specific Rotation
Sample solution: 10 mg/mL, in 6 N hydrochloric acid
Acceptance criteria: +33.0° to +36.5°, measured at 20°
Microbial Enumeration Tests 〈61〉 and Tests for Specified Microorganisms 〈62〉: The total aerobic microbial count is NMT 103 cfu/g, and the total combined molds and yeasts count is NMT 102 cfu/g.
Loss on Drying 〈731〉
Sample: Dry a sample at 130° for 3 h.
Acceptance criteria
Anhydrous: NMT 1.0%
Monohydrate: 11.5%–12.5%
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in well-closed, light-resistant containers. Store at room temperature.
Labeling: Label it to indicate whether it is anhydrous or the monohydrate.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Asparagine Anhydrous RS
USP Asparagine Monohydrate RS
USP Asparagine Related Compound A RS
2,2'-(3,6-Dioxopiperazine-2,5-diyl)diacetamide.
C8H12N4O4 228.21
USP Aspartic Acid RS


